Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins.

A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line (c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. These catheters are commonly placed in veins in the neck, chest, groin, or through veins in the arms.

The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein that receives venous return from the upper half of the body, above the diaphragm. Venous return from the lower half, below the diaphragm, flows through the inferior vena cava. The SVC is located in the anterior right superior mediastinum. It is the typical site of central venous access via a central venous catheter or a peripherally inserted central catheter. Mentions of "the cava" without further specification usually refer to the SVC.

The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra.

Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enlarged veins in the affected area, but some DVTs have no symptoms.

A dialysis catheter is a catheter used for exchanging blood to and from a hemodialysis machine and a patient.

Cardiac catheterization is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
Endovenous laser treatment (ELT) is a minimally invasive ultrasound-guided technique used for treating varicose veins using laser energy commonly performed by a phlebologist, interventional radiologist or vascular surgeon.

Inferior vena cava syndrome (IVCS) is a very rare constellation of symptoms resulting from either an obstruction, or stenosis of the inferior vena cava. It can be caused by physical invasion or compression by a pathological process or by thrombosis within the vein itself. It can also occur during pregnancy. Pregnancy leads to high venous pressure in the lower limbs, decreased blood return to the heart, decreased cardiac output due to obstruction of the inferior vena cava, sudden rise in venous pressure which can lead to placental separation, and a decrease in kidney function. All of these issues can arise from lying in the supine position during late pregnancy which can cause compression of the inferior vena cava by the uterus. Symptoms of late pregnancy inferior vena cava syndrome consist of intense pain in the right hand side, muscle twitching, hypotension, and fluid retention.

May–Thurner syndrome (MTS), also known as the iliac vein compression syndrome, is a condition in which compression of the common venous outflow tract of the left lower extremity may cause discomfort, swelling, pain or iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis.
Vascular access refers to a rapid, direct method of introducing or removing devices or chemicals from the bloodstream. In hemodialysis, vascular access is used to remove the patient's blood so that it can be filtered through the dialyzer. Three primary methods are used to gain access to the blood: an intravenous catheter, an arteriovenous fistula (AV) or a synthetic graft. In the latter two, needles are used to puncture the graft or fistula each time dialysis is performed.

Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography, percutaneous hepatic cholangiogram (PTHC) is a radiological technique used to visualize the anatomy of the biliary tract. A contrast medium is injected into a bile duct in the liver, after which X-rays are taken. It allows access to the biliary tree in cases where endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography has been unsuccessful. Initially reported in 1937, the procedure became popular in 1952.
The term venous translucence has been used in phlebology since 1996 by surgeon Pedro Fernandes Neto during ambulatory clinical exams in Brazil. His results were published in the annals of the national and international congresses of angiology. Venous translucence is the process of reflective image visualization of veins by light, which reaches up to the superficial venous system. It is a non-invasive method. Since it is a simple, low-cost technique it can be repeated as needed, which is useful in disease-process monitoring. It is a new diagnostic procedure, still undergoing investigation; more analysis is necessary to hone its technical aspects. Venous translucence is based on optical physics. It is caused by the refraction, absorption and reflection of light. The color which is not absorbed is reflected, and is the one that is seen. Therefore, venous translumination is based on the incidence of luminosity on the vein, where part of the light is absorbed and another reflected.

In medicine, a port is a small appliance that is installed beneath the skin. A catheter connects the port to a vein. Under the skin, the port has a septum through which drugs can be injected and blood samples can be drawn many times, usually with less discomfort for the patient than a more typical "needle stick".
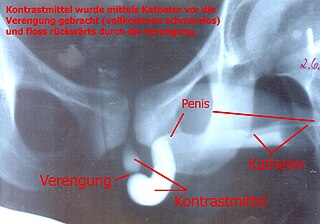
A retrograde urethrography is a routine radiologic procedure used to image the integrity of the urethra. Hence a retrograde urethrogram is essential for diagnosis of urethral injury, or urethral stricture.
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a medical condition in which blood pools in the veins, straining the walls of the vein. The most common cause of CVI is superficial venous reflux which is a treatable condition. As functional venous valves are required to provide for efficient blood return from the lower extremities, this condition typically affects the legs. If the impaired vein function causes significant symptoms, such as swelling and ulcer formation, it is referred to as chronic venous disease. It is sometimes called chronic peripheral venous insufficiency and should not be confused with post-thrombotic syndrome in which the deep veins have been damaged by previous deep vein thrombosis.

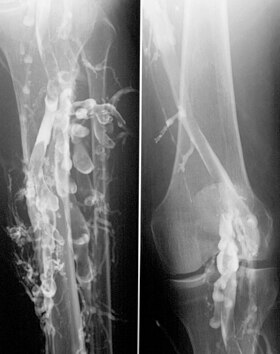
Congenital stenosis of vena cava is a congenital anomaly in which the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava has an aberrant interruption or coarctation.
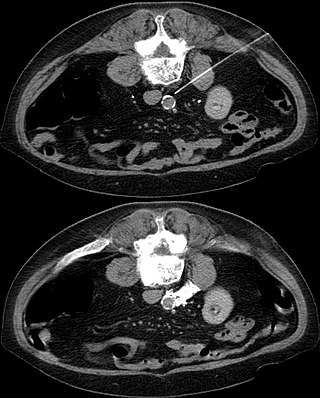
Sympathicolysis is a procedure for temporary or long-term elimination of sympathetic innervation. It is used to improve blood circulation in the legs or arms. The sympathetic nervous system causes the balance of the autonomic system to lean towards narrowing of blood vessels, with elimination of its function resulting in vasodilatation. Completely blocked arteries are not opened again, but the collaterals are better supplied with blood.
Venous access is any method used to access the bloodstream through the veins, either to administer intravenous therapy, parenteral nutrition, to obtain blood for analysis, or to provide an access point for blood-based treatments such as dialysis or apheresis. Access is most commonly achieved via the Seldinger technique, and guidance tools such as ultrasound and fluoroscopy can also be used to assist with visualizing access placement.
In medicine, vascular access is a means of accessing the bloodstream through the peripheral or central blood vessels in order to obtain blood or deliver medications including chemotherapy. A vascular access procedure involves insertion of a sterile plastic tube called a catheter into a blood vessel. Types of catheters can be either peripherally or centrally located. Peripheral catheters are approximately one inch (25 mm) long and are inserted into the small veins of the forearm. Central catheters are bigger and longer and are inserted into the large veins of the extremities, neck, or chest. Central venous catheters are the primary modality used for delivery of chemotherapeutic agents. The duration of central venous catheterization is dependent on the type of treatment given.