
Eriophorum gracile is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. It is known by the common name slender cottongrass, or slender cottonsedge. Eriophorum gracile is a plant with circumboreal distribution, extending south into mountain ranges of the Northern Hemisphere. It grows in wet areas such as bogs.
Carex alma is a species of sedge known by the common name sturdy sedge. It is native to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico, where it grows in moist spots in a number of habitat types. This sedge forms a thick clump of thin stems up to 90 centimeters in length and long, thready leaves. The leaves have basal sheaths with conspicuous red coloration, often spotting. The inflorescence is a dense to open cluster of many spikelets occurring both at the ends of stems and at nodes. Each cluster is up to 15 centimeters long and 1 to 2 wide. The plant is sometimes dioecious, with an individual sedge bearing either male or female flowers. The female, pistillate flowers have white or white-edged bracts. The male, staminate flowers have visible anthers 2 millimeters long or longer. The fruit is coated in a sac called a perigynium which is gold to dark brown in color and has a characteristic bit of spongy tissue at the base.

Carex buxbaumii is a species of sedge known as Buxbaum's sedge or club sedge. It is native to much of the northern Northern Hemisphere, from Alaska to Greenland to Eurasia, and including most of Canada and the United States. It grows in wet habitat, such as marshes and fens. This sedge grows in clumps from long rhizomes. The stems are 75–100 cm (30–39 in) in maximum height. The leaves are narrow and small. The inflorescence has a bract which is sometimes longer than the spikes. The fruits have dark-colored bracts and a sac called a perigynium or utricle which is gray-green and rough in texture.

Carex diandra is a species of sedge known by the common names lesser tussock-sedge and lesser panicled sedge.

Poa glauca is a species of grass known by the common names glaucous bluegrass, glaucous meadow-grass and white bluegrass. It has a circumboreal distribution, occurring throughout the northern regions of the Northern Hemisphere. It is also known from Patagonia. It is a common grass, occurring in Arctic and alpine climates and other areas. It can be found throughout the Canadian Arctic Archipelago in many types of habitat, including disturbed and barren areas.

Isolepis setacea is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family known by the common names bristle club-rush and bristleleaf bulrush. It is native to Eurasia and Africa, and possibly Australasia. It can be found in other places, including some areas in North America, where it is an introduced species. It grows in many types of moist and wet habitat, often in coastal regions, and sometimes inland. It is a perennial herb which forms mats of very thin, grooved, erect or arching stems up to about 20 centimeters tall. The leaves sheath the stem bases and have short, flat, thick blades. The inflorescence is a solitary spikelet just a few millimeters long, or a cluster of up to three spikelets. These are accompanied by a stiff bract extending past the flowers.

Carex lutea is a rare species of sedge known by the common names golden sedge and sulphur sedge. It is endemic to North Carolina, where it is known only from Pender and Onslow Counties in the Cape Fear River watershed. There are nine populations. The plant was discovered in 1991 and described to science as a new species in 1994, and it has not been thoroughly studied nor completely surveyed yet. Its rarity was obvious by 2002, however, when it was federally listed as an endangered species.

Carex specuicola is a rare species of sedge known by the common name Navajo sedge. It is native to a small section of the Colorado Plateau in the United States, its distribution straddling the border between Utah and Arizona, and completely within the Navajo Nation. There are several populations but they are limited to a specific type of habitat. The plants grow from the sides of steep, often vertical cliffs of red Navajo Sandstone, in areas where water trickles from the rock. It occurs at elevations between 5,700 and 6,000 feet, usually in shady spots. Though it is not a grass, the sedge grows in inconspicuous clumps resembling tufts of grass sticking out of the rock face. When the sedge was federally listed as a threatened species in 1985, it was known from only three populations in Coconino County, Arizona, with no more than 700 plants existing. The species has since been observed in northeastern Arizona and San Juan County, Utah.

Spiranthes delitescens is a rare species of orchid known by the common names reclusive lady's tresses, Canelo Hills lady's tresses, and Madrean lady's tresses. It is native to Arizona in the United States, where there are only four occurrences. It is threatened by the loss and degradation of its habitat. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.

Carex bigelowii is a species of sedge known by the common names Bigelow's sedge, Gwanmo sedge, and stiff sedge. It has an Arctic–alpine distribution in Eurasia and North America, and grows up to 50 centimetres (20 in) tall in a variety of habitats.
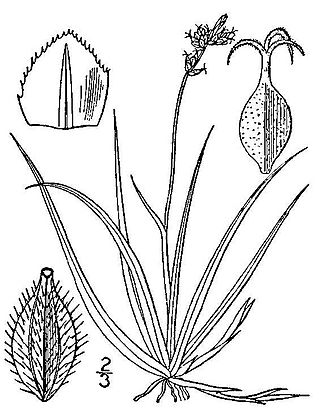
Carex concinna is a species of sedge known by the common names low northern sedge, northern elegant sedge, beauty sedge, and beautiful sedge. It is native to northern North America, where it occurs across Canada and in high elevations in the northern contiguous United States.

Carex garberi, commonly known as elk sedge and Garber's sedge, is a species of sedge native to North America.

Carex inops is a species of sedge known as long-stolon sedge and western oak sedge. It is native to northern North America, where it occurs throughout the southern half of Canada and the western and central United States.

Carex livida is a species of sedge known by the common names livid sedge and pale sedge.

Carex saxatilis is a species of sedge known by the common names rock sedge and russet sedge.

Carex vaginata is a species of sedge known by the common name sheathed sedge.

Eriophorum viridicarinatum is a species of sedge known by the common names thinleaf cottonsedge, green-keeled cottongrass, and bog cottongrass. It is native to northern North America, where it occurs in Alaska and throughout much of Canada, its range extending into the northern contiguous United States. Its distribution is more patchy in the west but it is widespread in eastern Canada.

Ribes americanum is a North American species of flowering plant in the gooseberry family known as wild black currant, American black currant, and eastern black currant. It is widespread in much of Canada and the northern United States.

Trichophorum alpinum, commonly known as alpine bulrush or cotton deergrass, is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family. It has a circumboreal distribution, occurring throughout the northern latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. It is present in Europe, Asia, and northern North America.

Schoenoplectiella hallii is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family known by the common name Hall's bulrush. It is native to the United States, where it has a disjunct distribution, occurring in widely spaced locations throughout the Midwest and East. It is a rare plant.




















