
The Alytidae are a family of primitive frogs. Their common name is painted frogs or midwife toads. Most are endemic to Europe, but three species occur in northwest Africa, and a species formerly thought to be extinct is found in Israel.

Hyphalosaurus is a genus of freshwater aquatic reptiles, belonging to the extinct order Choristodera. They lived during the early Cretaceous period, about 122 million years ago. The genus contains two species, H. lingyuanensis and H. baitaigouensis, both from the Yixian Formation of Liaoning Province, China. They are among the best-known animals from the Jehol Biota, with thousands of fossil specimens representing all growth stages in scientific and private collections.
The Xiagou Formation is the middle strata of the Xinminbao Group. It is named for its type site in Xiagou, in the Changma Basin of Gansu Province, northwestern China and is considered Early Cretaceous in age. It is known outside the specialized world of Chinese geology as the site of a Lagerstätte in which the fossils were preserved of Gansus yumenensis, the earliest true modern bird.

Longipteryx is a genus of prehistoric bird which lived during the Early Cretaceous. It contains a single species, Longipteryx chaoyangensis. Its remains have been recovered from the Jiufotang Formation at Chaoyang in Liaoning Province, China. Apart from the holotype IVPP V 12325 - a fine and nearly complete skeleton — another entire skeleton and some isolated bones are known to date.

Dongbeititan is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous-age Yixian Formation of Beipiao, Liaoning, China. It is based on holotype DNHM D2867, a partial postcranial skeleton including bones from the limbs, shoulder and pelvic girdles, and vertebrae, which was described in 2007. Its describers suggested it was as a basal titanosauriform, not as derived as Gobititan or Jiutaisaurus, but more derived than Euhelopus, Fusuisaurus, and Huanghetitan. The type species is D. dongi, and it is the first named sauropod from the Yixian Formation, which is part of the well-known Jehol Group. The genus name refers to the region Dongbei and to Greek titan, "giant". The specific name honours the Chinese paleontologist Dong Zhiming. Like other sauropods, Dongbeititan would have been a large quadrupedal herbivore.

The Jehol Biota includes all the living organisms – the ecosystem – of northeastern China between 133 and 120 million years ago. This is the Lower Cretaceous ecosystem which left fossils in the Yixian Formation and Jiufotang Formation. These deposits are composed of layers of tephra and sediment. It is also believed to have left fossils in the Sinuiju series of North Korea. The ecosystem in the Lower Cretaceous was dominated by wetlands and numerous lakes. Rainfall was seasonal, alternating between semiarid and mesic conditions. The climate was temperate. The Jehol ecosystem was interrupted periodically by ash eruptions from volcanoes to the west. The word "Jehol" is a historical transcription of the former Rehe Province.
The Jiufotang Formation is an Early Cretaceous geological formation in Chaoyang, Liaoning which has yielded fossils of feathered dinosaurs, primitive birds, pterosaurs, and other organisms. It is a member of the Jehol group. The exact age of the Jiufotang has been debated for years, with estimates ranging from the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. New uranium-lead dates reveal the formation is deposited in the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous. Fossils of Microraptor and Jeholornis are from the Jiufotang.

Similicaudipteryx, meaning "similar to Caudipteryx", is a genus of theropod dinosaur of the family Caudipteridae.

Mesophryne beipiaoensis is an extinct species of frog, from the Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Liaoning (China), and the only species in the genus Mesophryne. It is known from a single specimen collected near Heitizigou, 25 kilometres (16 mi) south of Beipiao, from which the specific epithet derives. The specimen has a snout–vent length of 69 millimetres (2.7 in). While some authors have suggested Mesophryne is a synonym of Liaobatrachus, this has been rejected by other authors. In a phylogenetic analysis it was found to be a crown group frog, which was more derived than Ascaphus and Leiopelma, but less so than alytids and other more advanced frogs.

