Related Research Articles
An air embolism, also known as a gas embolism, is a blood vessel blockage caused by one or more bubbles of air or other gas in the circulatory system. Air can be introduced into the circulation during surgical procedures, lung over-expansion injury, decompression, and a few other causes. In flora, air embolisms may also occur in the xylem of vascular plants, especially when suffering from water stress.

Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy.
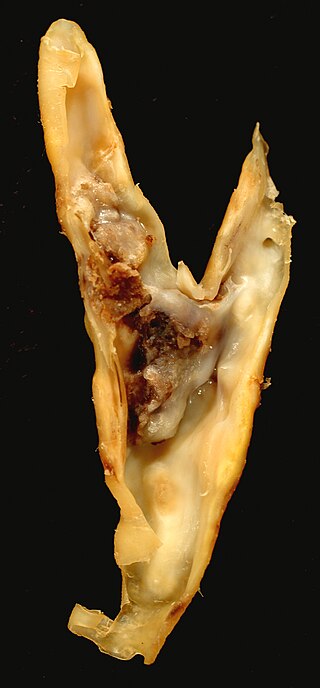
An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal accumulation of material in the inner layer of an arterial wall.
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) or intravascular echocardiography is a medical imaging methodology using a specially designed catheter with a miniaturized ultrasound probe attached to the distal end of the catheter. The proximal end of the catheter is attached to computerized ultrasound equipment. It allows the application of ultrasound technology, such as piezoelectric transducer or CMUT, to see from inside blood vessels out through the surrounding blood column, visualizing the endothelium of blood vessels.

Cerebral angiography is a form of angiography which provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain, thereby allowing detection of abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms. It was pioneered in 1927 by the Portuguese neurologist Egas Moniz at the University of Lisbon, who also helped develop thorotrast for use in the procedure.

Cardiac catheterization is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.

Pulmonary angiography is a medical fluoroscopic procedure used to visualize the pulmonary arteries and much less frequently, the pulmonary veins. It is a minimally invasive procedure performed most frequently by an interventional radiologist or interventional cardiologist to visualise the arteries of the lungs.

Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is a fluoroscopy technique used in interventional radiology to clearly visualize blood vessels in a bony or dense soft tissue environment. Images are produced using contrast medium by subtracting a "pre-contrast image" or mask from subsequent images, once the contrast medium has been introduced into a structure. Hence the term "digital subtraction angiography. Subtraction angiography was first described in 1935 and in English sources in 1962 as a manual technique. Digital technology made DSA practical starting in the 1970s.
An embolus, is described as a free-floating mass, located inside blood vessels that can travel from one site in the blood stream to another. An embolus can be made up of solid, liquid, or gas. Once these masses get "stuck" in a different blood vessel, it is then known as an "embolism." An embolism can cause ischemia—damage to an organ from lack of oxygen. A paradoxical embolism is a specific type of embolism in which the embolus travels from the right side of the heart to the left side of the heart and lodges itself in a blood vessel known as an artery. Thus, it is termed "paradoxical" because the embolus lands in an artery, rather than a vein.
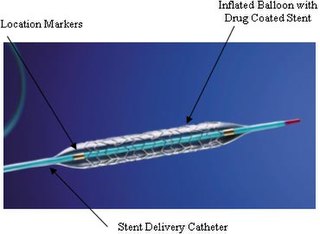
A drug-eluting stent (DES) is a peripheral or coronary stent placed into narrowed, diseased peripheral or coronary arteries that slowly release a drug to block cell proliferation. This prevents fibrosis that, together with clots (thrombi), could otherwise block the stented artery, a process called restenosis. The stent is usually placed within the peripheral or coronary artery by an interventional cardiologist or interventional radiologist during an angioplasty procedure.

3D ultrasound is a medical ultrasound technique, often used in fetal, cardiac, trans-rectal and intra-vascular applications. 3D ultrasound refers specifically to the volume rendering of ultrasound data. When involving a series of 3D volumes collected over time, it can also be referred to as 4D ultrasound or real-time 3D ultrasound.

