
Southwest National Park is an Australian national park located in the south-west of Tasmania, bounded by the Franklin-Gordon Wild Rivers National Park to the north and the Hartz Mountains National Park to the east. It is a part of a chain of national parks and state reserves that make up the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area. Covering an area of 6,183 km2 (2,387 sq mi), it is Tasmania's largest national park.

Lake Pedder, once a glacial outwash lake, is a man-made impoundment and diversion lake located in the southwest of Tasmania, Australia. In addition to its natural catchment from the Frankland Range, the lake is formed by the 1972 damming of the Serpentine and Huon rivers by the Hydro-Electric Commission for the purpose of hydroelectric power generation. Consequently, the lake is also known, somewhat derisively, as the Huon-Serpentine Impoundment.

The barramundi, Asian sea bass, or giant sea perch is a species of catadromous fish in the family Latidae of the order Carangiformes. The species is widely distributed in the Indo-West Pacific, spanning the waters of the Middle East, South Asia, Southeast Asia, East Asia, and Oceania.

The Galaxiidae are a family of mostly small freshwater fish in the Southern Hemisphere. The majority live in Southern Australia or New Zealand, but some are found in South Africa, southern South America, Lord Howe Island, New Caledonia, and the Falkland Islands. One galaxiid species, the common galaxias, is probably the most widely naturally distributed freshwater fish in the Southern Hemisphere. They are coolwater species, found in temperate latitudes, with only one species known from subtropical habitats. Many specialise in living in cold, high-altitude upland rivers, streams, and lakes.

Threatened fauna of Australia are those species and subspecies of birds, fish, frogs, insects, mammals, molluscs, crustaceans, and reptiles to be found in Australia that are in danger of becoming extinct. This article lists species classified as threatened species under the Commonwealth Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Lepidogalaxias salamandroides is a species of small freshwater fish of Western Australia. It is the only member of the family Lepidogalaxiidae and genus Lepidogalaxias. Common names for this fish include salamanderfish and Shannon mudminnow. Although it is not a lungfish, it resembles lungfish in several respects, including its ability to survive dry seasons by burrowing into the sand. It is on the IUCN Red List as Endangered.

The Tasmanian giant freshwater crayfish, also called Tasmanian giant freshwater lobster, is the largest freshwater invertebrate and the largest freshwater crayfish species in the world. The species is only found in the rivers below 400 metres (1,300 ft) above sea level in northern Tasmania, an island-state of Australia. It is listed as an endangered species on the IUCN Red List due to overfishing and habitat degradation, and it has been prohibited to catch the crayfish since 1998.

The common galaxias or inanga is a very widespread Southern Hemisphere fish in the family Galaxiidae. It is a slim, narrow fish with a forked tail and a mottled, spotty pattern, typically about 10 cm (4 in) long when fully grown. It lives in fresh water, but spawns at river mouths and spends the first six months of its life at sea, returning en masse in spring. Its vernacular names include cowfish, jollytail, common jollytail, eel gudgeon, inaka, native trout, pulangi, puye, slippery tarki, spotted minnow, Falklands minnow and whitebait.

The Pedder galaxias is an Australian freshwater fish. It is considered to be extinct in the wild since 2005 by the EPBC Act, and was originally found only in Lake Pedder in Tasmania.

The speckled longfin eel, Australian long-finned eel or marbled eel is one of 15 species of eel in the family Anguillidae. It has a long snake-like cylindrical body with its dorsal, tail and anal fins joined to form one long fin. The dorsal fin also often extends farther than the anal fin. It usually has a brownish green or olive green back and sides with small darker spots or blotches all over its body. Its underside is paler. It has a small gill opening on each side of its wide head, with thick lips. It is Australia's largest freshwater eel, and the female usually grows much larger than the male. It is also known as the spotted eel.

The Tasmanian mudfish, Neochanna cleaveri, is a small Australian amphidromous ray-finned fish in the family Galaxiidae.

Paragalaxias is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fish of the family Galaxiidae, endemic to the Central Highlands of Tasmania.

The Tasmanian whitebait, also known as the Australian whitebait or Derwent whitebait, is a semi-anadromous ray-finned fish of the family Galaxiidae, found only in Tasmania and southern Victoria, Australia. It is the only species in the genus Lovettia.

Galaxias fontanus, the Swan galaxias, is a species of fish in the family Galaxiidae. It is endemic to eastern Tasmania, Australia.

The black-stripe minnow is a small freshwater species of fish in the family Galaxiidae. It is endemic to southwestern Australia where it is found in slow-running streams, ponds, swamps and ditches.
Protoxotes lorentzi is a tropical freshwater fish found in streams and swamps of the Northern Territory of Australia, Western Papua, and Papua New Guinea. It was first named by Weber in 1910, and is commonly known as the primitive archerfish or Lorentz's archerfish.
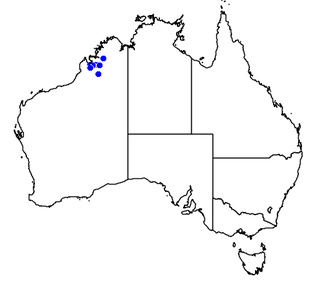
Toxotes kimberleyensis is a species of archerfish found in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. It was first named by Gerald R. Allen in 2004, and is commonly known as the Kimberley archerfish, largescale archerfish, or western archerfish.
Peter Robert Last is an Australian ichthyologist, curator of the Australian National Fish Collection and a senior principal research scientist at CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research (CMAR) in Hobart, Tasmania. He is an elasmobranch expert and has described many new species of shark.

Paragalaxias eleotroides also known as the is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish of the family Galaxiidae, endemic to Tasmania, Australia.
Paragalaxias julianus, also known as the Julian galaxias, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Galaxiidae. The species is only known from the Central Plateau of Tasmania in Australia and is usually 6 cm (2.4 in) long (SL), the largest specimen ever recorded was 10 cm (3.9 in) long (SL).


