Liaobatrachus is a genus of prehistoric frog, the first fossil specimen of which was recovered from the Yixian Formation of Liaoning Province, China. It was the first Mesozoic era frog ever found in China. The species Callobatrachus sanyanensis,Mesophryne beipiaoensis and Yizhoubatrachusmacilentus were classified as species of Liaobatrachus in one study, but this has been rejected by other authors. The genus has been considered a nomen dubium by some authors due to the poor preservation of the holotype specimen. Fossils were found in the Sihetun locality of the western part of Liaoning province, in the lower part of the Yixian Formation, and date to approximately 124.6 Ma. Another specimen was collected near Heitizigou, 25 kilometres (16 mi) south of Beipiao. The specimen has a snout–vent length of 69 millimetres (2.7 in). Liaobatrachus is considered to be the most basal member of Discoglossidae based on phylogenetic analysis.

The Tiaojishan Formation is a geological formation in Hebei and Liaoning, People's Republic of China, dating to the middle-late Jurassic period. It is known for its exceptionally preserved fossils, including those of plants, insects and vertebrates. It is made up mainly of pyroclastic rock interspersed with basic volcanic and sedimentary rocks. Previously, the Tiaojishan Formation was grouped together with the underlying Haifanggou Formation as a single "Lanqi Formation." The Tiaojishan Formation forms a key part of the Yanliao Biota assemblage, alongside the Haifanggou Formation.

The Yixian Formation is a geological formation in Jinzhou, Liaoning, People's Republic of China, that spans about 1.6 million years during the early Cretaceous period. It is known for its fossils, listed below.

Gobiconodontidae is a family of extinct mammals that ranged from the mid-Jurassic to the early Late Cretaceous, though most common during the Early Cretaceous. The Gobiconodontids form a diverse lineage of carnivorous non-therian mammals, and include some of the best preserved Mesozoic mammal specimens.
The Haifanggou Formation, also known as the Jiulongshan Formation, is a fossil-bearing rock deposit located near Daohugou village of Ningcheng County, in Inner Mongolia, northeastern China.

Longipterygidae is a family of early enantiornithean avialans from the Early Cretaceous epoch of China. All known specimens come from the Jiufotang Formation and Yixian Formation, dating to the early Aptian age, 125-120 million years ago.

Chuanqilong is a monospecific genus of basal ankylosaurid dinosaur from the Liaoning Province, China that lived during the Early Cretaceous in what is now the Jiufotang Formation. The type and only species, Chuanqilong chaoyangensis, is known from a nearly complete skeleton with a skull of a juvenile individual. It was described in 2014 by Fenglu Han, Wenjie Zheng, Dongyu Hu, Xing Xu, and Paul M. Barrett. Chuanqilong shows many similarities with Liaoningosaurus and may represent a later ontogenetic stage of the taxon.

Daliansaurus is a genus of small troodontid theropod dinosaur, measuring approximately 1 metre long, from the Early Cretaceous of China. It contains a single species, D. liaoningensis, named in 2017 by Shen and colleagues from a nearly complete skeleton preserved in three dimensions. Daliansaurus is unusual in possessing an enlarged claw on the fourth digit of the foot, in addition to the "sickle claw" found on the second digit of the feet of most paravians. It also has long metatarsal bones, and apparently possesses bird-like uncinate processes. In the Lujiatun Beds of the Yixian Formation, a volcanically-influenced region with a cold climate, Daliansaurus lived alongside its closest relatives - Sinovenator, Sinusonasus, and Mei, with which it forms the group Sinovenatorinae.
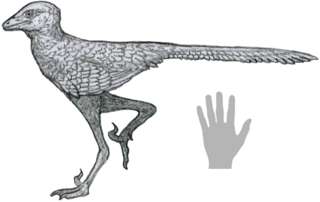
Liaoningvenator is a genus of troodontid theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of China. It contains a single species, L. curriei, named after paleontologist Phillip J. Currie in 2017 by Shen Cai-Zhi and colleagues from an articulated, nearly complete skeleton, one of the most complete troodontid specimens known. Shen and colleagues found indicative traits that placed Liaoningvenator within the Troodontidae. These traits included its numerous, small, and closely packed teeth, as well as the vertebrae towards the end of its tail having shallow grooves in place of neural spines on their top surfaces.














