
The garden dart is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is distributed throughout much of the Palearctic. Temperate regions of Europe, Central Asia and North Asia, as well as the mountains of North Africa. Absent from polar regions, on Iceland and some Mediterranean islands, as well as in Macaronesia.

Apamea crenata, known as the clouded-bordered brindle, is a moth in the family Noctuidae. It is distributed throughout the Palearctic realm. In the North it crosses the Arctic Circle, in the Mediterranean it is found only in cool locations and mountains avoiding very hot areas. In the Alps, it rises to an altitude of about 2000 metres.

Plemyria rubiginata, the blue-bordered carpet, is a moth of the family Geometridae found in Europe and across the Palearctic. The moth was first described by the Austrian lepidopterists Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775.
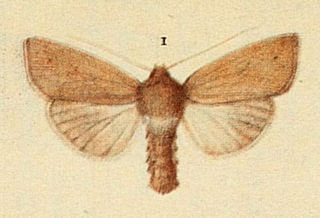
Mythimna favicolor, or Mathew's wainscot, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Charles Golding Barrett in 1896. It is found in Europe. The species is sometimes treated as a subspecies of Mythimna pallens, the common wainscot.

Aseptis is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. The genus was erected by James Halliday McDunnough in 1937.

Aseptis binotata, the rusty shoulder knot moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1865. It is found widespread in western North America, west of south-central Alberta, Wyoming, and Nebraska. Along the Pacific Coast it occurs from northern Mexico to south-central British Columbia. It can be found from sea level to altitudes over 2000 meters in a variety of habitats from dense forest to shrub desert.

Paraseptis is a monotypic moth genus in the family Noctuidae erected by Tomas Mustelin and Lars G. Crabo in 2015. Its only species, Paraseptis adnixa, was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1880. It is widely distributed along the Pacific Coast from northern Mexico to south-western British Columbia in a variety of forested habitats.

Aseptis catalina is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by John Bernhardt Smith in 1899. It is found in the deserts of Arizona, California and Baja California in Mexico.

Aseptis ethnica is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by John Bernhardt Smith in 1899. It is found in North America in Arizona, California, western Oregon, and Baja California Norte in Mexico. The habitat consists of open pine and oak forest and mountain chaparral, mostly at elevations of above 1500 meters in southern California but at lower elevations farther north.

Aseptis characta is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1880. It is widespread in western North America, where it is found in the western Great Plains, Great Basin, and Pacific regions from British Columbia, Alberta, and Saskatchewan to Colorado, Utah, northern Arizona and southern California. The species occurs in dry habitats like sagebrush steppe, juniper woodlands, and open forest from sea level to 2,500 meters.

Aseptis fumeola is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by George Hampson in 1908. It is found in the US state of Arizona, southern and central California, southern Nevada and south-eastern Utah. The habitat consists of foothills and mountains in dry chaparral, parkland, and conifer forest.

Hydraecia obliqua is a moth in the family Noctuidae first described by Leon F. Harvey in 1876. It is found in western North America, east to the Sierra Nevada in California and the crest of the Cascade Range in Oregon and Washington. It occurs continuously on the coast north to south-western British Columbia, with a disjunct northern population at Terrace, British Columbia. The habitat consists of the riparian zone along creeks and rivers of coastal rainforests, as well as oak savanna, mixed hardwood forests and valley grasslands.

Aseptis ferruginea is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Tomas Mustelin in 2000. It is endemic to southern California. All records are from San Diego County, from an area between Boulevard-Manzanita near the Mexican border north to Lake Henshaw at altitudes of 800–1600 meters. The habitat consist of open oak forest, foothill chaparral, and in the mountain-desert transition zone.

Aseptis fanatica is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Tomas Mustelin in 2006. It is found in western North America in Washington, Oregon, California, and Baja California Norte in Mexico. It is found in habitats like brush land and open forest in southern California, mostly at 1000–2000 meters, but occurs at lower elevations farther north.

Aseptis pseudolichena is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Tomas Mustelin and Ronald Henley Leuschner in 2000. It is endemic to southern California, with records from San Diego, Riverside, Los Angeles, Ventura, San Bernardino, and Tuolumne counties. The habitat consists of open pine and oak forest, open areas with grass and scrub, and foothill chaparral.

Aseptis serrula is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by William Barnes and James Halliday McDunnough in 1918. It is found in the lower mountain-desert transition zone and in high desert such as the Mojave, Colorado, and Sonora deserts of south-eastern California, Nevada, Arizona and Baja California.

Aseptis susquesa is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by John Bernhardt Smith in 1908. It is found in Arizona, California and Baja California in Mexico, at least as far south as Ensenada. The habitat consists of rocky areas in the mountain-desert transition zone and high desert.

Aseptis perfumosa is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by George Hampson in 1918. It is endemic to southern California, where it occurs in many habitats such as coastal chaparral and canyons, urban areas, brush land, and open oak forest from sea level to 2000 meters.

Viridiseptis is a monotypic moth genus in the family Noctuidae erected by Tomas Mustelin and Lars G. Crabo in 2015. Its only species, Viridiseptis marina, was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1874. It is found throughout coastal California and in south-western Oregon as far north as Douglas County. It is widely distributed in southern California. It is found in many habitats such as coastal chaparral, mountain forest, mountain-desert transition zone, and occasionally in the deserts from sea level to at least 2000 meters.

Macronoctua onusta, commonly known as the iris borer, is a species of cutworm or dart moth in the family Noctuidae. It is found in North America.




















