
The black sea bass is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea bass from the subfamily Serraninae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the groupers and anthias. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean, where it is an important species for commercial and recreational fisheries.

Conch is a common name of a number of different medium-to-large-sized sea snails. Conch shells typically have a high spire and a noticeable siphonal canal.

Strombidae, commonly known as the true conchs, is a taxonomic family of medium-sized to very large sea snails in the superfamily Stromboidea, and the Epifamily Neostromboidae. The term true conchs, being a common name, does not have an exact meaning. It may generally refer to any of the Strombidae but sometimes is used more specifically to include only Strombus and Lambis. The family currently includes 26 extant, and 10 extinct genera.

Aliger gigas, originally known as Strombus gigas or more recently as Lobatus gigas, commonly known as the queen conch, is a species of large sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family of true conches, the Strombidae. This species is one of the largest molluscs native to the Caribbean Sea, and tropical northwestern Atlantic, from Bermuda to Brazil, reaching up to 35.2 centimetres (13.9 in) in shell length. A. gigas is closely related to the goliath conch, Lobatus goliath, a species endemic to Brazil, as well as the rooster conch, Aliger gallus.

The cherubfish, also known as the pygmy angelfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a marine angelfish belonging to the family Pomacanthidae. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean.

The belted sandfish, also known as the dwarf sea bass or stubby sea bass, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea bass from the subfamily Serraninae, classified as part of the family Serranidae which includes the groupers and anthias. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean. This species is found in the aquarium trade.

The boa catshark is a catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found on the continental shelves and insular slopes of the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, between latitudes 20° N and 9° N, at depths between 330 and 675 m. It can grow up to a length of 54 cm. The reproduction of this catshark is oviparous.
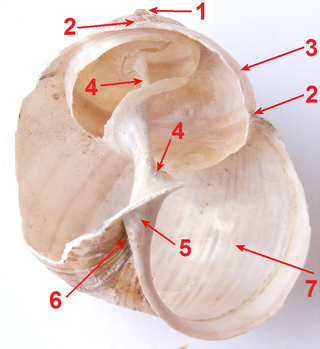
The columella or pillar is a central anatomical feature of a coiled snail shell, a gastropod shell. The columella is often only clearly visible as a structure when the shell is broken, sliced in half vertically, or viewed as an X-ray image.

Atrina rigida, commonly called the rigid pen shell, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Pinnidae.

Serranus tortugarum, the chalk bass, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea bass from the subfamily Serraninae, classified as part of the family Serranidae which includes the groupers and anthias. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean. This species is found in the aquarium trade.

Arothron stellatus, also known as the stellate pufferfish, starry puffer, or starry toadfish, is a demersal marine fish belonging to the family Tetraodontidae. It is found in shallow water in the Indo-Pacific region.

Apogon imberbis, the cardinalfish, the Mediterranean cardinalfish or king of the mullets, is a species of ray-finned fish, a cardinalfish belonging to the family Apogonidae. It is widely distributed in the Mediterranean and along the warm temperate and tropical eastern Atlantic coasts from Portugal south to the Gulf of Guinea.

Fasciolaria tulipa, common name the true tulip, is a species of large sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Fasciolariidae.

Liopropoma rubre, the peppermint bass or swissguard basslet, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, related to the groupers and classified within the subfamily Epinephelinae of the family Serranidae. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean. This species is utilised in the aquarium trade.

Macrostrombus costatus, formerly known as Strombus costatus and Lobatus costatus, or commonly known as the milk conch, is a species of large sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Strombidae, the true conchs. They are an edible species and important food source for the inhabitants of where they are found. Conchs are most notable for their medium to large-sized ornamental shells. Milk conchs are dispersed among the tropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean, along the coasts and islands of North, Central, and South America.

Pinna carnea, commonly called the amber pen shell, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Pinnidae.

Acanthurus tractus, the five-band surgeonfish, ocean surgeon, or ocean surgeonfish, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Acanthuridae found in the western Atlantic Ocean, Florida, the Bahamas, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. Until recently, it was considered a synonym of Acanthurus bahianus, but its status as a separate species was resurrected in 2011.

Astronesthes niger, commonly known as snaggletooth, is a species of small, deep sea fish in the family Stomiidae. It occurs in the tropical and subtropical Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, as well as the Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean, at depths to 1,000 m (3,300 ft).

Kyphosus bigibbus, the brown chub, grey drummer, darkfin drummer, insular rudderfish, grey chub, grey sea chub, southern drummer or topsail drummer is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea chub from the family Kyphosidae. It is a herbivorous species which is found in subtropical and tropical seas worldwide.

Paguristes puncticeps is a hermit crab, in the family Diogenidae. It is found in shallow waters in the tropical western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. Like other hermit crabs, it lives inside an empty mollusc shell, which it changes periodically as it grows.





















