
Baltic amber or succinite is amber from the Baltic region, home of its largest known deposits. It was produced sometime during the Eocene epoch, but exactly when is controversial. It has been estimated that this forested region provided the resin for more than 100,000 tons of amber. Today, more than 90% of the world's amber comes from Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. It is a major source of income for the region; the local Kaliningrad Amber Combine extracted 250 tonnes of it in 2014 and 400 tonnes in 2015.
Fibla carpenteri is an extinct species of snakefly in the Inocelliidae genus Fibla. F. carpenteri is named in honor of the paleoentomologist Dr Frank Carpenter, for his vast knowledge and interest in Raphidioptera.

Aspidopleura is an extinct monotypic genus of parasitic wasp in the Eupelmidae subfamily Neanastatinae and at present, it contains the single species Aspidopleura baltica. The genus is solely known from the Early Eocene Baltic amber deposits in the Baltic Sea region of Europe.
Metapelma archetypon is an extinct species of parasitic wasp in the Metapelmatidae genus Metapelma. The species is solely known from the Early Eocene Baltic amber deposits in the Baltic Sea region of Europe. Of the thirty seven described species in the genus Metapelma, M. archetypon is the only species known from the fossil record.

Neanaperiallus is an extinct monotypic genus of parasitic wasp in the Eupelmidae subfamily Neanastatinae containing only a single species, Neanaperiallus masneri. The genus is solely known from the Early Eocene Baltic amber deposits in the Baltic Sea region of Europe.

Baltimartyria is an extinct genus of primitive metallic moths in the family Micropterigidae. The genus is solely known from the Early Eocene Baltic amber deposits in the Baltic Sea region of Europe. The genus currently contains two described species, Baltimartyria proavitella and Baltimartyria rasnitsyni.
Glisachaemus is an extinct monotypic genus of planthopper in the Cixiidae subfamily Cixiinae and at present, it contains the single species Glisachaemus jonasdamzeni. The genus is solely known from the Early Eocene Baltic amber deposits in the Baltic Sea region of Europe.

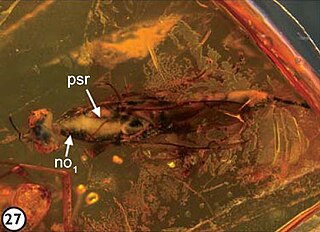
Diochus electrus is an extinct species of rove beetle in genus Diochus, the only definitive fossil species in subfamily Staphylininae. The species is known only from the middle Eocene, Lutetian stage Baltic amber found in the Blaue Erde deposits, Baltic region, Northern Europe.

Amarantoraphidia is an extinct genus of snakefly in the family Mesoraphidiidae. The genus is solely known from Early Cretaceous, Albian age, fossil amber found in Spain. Currently the genus comprises only a single species Amarantoraphidia ventolina.

Alavaraphidia is an extinct genus of snakefly in the family Mesoraphidiidae. The genus is solely known from an Early Cretaceous, Albian age, fossil amber found in Spain. Currently, the genus comprises a single species, Alavaraphidia imperterrita.

Arostropsis is an extinct genus of broad-nosed weevil in the beetle family Curculionidae known from an Upper Eocene fossil found in Europe. The genus contains a single described species, Arostropsis groehni.
Protostephanus is an extinct genus of crown wasp in the Hymenoptera family Stephanidae known from an Eocene fossil found in the United States of America. The genus contains a single described species, Protostephanus ashmeadi placed in the stephanid subfamily Stephaninae.
Hyptia deansi is an extinct species of ensign wasp in the family Evaniidae known from a solitary Late Oligocene to Early Miocene fossil found in Mexico. H. deansi is the only species in the genus Hyptia to have been described from fossils and the only ensign wasp described from Mexican amber.

Aphaenogaster oligocenica is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae known from a pair of Middle Eocene fossils found in Europe. A. oligocenica is one of three species in the ant genus Aphaenogaster to have been noted from fossils found in Baltic amber by William Morton Wheeler.

Emplastus is an extinct morphogenus of ants in the subfamily Dolichoderinae, known from fossils found in Asia and Europe. The genus contains twelve species described from sites in England, Eastern Europe and Far Eastern Russia.

Yantaromyrmex is an extinct genus of ants first described in 2013. Members of this genus are in the subfamily Dolichoderinae of the family Formicidae, known from Middle Eocene to Early Oligocene fossils found in Europe. The genus currently contains five described species, Y. constrictus, Y. geinitzi, Y. intermedius, Y. mayrianum and Y. samlandicus. The first specimens were collected in 1868 and studied by Austrian entomologist Gustav Mayr, who originally placed the fossils in other ant genera until the fossils were reviewed and subsequently placed into their own genus. These ants are small, measuring from 4 to 6 mm in length and can be characterized by their trapezoidal shaped head-capsules and oval compound eyes that are located slightly to the rear of the capsules midpoint, with no known ocelli present.

Protopone is an extinct genus of ants in the formicid subfamily Ponerinae described from fossils found in Europe and Asia. There are seven described species placed into the genus, Protopone? dubia, Protopone germanica, Protopone magna, Protopone oculata, Protopone primigena, Protopone sepulta, and Protopone vetula. Protopone is one several Lutetian Ponerinae genera.

Paraneuretus is an extinct genus of formicid in the ant subfamily Aneuretinae known from fossils found in Asia and Europe. The genus contains three middle to late Eocene age species, Paraneuretus dubovikoffi, Paraneuretus longicornis, and Paraneuretus tornquisti.

Bradoponera is an extinct genus of ant in the Formicidae subfamily Proceratiinae, and is one of four genera of the subfamily. The genus contains four described species Bradoponera electrina, Bradoponera meieri, Bradoponera similis, and Bradoponera wunderlichi. The species are known from several Middle Eocene amber fossils which were found in Europe.
The Prussian Formation, previously known as the Amber Formation, is a geologic formation in Prussia, today mostly Kaliningrad Oblast that dates to the Eocene. It holds 90% of the world's amber supply and Baltic amber is found exclusively in the Prussian Formation.