Computed tomography angiography is a computed tomography technique used for angiography—the visualization of arteries and veins—throughout the human body. Using contrast injected into the blood vessels, images are created to look for blockages, aneurysms, dissections, and stenosis. CTA can be used to visualize the vessels of the heart, the aorta and other large blood vessels, the lungs, the kidneys, the head and neck, and the arms and legs. CTA can also be used to localise arterial or venous bleed of the gastrointestinal system.
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is a diagnostic technique used in coronary catheterization. FFR measures pressure differences across a coronary artery stenosis to determine the likelihood that the stenosis impedes oxygen delivery to the heart muscle.

Carotid ultrasonography is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique to evaluate structural details of the carotid arteries. Carotid ultrasound is used to diagnose carotid artery stenosis (CAS) and can assess atherosclerotic plaque morphology and characteristics. Carotid duplex and contrast-enhanced ultrasound are two of the most common imaging techniques used to evaluate carotid artery disease.

Arterial embolism is a sudden interruption of blood flow to an organ or body part due to an embolus adhering to the wall of an artery blocking the flow of blood, the major type of embolus being a blood clot (thromboembolism). Sometimes, pulmonary embolism is classified as arterial embolism as well, in the sense that the clot follows the pulmonary artery carrying deoxygenated blood away from the heart. However, pulmonary embolism is generally classified as a form of venous embolism, because the embolus forms in veins. Arterial embolism is the major cause of infarction.

Coronary CT angiography is the use of computed tomography (CT) angiography to assess the coronary arteries of the heart. The patient receives an intravenous injection of radiocontrast and then the heart is scanned using a high speed CT scanner, allowing physicians to assess the extent of occlusion in the coronary arteries, usually in order to diagnose coronary artery disease.

Cardiac imaging refers to minimally invasive imaging of the heart using ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), or nuclear medicine (NM) imaging with PET or SPECT. These cardiac techniques are otherwise referred to as echocardiography, Cardiac MRI, Cardiac CT, Cardiac PET and Cardiac SPECT including myocardial perfusion imaging.

James S. Forrester III is an American cardiologist. Born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, he received his medical training at the University of Pennsylvania, UCLA, and Harvard University. During the 1970s through 1990s, his research led to three major advancements in the practice of cardiology. Later in his career, he would return to UCLA, this time as a professor, while simultaneously being the Chief of the Division of Cardiology at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center. Forrester has published hundreds of papers and manuscripts dealing with the subject of cardiology, and is the recipient of numerous awards, including being the second person to ever receive the Lifetime Achievement Award of the American College of Cardiology in 2009.
A scanning fiber endoscope is a technology that uses a flexible, small peripheral or coronary catheter to provide wide-field, high-quality, full-color, laser-based video imaging. These differences distinguish SFE applications from current imaging approaches such as IVUS and Intracoronary OCT. Applications for the device, are expected to include medical diagnosis and support in determining interventional treatments such as surgery or biopsy. Providing both full-color images and a wide-field, real-time surgical view into the inner depths of arteries, enables physicians to circumnavigate hard to reach internal tissues to assess for potential disease.

Arterial occlusion is a condition involving partial or complete blockage of blood flow through an artery. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to body tissues. An occlusion of arteries disrupts oxygen and blood supply to tissues, leading to ischemia. Depending on the extent of ischemia, symptoms of arterial occlusion range from simple soreness and pain that can be relieved with rest, to a lack of sensation or paralysis that could require amputation.
References
- 1 2 McVeigh PZ, Sacho R, Weersink RA, Pereira VM, Kucharczyk W, Seibel EJ, Wilson BC, Krings T (August 2014). "High-resolution angioscopic imaging during endovascular neurosurgery". Neurosurgery. 75 (2): 171–80, discussion 179–80. doi:10.1227/NEU.0000000000000383. PMC 4086773 . PMID 24762703.
- ↑ MDGuidelines > Arterial Embolism And Thrombosis Archived 2018-02-02 at the Wayback Machine From The Medical Disability Advisor by Presley Reed, MD. Retrieved on April 30, 2010
- ↑ Forrester JS, Litvack F, Grundfest W, Hickey A (1987). "A perspective of coronary disease seen through the arteries of living man". Circulation. 75 (3): 505–13. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.3.505 . PMID 3815762.