A transient ischemic attack (TIA), commonly known as a mini-stroke, is a temporary (transient) stroke with noticeable symptoms that end within 24 hours. A TIA causes the same symptoms associated with a stroke, such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, sudden dimming or loss of vision, difficulty speaking or understanding language or slurred speech.
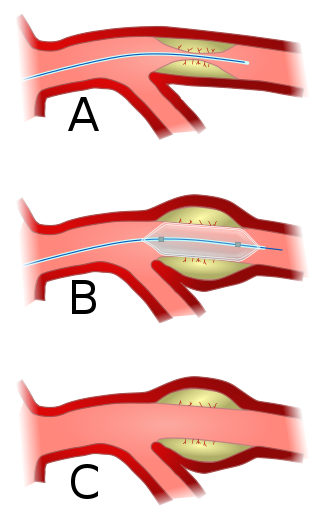
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis.

In medicine, a stent is a tube usually constructed of a metallic alloy or a polymer. It is inserted into the lumen of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open.

Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy.
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement, and angioplasty of narrowed structures.
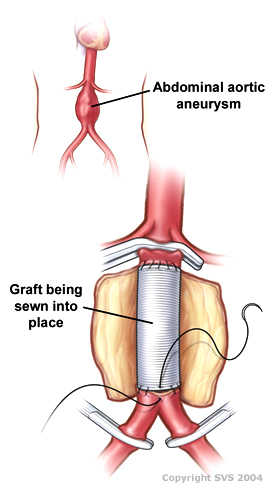
Vascular surgery is a surgical subspecialty in which vascular diseases involving the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures and surgical reconstruction. The specialty evolved from general and cardiovascular surgery where it refined the management of just the vessels, no longer treating the heart or other organs. Modern vascular surgery includes open surgery techniques, endovascular techniques and medical management of vascular diseases - unlike the parent specialities. The vascular surgeon is trained in the diagnosis and management of diseases affecting all parts of the vascular system excluding the coronaries and intracranial vasculature. Vascular surgeons also are called to assist other physicians to carry out surgery near vessels, or to salvage vascular injuries that include hemorrhage control, dissection, occlusion or simply for safe exposure of vascular structures.

Restenosis is the recurrence of stenosis, a narrowing of a blood vessel, leading to restricted blood flow. Restenosis usually pertains to an artery or other large blood vessel that has become narrowed, received treatment to clear the blockage, and subsequently become re-narrowed. This is usually restenosis of an artery, or other blood vessel, or possibly a vessel within an organ.

Interventional cardiology is a branch of cardiology that deals specifically with the catheter based treatment of structural heart diseases. Andreas Gruentzig is considered the father of interventional cardiology after the development of angioplasty by interventional radiologist Charles Dotter.

Cerebral angiography is a form of angiography which provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain, thereby allowing detection of abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms. It was pioneered in 1927 by the Portuguese neurologist Egas Moniz at the University of Lisbon, who also helped develop thorotrast for use in the procedure.
Intermittent claudication, also known as vascular claudication, is a symptom that describes muscle pain on mild exertion, classically in the calf muscle, which occurs during exercise, such as walking, and is relieved by a short period of rest. It is classically associated with early-stage peripheral artery disease, and can progress to critical limb ischemia unless treated or risk factors are modified and maintained.
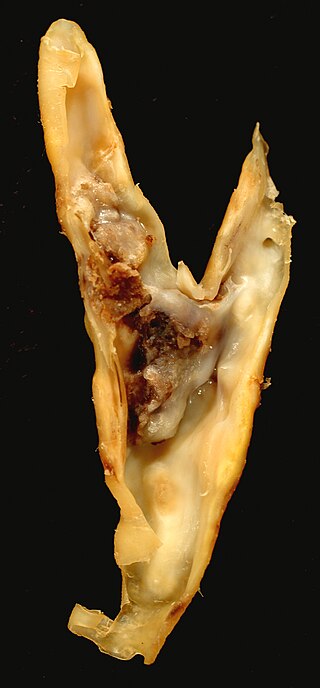
Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure used to reduce the risk of stroke from carotid artery stenosis. In endarterectomy, the surgeon opens the artery and removes the plaque. The plaque forms and thickens the inner layer of the artery, or intima, hence the name of the procedure which simply means removal of part of the internal layers of the artery.

