Conserved domains
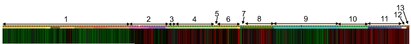
In the predicted protein product, C12orf60 contains a conserved protein domain of 225 amino acids. This domain (DUF4533) is within the pfam15047 family of proteins. Only one other gene is listed within this family: C12orf69 , which is also known as SMOC3 (single-pass membrane protein with coiled-coil domains 3). [15]
Analysis of human C12orf60 and 9 of its orthologs reveals a highly conserved ERL motif starting at the 10th residue of the human protein sequence. It is not known whether this motif occurs in other proteins.
Other conserved residues are Asp25, Ser28, Phe37, Met41, Glu69, Leu85, Lys88, Leu143, Pro147, Ile148, Leu151, Gln164, Lys189, Leu191, Ala207, and Glu212, Leu225, and Lys227. Furthermore, these residues lie within DUF4533, suggesting that these conserved amino acids are important for the function of the domain. Also, the region between the 100 and 150 residues are not conserved. Thus, this region is not likely vital to the protein's function.