Related Research Articles

The Miami are a Native American nation originally speaking the Miami–Illinois language, one of the Algonquian languages. Among the peoples known as the Great Lakes tribes, they occupied territory that is now identified as north-central Indiana, southwest Michigan, and western Ohio. The Miami were historically made up of several prominent subgroups, including the Piankeshaw, Wea, Pepikokia, Kilatika, Mengakonkia, and Atchakangouen. In modern times, Miami is used more specifically to refer to the Atchakangouen. By 1846, most of the Miami had been forcefully displaced to Indian Territory. The Miami Tribe of Oklahoma are the federally recognized tribe of Miami Indians in the United States. The Miami Nation of Indiana, a nonprofit organization of self-identified descendants of Miamis who were exempted from removal, have unsuccessfully sought separate recognition.

Maumee is a city in Lucas County, Ohio, United States. Located along the Maumee River, it is a suburb about 10 miles (16 km) southwest of Toledo. The population was 13,896 at the 2020 census. Maumee was declared an All-America City by the National Civic League in June 2006.

Ottawa is a village and the county seat of Putnam County, Ohio, United States. It is located about 51 miles (82 km) southwest of Toledo. The population is 4,456 as of the 2020 census.

The Maumee River is a river running in the United States Midwest from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph and St. Marys rivers, where Fort Wayne, Indiana has developed, and meanders northeastwardly for 137 miles (220 km) through an agricultural region of glacial moraines before flowing into the Maumee Bay of Lake Erie. The city of Toledo is located at the mouth of the Maumee. The Maumee was designated an Ohio State Scenic River on July 18, 1974. The Maumee watershed is Ohio's breadbasket; it is two-thirds farmland, mostly corn and soybeans. It is the largest watershed of any of the rivers feeding the Great Lakes, and supplies five percent of Lake Erie's water.
The Odawa are an Indigenous American people who primarily inhabit land in the Eastern Woodlands region, now in jurisdictions of the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. Their territory long preceded the creation of the current border between the two countries in the 18th and 19th centuries.

The Auglaize River is a 113-mile-long (182 km) tributary of the Maumee River in northwestern Ohio in the United States. It drains a primarily rural farming area in the watershed of Lake Erie. The name of the river was derived from the French term for it. The French called it "rivière à la Grande Glaize", referring to the soil in the area.
White Rock is an unincorporated community in Huron County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The community is located within Sherman Township. As an unincorporated community, White Rock has no legal autonomy, defined boundaries, or population statistics of its own. It is located at 43°42′35″N82°36′31″W, about three miles north of Forestville and about nine miles south of Harbor Beach on M-25 at the junction with White Rock Road.
The Treaty of Detroit was a treaty between the United States and the Ottawa, Chippewa, Wyandot and Potawatomi Native American nations. The treaty was signed in Detroit, Michigan on November 17, 1807, with William Hull, governor of the Michigan Territory and superintendent of Indian affairs, the sole representative of the U.S.
The Treaty of Fort McIntosh was a treaty between the United States government and representatives of the Wyandotte, Delaware, Chippewa and Ottawa nations of Native Americans. The treaty was signed at Fort McIntosh on January 21, 1785. It contained 10 articles and an addendum.

The Treaty of Fort Meigs, also called the Treaty of the Maumee Rapids, formally titled, "Treaty with the Wyandots, etc., 1817", was the most significant Indian treaty by the United States in Ohio since the Treaty of Greenville in 1795. It resulted in cession by bands of several tribes of nearly all their remaining Indian lands in northwestern Ohio. It was the largest wholesale purchase by the United States of Indian land in the Ohio area. It was also the penultimate one; a small area below the St. Mary's River and north of the Greenville Treaty Line was ceded in the Treaty of St. Mary's in 1818.
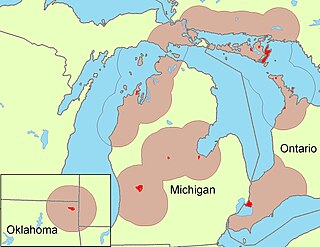
The Ottawa Tribe of Oklahoma is one of four federally recognized Native American tribes of Odawa people in the United States. Its Algonquian-speaking ancestors had migrated gradually from the Atlantic coast and Great Lakes areas, reaching what are now the states of Michigan and Ohio in the 18th century. In the late 1830s the United States removed the Ottawa to west of the Mississippi River, first to Iowa, then to Kansas in what was Indian Territory.

