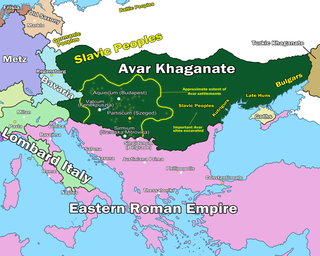
The Pannonian Avars were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai, or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine sources, and the Apar to the Göktürks. They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century.

Great Moravia, or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Austria, Germany, Poland, Romania, Croatia, Serbia, Ukraine and Slovenia. The formations preceding it in these territories were Samo's tribal union and the Pannonian Avar state.

The Duchy of Bavaria was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (duces) under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm, which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire.

Pepin the Short, was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
Bayan I reigned as the first khagan of the Avar Khaganate between 562 and 602.

Mojmir I, Moimir I or Moymir I was the first known ruler of the Moravian Slavs (820s/830s–846) and eponym of the House of Mojmir. In modern scholarship, the creation of the early medieval state known as Great Moravia is attributed either to his or to his successors' expansionist policy. He was deposed in 846 by Louis the German, king of East Francia.

The Principality of Nitra, also known as the Duchy of Nitra, was a West Slavic polity encompassing a group of settlements that developed in the 9th century around Nitra, in present-day Slovakia. Its history remains uncertain because of a lack of contemporary sources. The territory's status is subject to scholarly debate: some modern historians describe it as an independent polity that was annexed either around 833 or 870 by the Principality of Moravia, while others say that it was under the influence of the neighbouring West Slavs from Moravia from its inception.

The March of Pannonia or Eastern March was a frontier march of the Carolingian Empire, named after the former Roman province of Pannonia and carved out of the preceding and larger Avar March.

The Margraviate of Austria was a medieval frontier march, centered along the river Danube, between the river Enns and the Vienna Woods, within the territory of the modern Austrian provinces of Upper Austria and Lower Austria. It existed from c. 970 to 1156.
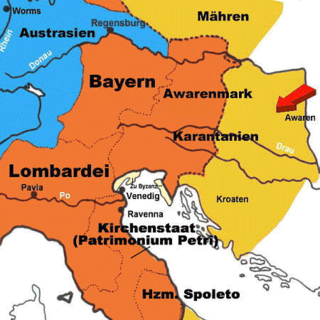
The Avar March was a southeastern frontier province of the Frankish Empire, established after successful Frankish campaigns and conquests of Avarian territories along the river Danube, to the east from the river Enns, in what is today Lower Austria and northwestern Hungary. Since the Frankish conquest in the late 8th century, there were several administrative changes in those regions. Territory along the river Danube, from the river Enns to the Vienna Woods, was ruled directly, as a frontier extension (march) of the Frankish Bavaria, while regions further to the east, up to the river Rába, were initially designated to remaining Avarian princes, under the Frankish supreme rule. During the 820s and 830s, additional administrative changes were made in the wider region of Frankish Pannonia, inhabited mainly by Pannonian Slavs. Territories of the remaining Avarian princes were fully incorporated, and Avars eventually disappeared from the region.
Maurice's Balkan campaigns were a series of military expeditions conducted by Roman Emperor Maurice in an attempt to defend the Balkan provinces of the Roman Empire from the Avars and the South Slavs. Maurice was the only East Roman emperor, other than Anastasius I, who did his best to implement determined Balkan policies during Late Antiquity by paying adequate attention to the safety of the northern frontier against barbarian incursions. During the second half of his reign, the Balkan campaigns were the main focus of Maurice's foreign policies, as a favourable peace treaty with Persian Empire in 591 enabled him to shift his experienced troops from the Persian front to the region. The refocusing of Roman efforts soon paid off: the frequent Roman failures before 591 were succeeded by a string of successes afterwards.
Gerold was a franconian nobleman who served the Frankish King, Charlemagne, as Margrave of the Avar March and Prefect of Bavaria in what is now South-Eastern Germany. Gerold played a significant role in the integration of Bavaria into the Frankish Kingdom during Carolingian expansion in the late 8th, and early 9th centuries. Gerold both aided the continuity of Agilofing rule of Bavaria, as well as took steps to integrate Bavarians into the wider scope of the Frankish Kingdom. Gerold was related both to the Agilofing family, the ruling class of Bavaria, as well as the Carolingian family. The Agilofings had ruled Bavaria since Duke Garibald I in 548. Gerold was born into the Agilofings, and his sister Hildegard was married to Charlemagne in 771. From these familial connections, he was appointed Prefect of Bavaria following the deposition of Duke Tassilo III in 788. Gerold was heralded as a superb military commander, giving rise to his promotion to Prefect as a defender of the eastern border of the Frankish Kingdom. In 799, Gerold is said to have fallen in battle against the Avars, shortly after the same Avars killed his brother and ally, Eric, Duke of Friuli, through treachery.

The Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, also known as the Hungarian conquest or the Hungarian land-taking, was a series of historical events ending with the settlement of the Hungarians in Central Europe in the late 9th and early 10th century. Before the arrival of the Hungarians, three early medieval powers, the First Bulgarian Empire, East Francia, and Moravia, had fought each other for control of the Carpathian Basin. They occasionally hired Hungarian horsemen as soldiers. Therefore, the Hungarians who dwelt on the Pontic-Caspian Steppe east of the Carpathian Mountains were familiar with what would become their homeland when their conquest started.
Boruth, also Borut or Borouth, was the first documented Slavic prince (Knyaz) of Carantania, ruling from about 740 until his death. He was one of the few pagan leaders of the Carantanians to convert to Christianity.

Samo's Empire is the historiographical term for the West Slavic tribal union established by King ("Rex") Samo. It existed between 623/631 and 658 in Central Europe. The extent of Samo's power before and after 631 is disputed.
Praedenecenti was an early medieval Slavic tribe, mentioned only in the Royal Frankish Annals in 822 and 824. They lived in the buffer zone between the Carolingian and Bulgarian empires. The Royal Frankish Annals associated them with the Abodriti, while modern scholars have also connected them to other Slavic tribes, especially the Braničevci or Merehani. The Praedenecenti sought assistance from the Franks against the Bulgars, but they obviously lost their independence because they were not mentioned after 824.
Radbod was the East Frankish prefect of the Eastern March, the Bavarian frontier towards the Slavs, appointed in 833. He had been appointed the office after Louis the German's conquest in 828, and subsequent Christianization of the Moravians (828–33). In 833, according to the Conversio Bagoariorum et Carantanorum, a Slavic prince, Pribina, had been "driven across the Danube by Mojmir, duke of the Moravians", and fled to Radbod in East Francia around 833. Radbod introduced him to King Louis the German, who ordered that Pribina should be "instructed in the faith and baptized", and that he serve with his followers in Radbod's army. Before long, however, Radbod and Pribina fell out, and the latter, fearing for his life, fled with his son Koceľ to the First Bulgarian Empire, and then to Lower Pannonia ruled by a Slavic duke, Ratimir. Since Lower Pannonia was part of Radbod's prefecture, Ratimir's harboring of Pribina was tantamount to rebellion, therefore, in 838, Louis the German sent Radbod at the head of a large Bavarian army to crush Ratimir, but Pribina and his followers took refuge with the count of Carniola, Salacho. In short time the latter brokered a reconciliation between Radbod and Pribina, and Louis solved the ongoing instability by appointing Pribina as his faithful dux with lands in around the Zala river. Radbod held contacts with Rastislav, ruler of the Moravians, who had long posed a danger to Bavaria. According to the Annals of St-Bertin, in 853 Charles the Bald, king of West Francia, bribed the Bulgarians to ally with the Slavs and together attack Louis the German's kingdom. In the course of the Bulgarian–Moravian attack, Louis the German deposed Radbod in 854 for infidelity, after an uprising. Radbod then formed a rebel alliance with Rastislav. In 855, Rastislav (Rastiz) rebelled, and Carloman was made prefect in Radbod's place in 856. Carloman's 858 campaign forced Rastislav to make peace.

The Avar–Byzantine wars were a series of conflicts between the Byzantine Empire and the Avar Khaganate. The conflicts were initiated in 568, after the Avars arrived in Pannonia, and claimed all the former land of the Gepids and Lombards as their own. This led to an unsuccessful attempt to seize the city of Sirmium from Byzantium, which had previously retaken it from the Gepids. Most subsequent conflicts came as a result of raids by the Avars, or their subject Slavs, into the Balkan provinces of the Byzantine Empire.
The history of Christianity in Hungary started in the Roman province of Pannonia, centuries before the arrival of the Magyars, or Hungarians.
Autchar was a Frankish nobleman. He served Pippin III as a diplomat in 753 and followed Carloman I after the division of the kingdom in 768. In 772, refusing to accept Carloman's brother Charlemagne as king, he went into exile in the Lombard kingdom with Carloman's widow and sons. He was captured when Charlemagne invaded the kingdom in 773. His role in the fall of the Lombard kingdom was the subject of legendary embellishment a century later and in the chansons de geste he evolved into the figure of Ogier the Dane.
















