
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fires.

Licking County is a county located in the central portion of the U.S. state of Ohio. At the 2020 census, the population was 178,519. Its county seat is Newark. The county was formed on January 30, 1808, from portions of Fairfield County.

Brownsville is a borough in Fayette County, Pennsylvania, United States, first settled in 1785 as the site of a trading post a few years after the defeat of the Iroquois enabled a resumption of westward migration after the Revolutionary War. The trading post soon became a tavern and inn and was receiving emigrants heading west, as it was located above the cut bank overlooking the first ford that could be reached to those descending from the Allegheny Mountains. Brownsville is located 40 miles (64 km) south of Pittsburgh along the east bank of the Monongahela River.
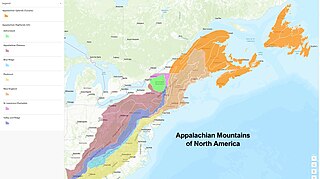
The geology of the Appalachians dates back more than 1.1 billion years to the Mesoproterozoic era when two continental cratons collided to form the supercontinent Rodinia, 500 million years prior to the later development of the range during the formation of the supercontinent Pangea. The rocks exposed in today's Appalachian Mountains reveal elongate belts of folded and thrust faulted marine sedimentary rocks, volcanic rocks and slivers of ancient ocean floor – strong evidence that these rocks were deformed during plate collision. The birth of the Appalachian ranges marks the first of several mountain building plate collisions that culminated in the construction of the supercontinent Pangea with the Appalachians and neighboring Anti-Atlas mountains near the center. These mountain ranges likely once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before they were eroded.

The Ouachita Mountains, simply referred to as the Ouachitas, are a mountain range in western Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma. They are formed by a thick succession of highly deformed Paleozoic strata constituting the Ouachita Fold and Thrust Belt, one of the important orogenic belts of North America. The Ouachitas continue in the subsurface to the northeast, where they make a poorly understood connection with the Appalachians and to the southwest, where they join with the Marathon uplift area of West Texas. Together with the Ozark Plateaus, the Ouachitas form the U.S. Interior Highlands. The highest natural point is Mount Magazine at 2,753 feet (839 m).

The Allegheny Front is the major southeast- or east-facing escarpment in the Allegheny Mountains in southern Pennsylvania, western Maryland, eastern West Virginia, and western Virginia, USA. The Allegheny Front forms the boundary between the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians to its east and the Appalachian Plateau to its west. The Front is closely associated with the Appalachian Mountains' Eastern Continental Divide, which in this area divides the waters of the Ohio/Mississippi river system, flowing to the Gulf of Mexico, from rivers flowing into Chesapeake Bay and from there into the Atlantic Ocean.

Brownsville is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in northeastern Bowling Green Township, Licking County, Ohio, United States. As of the 2020 census, it had a population of 214. It lies at the intersection of U.S. Route 40 with State Route 668.

The Silurian Tuscarora Formation — also known as Tuscarora Sandstone or Tuscarora Quartzite — is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, Maryland, West Virginia, and Virginia, US.

The Ordovician Reedsville Formation is a mapped surficial bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, and Tennessee, that extends into the subsurface of Ohio. This rock is a slope-former adjacent to the prominent ridge-forming Bald Eagle sandstone unit in the Appalachian Mountains. It is often abbreviated Or on geologic maps.

The Pennsylvanian Pottsville Formation is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, western Maryland, West Virginia, Ohio, and Alabama. It is a major ridge-former in the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians of the eastern United States. The Pottsville Formation is conspicuous at many sites along the Allegheny Front, the eastern escarpment of the Allegheny or Appalachian Plateau.

The Bedford Shale is a shale geologic formation in the states of Ohio, Michigan, Pennsylvania, Kentucky, West Virginia, and Virginia in the United States.

The Casselman Formation mapped sedimentary bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, Maryland, and West Virginia, of Pennsylvanian age. It is the uppermost of two formations in the Conemaugh Group, the lower being the Glenshaw Formation. The boundary between these two units is the top of the marine Ames Limestone. The Conemaugh Group overlies the Upper Freeport coal bed of the Allegheny Formation and underlies the Pittsburgh coal seam of the Monongahela Group.

Berea Sandstone, also known as Berea Grit, is a sandstone formation in the U.S. states of Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Kentucky. It is named after Berea, Ohio. The sandstone has been used as a building stone and is a source of oil and gas.
Redstone Creek is a historically important widemouthed canoe and river boat-navigable brook-sized tributary stream of the Monongahela River in Fayette County, Pennsylvania. The creek is 28.4 miles (45.7 km) long, running from headwaters on Chestnut Ridge north through the city of Uniontown and reaching the Monongahela at Brownsville. Located in a 1/4-mile-wide valley with low streambanks, the site was ideal for ship building in a region geologically most often characterized by steep-plunging relatively inaccessible banks — wide enough to launch and float several large boats, and indeed steamboats after 1811, and slow-moving enough to provide good docks and parking places while craft were outfitting.

The Glenshaw Formation is a mapped sedimentary bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, Maryland, West Virginia, and Ohio, of Pennsylvanian age. It is the lower of two formations in the Conemaugh Group, the upper being the Casselman Formation. The boundary between these two units is the top of the marine Ames Limestone. The Conemaugh Group overlies the Upper Freeport coal bed of the Allegheny Formation and underlies the Pittsburgh coal seam of the Monongahela Group.
Horse Creek is a tributary of Goose Creek river in Clay County in the U.S. state of Kentucky. The Cumberland and Manchester Railway built a spur line up the creek, and it has been the site of operations of at least eight coal mining companies. The name comes, according to local tradition, from the proliferation of "horseweed" in the creek valley.
The Oriskany Sandstone is a Middle Devonian age unit of sedimentary rock found in eastern North America. The type locality of the unit is located at Oriskany Falls in New York. The Oriskany Sandstone extends throughout much of the Appalachian Basin.

Blair Gap, one of the gaps of the Allegheny, is a water gap along the eastern face atop the Allegheny Front escarpment. Like other gaps of the Allegheny, the slopes of Blair Gap were amenable to foot travel, pack mules, and possibly wagons allowing Amerindians, and then, after about 1778–1780 settlers, to travel west into the relatively depopulated Ohio Country decades before the railroads were born and tied the country together with steel.
The geology of Ohio formed beginning more than one billion years ago in the Proterozoic eon of the Precambrian. The igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock is poorly understood except through deep boreholes and does not outcrop at the surface. The basement rock is divided between the Grenville Province and Superior Province. When the Grenville Province crust collided with Proto-North America, it launched the Grenville orogeny, a major mountain building event. The Grenville mountains eroded, filling in rift basins and Ohio was flooded and periodically exposed as dry land throughout the Paleozoic. In addition to marine carbonates such as limestone and dolomite, large deposits of shale and sandstone formed as subsequent mountain building events such as the Taconic orogeny and Acadian orogeny led to additional sediment deposition. Ohio transitioned to dryland conditions in the Pennsylvanian, forming large coal swamps and the region has been dryland ever since. Until the Pleistocene glaciations erased these features, the landscape was cut with deep stream valleys, which scoured away hundreds of meters of rock leaving little trace of geologic history in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic.

Upper Mercer flint or Upper Mercer chert is a type of flint, or a pure form of chert, found in Coshocton, Hocking, and Perry counties of Ohio. Made of forms of silica and quartz, the hard and brittle stone was used by prehistoric people to make tools and weapons. To create stone tools, flint was heated to make chipping away at the stone easier, and then the flint was chipped to form razor-sharp edges. Resulting tools included spearheads, scrapers, knives, and arrows.


















