
The fauna of Australia consists of a large variety of animals; some 46% of birds, 69% of mammals, 94% of amphibians, and 93% of reptiles that inhabit the continent are endemic to it. This high level of endemism can be attributed to the continent's long geographic isolation, tectonic stability, and the effects of a unique pattern of climate change on the soil and flora over geological time. A unique feature of Australia's fauna is the relative scarcity of native placental mammals. Consequently, the marsupials – a group of mammals that raise their young in a pouch, including the macropods, possums and dasyuromorphs – occupy many of the ecological niches placental animals occupy elsewhere in the world. Australia is home to two of the five known extant species of monotremes and has numerous venomous species, which include the platypus, spiders, scorpions, octopus, jellyfish, molluscs, stonefish, and stingrays. Uniquely, Australia has more venomous than non-venomous species of snakes.

Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the world's oceans, in freshwater, and on land. They are generally covered with a thick exoskeleton. They generally have five pairs of legs, and they have pincer claws on the ends of the frontmost pair. They first appeared during the Jurassic period, around 200 million years ago.

Malacostraca is the second largest of the six classes of pancrustaceans behind insects, containing about 40,000 living species, divided among 16 orders. Its members, the malacostracans, display a great diversity of body forms and include crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, woodlice, amphipods, mantis shrimp, tongue-eating lice and many other less familiar animals. They are abundant in all marine environments and have colonised freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are segmented animals, united by a common body plan comprising 20 body segments, and divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen.

The Tasmanian giant crab, also known as the giant deepwater crab, giant southern crab, queen crab, or bullcrab, is a very large species of crab that resides on rocky and muddy bottoms in the oceans off Southern Australia. It is the only extant species in the genus Pseudocarcinus.

Carcinus maenas is a common littoral crab. It is known by different names around the world. In the British Isles, it is generally referred to as the shore crab, or green shore crab. In North America and South Africa, it bears the name European green crab.

Leptograpsus variegatus, known as the purple rock crab, is a marine large-eyed crab of the family Grapsidae, found in southern subtropical Indo-Pacific Oceans. It grows to around 50 millimetres (2.0 in) shell width. It is the only species in the genus Leptograpsus.

Parathelphusinae is a subfamily of freshwater crabs, which was formerly placed in the family Parathelphusidae; they are mainly found in South and Southeast Asia, but also found elsewhere in Asia and in Australia. The family is now considered as a junior synonym of the family Gecarcinucidae.

The Gecarcinucidae are a family of true freshwater crabs. They are found throughout South Asia, Southeast Asia and New Guinea, with a single genus found in Australia.

Pseudothelphusidae is a family of freshwater crabs found chiefly in mountain streams in the Neotropics. They are believed to have originated in the Greater Antilles and then crossed to Central America via a Pliocene land bridge. Some species of this family are troglobitic.

Potamon fluviatile is a freshwater crab found in or near wooded streams, rivers and lakes in Southern Europe. It is an omnivore with broad ecological tolerances, and adults typically reach 50 mm (2 in) in size during their 10–12 year lifespan. They inhabit burrows and are aggressive, apparently outcompeting native crayfish.

Ranina ranina, also known as the Huỳnh Đế crab, (red) frog crab or spanner crab, is a species of crab found throughout tropical and subtropical habitats. It is often fished for its meat.
Johora singaporensis, the Singapore stream crab or Singapore freshwater crab, is a critically endangered species of freshwater crab endemic to Singapore. It grows to a size of 30 millimetres (1.2 in) wide.

Potamonautes sidneyi is a species of freshwater crab in the family Potamonautidae. The common name is the Natal river crab or Sidney's river crab, although they may also be referred to as "river crabs", "fresh water crabs" or "land crabs".

Amarinus lacustris is a species of freshwater crab from Australia, New Zealand and nearby islands, where it lives in water of various salinities. It grows up to 10 mm (0.4 in) wide, with an H-shaped groove on its back. It is an omnivore and is eaten by crayfish and fish. It was first discovered in Lake Pupuke, near Auckland, and is the only freshwater crab in New Zealand.

Around 1,300 species of freshwater crabs are distributed throughout the tropics and subtropics, divided among eight families. They show direct development and maternal care of a small number of offspring, in contrast to marine crabs, which release thousands of planktonic larvae. This limits the dispersal abilities of freshwater crabs, so they tend to be endemic to small areas. As a result, a large proportion are threatened with extinction.
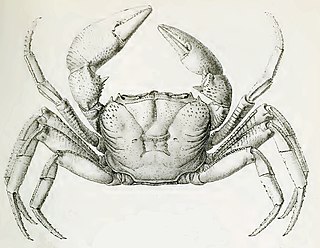
Seychellum alluaudi is a species of freshwater crab endemic to the Seychelles, and the only true freshwater crab in that country. It lives in rainforest streams on the archipelago's granitic high islands. Although it may be abundant, little is known about its biology. If its habitat were to decline in quality, S. alluaudi might become endangered, but it is currently listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List.

Ocypode convexa, commonly known as the golden ghost crab, or alternatively the western ghost crab or yellow ghost crab, is a species of ghost crabs endemic to the coast of Western Australia, from Broome to Perth. They are relatively large ghost crabs, with a carapace growing up to 45 mm (1.8 in) long and 52 mm (2.0 in) wide. They are easily recognisable by their golden yellow colouration. Like other ghost crabs they have box-like bodies with unequally sized claws. They also have large eyestalks with the cornea occupying most of the bottom part.

Austrothelphusa transversa(von Martens, 1868), also known as the inland crab, freshwater crab, or tropical freshwater crab is a species of freshwater crab endemic to Australia. A. transversa is the most widely-dispersed species of its genus, as it has adaptations giving it a high tolerance to drought and arid conditions.

Nanhaipotamon is a genus of freshwater crabs, in the subfamily Potamiscinae, found in southern China and Taiwan. As of 2018, 18 species have been described. The genus is named after the South China Sea, for it occurs mostly in coastal areas. The genus was first described by R. Bott in 1968 as Isolapotamon (Nanhaipotamon), i.e., a subgenus of Isolapotamon.

Geothelphusa is a genus of Asian freshwater crabs, erected by W. Stimpson in 1858.


