Carotid artery stenosis is a narrowing or constriction of any part of the carotid arteries, usually caused by atherosclerosis.

Cerebral infarction, also known as an ischemic stroke, is the pathologic process that results in an area of necrotic tissue in the brain. In mid to high income countries, a stroke is the main reason for disability among people and the 2nd cause of death. It is caused by disrupted blood supply (ischemia) and restricted oxygen supply (hypoxia). This is most commonly due to a thrombotic occlusion, or an embolic occlusion of major vessels which leads to a cerebral infarct. In response to ischemia, the brain degenerates by the process of liquefactive necrosis.

A watershed stroke is defined as a brain ischemia that is localized to the vulnerable border zones between the tissues supplied by the anterior, posterior and middle cerebral arteries. The actual blood stream blockage/restriction site can be located far away from the infarcts. Watershed locations are those border-zone regions in the brain supplied by the major cerebral arteries where blood supply is decreased. Watershed strokes are a concern because they comprise approximately 10% of all ischemic stroke cases. The watershed zones themselves are particularly susceptible to infarction from global ischemia as the distal nature of the vasculature predisposes these areas to be most sensitive to profound hypoperfusion.

Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a minimally invasive non-surgical procedure used to treat narrowing of the coronary arteries of the heart found in coronary artery disease. The procedure is used to place and deploy coronary stents, a permanent wire-meshed tube, to open narrowed coronary arteries. PCI is considered 'non-surgical' as it uses a small hole in a peripheral artery (leg/arm) to gain access to the arterial system; an equivalent surgical procedure would involve the opening of the chest wall to gain access to the heart area. The term 'coronary angioplasty with stent' is synonymous with PCI. The procedure visualises the blood vessels via fluoroscopic imaging and contrast dyes. PCI is performed by an interventional cardiologists in a catheterization laboratory setting.
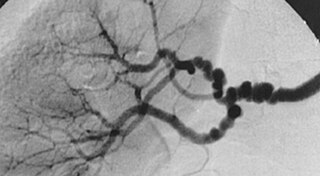
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a non-atherosclerotic, non-inflammatory disease of the blood vessels that causes abnormal growth within the wall of an artery. FMD has been found in nearly every arterial bed in the body, although the most commonly affected are the renal and carotid arteries.

Carotid artery dissection is a serious condition in which a tear forms in one of the two main carotid arteries in the neck, allowing blood to enter the artery wall and separate its layers (*dissection*). This separation can lead to the formation of a blood clot, narrowing of the artery, and restricted blood flow to the brain, potentially resulting in stroke. Symptoms vary depending on the extent and location of the dissection and may include a sudden, severe headache, neck or facial pain, vision changes, a drooping eyelid, and stroke-like symptoms such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, or loss of coordination.
Transradial catheterization is an endovascular procedure or catheterization procedure performed to diagnose and treat arterial disease. Endovascular procedure can be performed achieving access in to body’s arterial system from either femoral artery, brachial artery or radial artery in the wrist. The transfemoral approach to perform cardiac catheterization has typically been more prevalent in invasive cardiology. But radial access has gained popularity due to technical advances with catheters and lower complication rates than transfemoral access. The European Society of Cardiology and the American Heart Association both support a radial-first approach in acute coronary syndrome.
Interventional neuroradiology (INR) also known as neurointerventional surgery (NIS), endovascular therapy (EVT), endovascular neurosurgery, and interventional neurology is a medical subspecialty of neurosurgery, neuroradiology, intervention radiology and neurology specializing in minimally invasive image-based technologies and procedures used in diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the head, neck, and spine.

Brajesh K. Lal, born in 1963 in Varanasi, India and of Indian origin, is an American surgeon, and an expert in vascular disease, particularly the prevention and treatment of stroke and venous disease. He is a tenured Professor of Vascular Surgery at the University of Maryland and Professor of Neurology at Mayo Clinic. He holds additional appointments at the Departments of Bioengineering at the University of Maryland and George Mason University. He founded and currently directs the multi-specialty Center for Vascular Research and the NIH Vascular Imaging Core Facility at the University of Maryland. He has been elected as a Distinguished Fellow of the Society for Vascular Surgery and Distinguished Fellow of the American Venous Forum.