Mary Jane Thurston State Park is a 105-acre (42 ha) public recreation area one mile west of Grand Rapids in Wood and Henry counties, Ohio, United States. The state park lies along the south bank of the Maumee River near remains of the historic Miami and Erie Canal. It is named for Mary Jane Thurston, a schoolteacher from Grand Rapids who bequeathed land for the establishment of a park. The park's year-round recreation includes hunting, fishing, boating, picnicking, and camping.

The Treaty of Brownstown was between the United States and the Council of Three Fires, Wyandott, and Shawanoese Indian Nations. It was concluded November 25, 1808, at Brownstown in Michigan Territory, and provided cession of a strip of Indian land for a road to connect two disconnected areas of land previously ceded by Indians in Michigan and Ohio.
Turnpike Lands were a group of land tracts granted by the United States Congress to the state of Ohio in 1827 along the path of a proposed road in the northwest corner of the state.
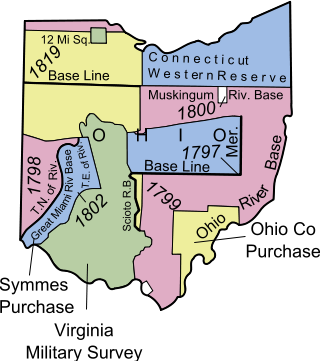
The Twelve Mile Square Reservation, also called the Twelve Mile Square Reserve, was a tract of land in Ohio ceded by Indians to the United States of America in the Treaty of Greenville in 1795. This particular area of land immediately surrounding Fort Miami was considered to be of strategic importance by the United States government representatives. It was subsequently surveyed in a manner different from surrounding land, and lots sold, or granted, to settlers.

Indian Land Grants were land tracts granted to various Indians by Treaty or by United States Congressional action in the Nineteenth century in northwestern Ohio.
Indian removals in Ohio started in the late eighteenth century after the American victory in the Revolutionary War and the consequent opening of the Northwestern United States to European-American settlement. Native American tribes residing in the region banded together to resist settlement, resulting in the disastrous Northwest Indian War where the Native tribes ceded large swathes of territory to the American government. After the American victory in the war, several Indian reservations were established to forcibly relocate landless tribes to. The process of obtaining full American sovereignty over Indian territories in Ohio was complete around 1818, but continued in Indiana until 1840.
References
This article needs additional citations for verification .(October 2017) |
- ↑ "Native Americans in Ottawa Ohio Historical Marker". hmdb.org. Retrieved 18 December 2024.
- ↑ "Treaty of the Maumee Rapids (1817)". Ohio History Central. Retrieved 2017-10-22.
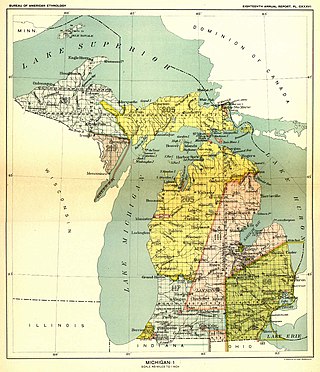
- 1 2 Smithsonian Institution. Bureau of American Ethnology (1901). Bulletin. Washington: Government Publishing Office. pp. 153.
- ↑ Royce, Charles. 1898. Eighteenth Annual Report. Bureau of American Ethnology. Plate 157 : "Ohio (Detail)".
- ↑ "History Archives Library". Ottawa Tribe of Oklahoma. Retrieved 2017-10-22.