
Equidae is the taxonomic family of horses and related animals, including the extant horses, asses, and zebras, and many other species known only from fossils. The family evolved around 50 million years ago from a small, multi-toed ungulate into larger, single-toed animals. All extant species are in the genus Equus, which originated in North America. Equidae belongs to the order Perissodactyla, which includes the extant tapirs and rhinoceros, and several extinct families. It is more specifically grouped within the superfamily Equoidea, the only other family being the extinct Palaeotheriidae.

Perissodactyla is an order of ungulates. The order includes about 17 living species divided into three families: Equidae, Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs). They typically have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three or one of the five original toes, though tapirs retain four toes on their front feet. The nonweight-bearing toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or positioned posteriorly. By contrast, artiodactyls bear most of their weight equally on four or two of the five toes: their third and fourth toes. Another difference between the two is that perissodactyls digest plant cellulose in their intestines, rather than in one or more stomach chambers as artiodactyls, with the exception of Suina, do.

Ungulates are members of the diverse clade Euungulata, which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined to be a polyphyletic and thereby invalid clade based on molecular data. As a result, true ungulates had since been reclassified to the newer clade Euungulata in 2001 within the clade Laurasiatheria while Paenungulata has been reclassified to a distant clade Afrotheria. Living ungulates are divided into two orders: Perissodactyla including equines, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and Artiodactyla including cattle, antelope, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses, among others. Cetaceans such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also classified as artiodactyls, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. Two other orders of ungulates, Notoungulata and Litopterna, both native to South America, became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene, around 12,000 years ago.

Paenungulata is a clade of "sub-ungulates", which groups three extant mammal orders: Proboscidea, Sirenia, and Hyracoidea (hyraxes). At least two more possible orders are known only as fossils, namely Embrithopoda and Desmostylia.

Condylarthra is an informal group – previously considered an order – of extinct placental mammals, known primarily from the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. They are considered early, primitive ungulates and is now largely considered to be a wastebasket taxon, having served as a dumping ground for classifying ungulates which had not been clearly established as part of either Perissodactyla or Artiodactyla, being composed thus of several unrelated lineages.

Paraceratherium is an extinct genus of hornless rhinocerotoids belonging to the family Paraceratheriidae. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has ever existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch. The first fossils were discovered in what is now Pakistan, and remains have been found across Eurasia between China and the Balkans. Paraceratherium means "near the hornless beast", in reference to Aceratherium, the genus in which the type species P. bugtiense was originally placed.

Chalicotheriidae is an extinct family of herbivorous, odd-toed ungulate (perissodactyl) mammals that lived in North America, Eurasia, and Africa from the Middle Eocene to the Early Pleistocene. They are often called chalicotheres, a term which is also applied to the broader grouping of Chalicotherioidea. They are noted for their unusual morphology compared to other ungulates, such as their clawed forelimbs. Members of the subfamily Chalicotheriinae developed elongate gorilla-like forelimbs that are thought to have been used to grasp vegetation. They are thought to have been browsers on foliage as well as possibly bark and fruit.
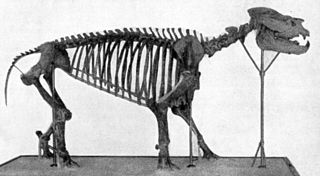
Metamynodon is an extinct genus of amynodont that lived in North America and Asia from the late Eocene until early Oligocene, although the questionable inclusion of M. mckinneyi could extend their range to the Middle Eocene. The various species were large, displaying a suit of semiaquatic adaptations more similar to those of the modern hippopotamus, despite their closer affinities with rhinoceroses.

Palaeotheriidae is an extinct family of herbivorous perissodactyl mammals that inhabited Europe, with less abundant remains also known from Asia, from the mid-Eocene to the early Oligocene. They are classified in Equoidea, along with the living family Equidae.

Phenacodontidae is an extinct family of large herbivorous mammals traditionally placed in the “wastebasket taxon” Condylarthra, which may instead represent early-stage perissodactyls. They lived from the late early Paleocene to early middle Eocene and their fossil remains have been found in North America and Europe. The only unequivocal Asian phenacodontid is Lophocion asiaticus.

Rhinocerotoidea is a superfamily of perissodactyls that appeared 56 million years ago in the Paleocene. They included four extinct families, the Amynodontidae, the Hyracodontidae, the Paraceratheriidae, and the Eggysodontidae. The only extant family is the Rhinocerotidae, which survives as five living species. Extinct non-rhinocerotid members of the group are sometimes considered rhinoceroses in a broad sense. Although the term 'rhinoceroses' is sometimes used to refer to all of these, a less ambiguous vernacular term for this group is 'rhinocerotoids'. The family Paraceratheriidae contains the largest land mammals known to have ever existed.

Homogalax is an extinct genus of tapir-like odd-toed ungulate. It was described on the basis of several fossil finds from the northwest of the United States, whereby the majority of the remains come from the state of Wyoming. The finds date to the Lower Eocene between 56 and 48 million years ago. In general, Homogalax was very small, only reaching the weight of today's peccaries, with a maximum of 15 kg. Phylogenetic analysis suggests the genus to be a basal member of the clade that includes today's rhinoceros and tapirs. In contrast to these, Homogalax was adapted to fast locomotion.

Altungulata or Pantomesaxonia is an invalid clade (mirorder) of ungulate mammals comprising the perissodactyls, hyracoids, and tethytheres.
Urtinotherium is an extinct genus of paracerathere mammals. It was a large animal that was closely related to Paraceratherium, and found in rocks dating from the Late Eocene to Early Oligocene period. The remains were first discovered in the Urtyn Obo region in Inner Mongolia, which the name Urtinotherium is based upon. Other referred specimens are from northern China.

Forstercooperia is an extinct genus of forstercooperiine paraceratheriid rhinocerotoids from the Middle Eocene of Asia.

Cambaytherium is an extinct genus of placental mammals in the family Cambaytheriidae whose fossils were found in an open pit coal mine located in Gujarat, India. The mine was a treasure trove full of teeth and bones, over 200 of which were identified as belonging to Cambaytherium thewissi. The fossils were dated to the Early Eocene, 54.5 million years ago, making them slightly younger than the oldest known fossils belonging to the order Perissodactyla.
Ronzotherium is an extinct genus of perissodactyl mammal from the family Rhinocerotidae. The name derives from the hill of 'Ronzon', the French locality near Le Puy-en-Velay at which it was first discovered, and the Greek suffix 'therium' meaning 'beast'. At present 5 species have been identified from several localities in Europe and Asia, spanning the Late Eocene to Upper Oligocene.
Allacerops is an extinct genus of odd-toed ungulate belong to the rhinoceros-like family Eggysodontidae. It was a small, ground-dwelling browser, and fossils have been found in Oligocene deposits throughout Central and East Asia.

Hyainailouridae ("hyena-cats") is a family of extinct predatory mammals within the superfamily Hyainailouroidea within extinct order Hyaenodonta. Hyaenodontids arose during the middle Eocene and persisted well into the middle Miocene. Fossils of this group have been found in Asia, Africa, North America and Europe.

Rostriamynodon is an extinct genus of amynodontid that inhabited China during the Eocene epoch. It is a monotypic genus that contains the species Rostriamynodon grangeri.






















