
Adetomyrma is a genus of ants endemic to Madagascar. Workers of this genus are blind. The type species Adetomyrma venatrix was described in 1994, with the genus being an atypical member of its tribe, the Amblyoponini. This tribe includes the Dracula ants, members of which can feed on the hemolymph of larvae and pupae.

Leptomyrmex, or spider ants, is a genus of ants and a distinctive member of the ant subfamily Dolichoderinae. Commonly known as "spider ants" for their long legs and spider-like movements, these orange and black ants are prominent residents of intact wet forest and sclerophyll habitats throughout their range. One extant species, Leptomyrmex relictus, is known from central Brazil; otherwise, the global distribution of this genus is restricted to eastern Australia, New Caledonia and New Guinea, as well as the nearby Indonesian islands of Aru and Seram.
Megalomyrmex is a genus of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae. The genus is known only from the Neotropics, where some of the species are specialized parasites or predators of Attini.

Opamyrma hungvuong is a species of ant found in central Vietnam, first described in 2008. It is the only species in the genus Opamyrma. While originally classified in the subfamily Amblyoponinae, it is presently considered to belong to the subfamily Leptanillinae.

Agroecomyrmecinae is a subfamily of ants containing two extant and two fossil genera. The subfamily was originally classified in 1930 by Frank M. Carpenter as Agroecomyrmecini, a Myrmicinae tribe. Bolton raised the tribe to subfamily status in 2003, suggesting that Agroecomyrmecinae might be the sister taxon to Myrmicinae. It has since been discovered to be one of the earliest lineages of ants, a clade from the basal polytomy for all ants. In 2014, the subfamily was expanded to two tribes. The tribe Ankylomyrmini was moved from the subfamily Myrmicinae to Agroemyrmecinae.

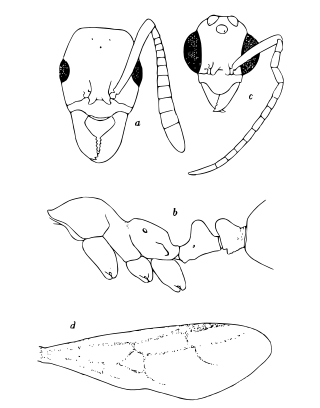
Tatuidris, or armadillo ant, is a rare genus of ants consisting of a single species, Tatuidris tatusia. The ants are small in size and inhabit the leaf litter of Neotropical forests in Central and South America, from Mexico to Brazil. Workers are ferruginous-colored to dark red and present a distinctive morphology, consisting of a shield-like head with a broad vertex, ventrally-turned heavy mandibles which do not overlap at full closure, and unique among ants – an antenna socket apparatus sitting upside-down. Little is known about the biology of the ants, but they are likely nocturnal and specialist predators.

Yavnella is a genus of ants in the subfamily Leptanillinae. Its two species are distributed in India and Israel. The genus is known only from male specimens.

Protanilla is a genus of subterranean ants in the subfamily Leptanillinae. Known from the Indomalayan realm, the genus contains about thirteen species. The genus was erected by Taylor (1990) for the type species P. rafflesi, described from workers from Peninsular Malaysia. Species in this genus have long and downcurved mandibles with peg-like tooth on the inner margins. Four species are known from China, one from Taiwan, one from Sri Lanka and a couple from India.

Leptanilloides is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dorylinae. Leptanilloides is an uncommonly collected genus with subterranean habits in the New World Andean and sub-Andean tropics.

Cerapachys is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dorylinae. Species are mainly myrmecophagous ants which raid the nests of other ants for prey. The genus is distributed widely throughout the Indomalayan region. The genus was revised by BoroWiec (2016) who split a number of previously synonymized genera out of Cerapachys, leaving only 5 species in the genus.

Sphinctomyrmex is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dorylinae. The genus is a tropical and distinctive group, originally described by Mayr based on a single gyne collected in Brazil. Morphologically, the genus is characterized by the unique arrangement of the gastric segments, which are nearly equal in length and separated from each other by distinct constrictions. Very little is known on the natural history of Sphinctomyrmex. The few observations so far suggest that ants of this genus are nomadic predators of other ants. The genus Zasphinctus and approximately 20 species were formerly included, but were split out during revision of the Dorylinae genera by Borowiec (2016).

Brownimecia is an extinct genus of ants, the only genus in the tribe Brownimeciini and subfamily Brownimeciinae of the Formicidae. Fossils of the identified species, Brownimecia clavata and Brownimecia inconspicua, are known from the Late Cretaceous of North America. The genus is one of several ants described from Late Cretaceous ambers of New Jersey. Brownimecia was initially placed in the subfamily Ponerinae, until it was transferred to its own subfamily in 2003; it can be distinguished from other ants due to its unusual sickle-like mandibles and other morphological features that makes this ant unique among the Formicidae. B. clavata is also small, measuring 3.43 millimetres (0.135 in), and a stinger is present in almost all of the specimens collected. The morphology of the mandibles suggest a high level of feeding specialization.

Tyrannomyrmex is a rare tropical genus of ants in the subfamily Myrmicinae. Three similar species, only known from workers, are recognized and share small eyes and edentate mandibles.

Asphinctopone is a small genus of rarely encountered Afrotropical ants in the subfamily Ponerinae.

Chrysapace is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dorylinae containing four described species. The genus is distributed across the Malaysian peninsula, Indonesia, and the Philippines, with undescribed species from Madagascar and from Baltic amber Chrysapace was described by Crawley (1924) and later placed as a junior synonym of Cerapachys by Brown (1975). Chrysapace was resurrected as a valid genus by Borowiec (2016) during redescription of the doryline genera.

Ooceraea is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dorylinae containing approximately 16 described species. The genus is distributed across the Australasia, Indomalaya, Malagasy, Neotropical, Oceania, and Palearctic bioregions. Ooceraea was described by Roger (1862) and later placed as a junior synonym of Cerapachys by Brown (1973). Ooceraea was resurrected as a valid genus by Borowiec (2016) during redescription of the doryline genera.
Armaniinae is subfamily of extinct ant-like hymenopterans known from a series of Cretaceous fossils found in Asia and Africa. It is usually treated as one of the stem-group subfamilies in family Formicidae, although some myrmecologists treat it as a distinct family. A 2007 study analysing petiole and antenna morphology led to the proposal that at least some of the armaniid genera be placed in Sphecomyrminae, although others are unconvinced by the arguments and retain Armaniinae. The subfamily contains seven genera with fourteen described species.
Stigmatomma scrobiceps is a species of ant in the genus Stigmatomma. It was described as Bannapone scrobiceps by Guénard et al. in 2013, based on two specimens collected in Yunnan Province, China, and placed as the second species in Bannapone. It was moved to Stigmatomma by Ward and Fisher (2016).















