Related Research Articles
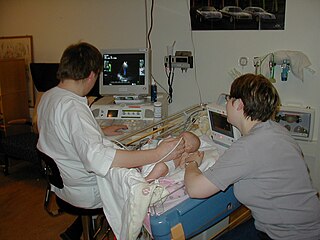
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics or to generate an informative audible sound. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography, or echography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. The machine used is called an ultrasound machine, a sonograph or an echograph. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ultrasonogram, a sonogram or an echogram.

Cytopathology is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in 1928. Cytopathology is generally used on samples of free cells or tissue fragments, in contrast to histopathology, which studies whole tissues. Cytopathology is frequently, less precisely, called "cytology", which means "the study of cells".

Mammography is the process of using low-energy X-rays to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications.

A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions.

Technetium (99mTc) sestamibi (INN) is a pharmaceutical agent used in nuclear medicine imaging. The drug is a coordination complex consisting of the radioisotope technetium-99m bound to six (sesta=6) methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) ligands. The anion is not defined. The generic drug became available late September 2008. A scan of a patient using MIBI is commonly known as a "MIBI scan".
Computed tomography laser mammography (CTLM) is the trademark of Imaging Diagnostic Systems, Inc. for its optical tomographic technique for female breast imaging.

Phyllodes tumors, are a rare type of biphasic fibroepithelial mass that form from the periductal stromal and epithelial cells of the breast. They account for less than 1% of all breast neoplasms. They were previously termed cystosarcoma phyllodes, coined by Johannes Müller in 1838, before being renamed to phyllodes tumor by the World Health Organization in 2003. Phullon, which means 'leaf' in Greek, describes the unique papillary projections characteristic of phyllodes tumors on histology. Diagnosis is made via a core-needle biopsy and treatment is typically surgical resection with wide margins (>1 cm), due to their propensity to recur.
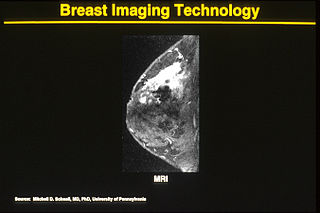
One alternative to mammography, breast MRI or contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), has shown substantial progress in the detection of breast cancer.

Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a breast lump one can feel, typically being detected through screening mammography. It has been diagnosed in a significant percentage of men.

Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of medical images. Imaging techniques in X-ray, MRI, Endoscopy, and ultrasound diagnostics yield a great deal of information that the radiologist or other medical professional has to analyze and evaluate comprehensively in a short time. CAD systems process digital images or videos for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases, in order to offer input to support a decision taken by the professional.
Breast cancer management takes different approaches depending on physical and biological characteristics of the disease, as well as the age, over-all health and personal preferences of the patient. Treatment types can be classified into local therapy and systemic treatment. Local therapy is most efficacious in early stage breast cancer, while systemic therapy is generally justified in advanced and metastatic disease, or in diseases with specific phenotypes.

Breast cancer screening is the medical screening of asymptomatic, apparently healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to achieve an earlier diagnosis. The assumption is that early detection will improve outcomes. A number of screening tests have been employed, including clinical and self breast exams, mammography, genetic screening, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.

Molecular breast imaging (MBI), also known as scintimammography, is a type of breast imaging test that is used to detect cancer cells in breast tissue of individuals who have had abnormal mammograms, especially for those who have dense breast tissue, post-operative scar tissue or breast implants.

A breast biopsy is usually done after a suspicious lesion is discovered on either mammography or ultrasound to get tissue for pathological diagnosis. Several methods for a breast biopsy now exist. The most appropriate method of biopsy for a patient depends upon a variety of factors, including the size, location, appearance and characteristics of the abnormality. The different types of breast biopsies include fine-needle aspiration (FNA), vacuum-assisted biopsy, core needle biopsy, and surgical excision biopsy. Breast biopsies can be done utilizing ultrasound, MRI or a stereotactic biopsy imaging guidance. Vacuum assisted biopsies are typically done using stereotactic techniques when the suspicious lesion can only be seen on mammography. On average, 5–10 biopsies of a suspicious breast lesion will lead to the diagnosis of one case of breast cancer. Needle biopsies have largely replaced open surgical biopsies in the initial assessment of imaging as well as palpable abnormalities in the breast.

Positron emission mammography (PEM) is a nuclear medicine imaging modality used to detect or characterise breast cancer. Mammography typically refers to x-ray imaging of the breast, while PEM uses an injected positron emitting isotope and a dedicated scanner to locate breast tumors. Scintimammography is another nuclear medicine breast imaging technique, however it is performed using a gamma camera. Breasts can be imaged on standard whole-body PET scanners, however dedicated PEM scanners offer advantages including improved resolution.
Automated whole-breast ultrasound (AWBU) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to obtain volumetric ultrasound data of the entire breast.
Interventional oncology is a subspecialty field of interventional radiology that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer and cancer-related problems using targeted minimally invasive procedures performed under image guidance. Interventional oncology has developed to a separate pillar of modern oncology and it employs X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help guide miniaturized instruments to allow targeted and precise treatment of solid tumours located in various organs of the human body, including but not limited to the liver, kidneys, lungs, and bones. Interventional oncology treatments are routinely carried out by interventional radiologists in appropriate settings and facilities.
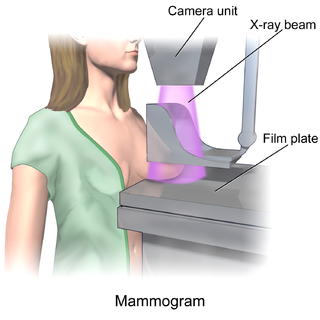
In medicine, breast imaging is a sub-speciality of diagnostic radiology that involves imaging of the breasts for screening or diagnostic purposes. There are various methods of breast imaging using a variety of technologies as described in detail below. Traditional screening and diagnostic mammography uses x-ray technology and has been the mainstay of breast imaging for many decades. Breast tomosynthesis is a relatively new digital x-ray mammography technique that produces multiple image slices of the breast similar to, but distinct from, computed tomography (CT). Xeromammography and galactography are somewhat outdated technologies that also use x-ray technology and are now used infrequently in the detection of breast cancer. Breast ultrasound is another technology employed in diagnosis and screening that can help differentiate between fluid filled and solid lesions, an important factor to determine if a lesion may be cancerous. Breast MRI is a technology typically reserved for high-risk patients and patients recently diagnosed with breast cancer. Lastly, scintimammography is used in a subgroup of patients who have abnormal mammograms or whose screening is not reliable on the basis of using traditional mammography or ultrasound.
Ultrasonography of liver tumors involves two stages: detection and characterization.
A specific branch of contrast-enhanced ultrasound, acoustic angiography is a minimally invasive and non-ionizing medical imaging technique used to visualize vasculature. Acoustic angiography was first developed by the Dayton Laboratory at North Carolina State University and provides a safe, portable, and inexpensive alternative to the most common methods of angiography such as Magnetic Resonance Angiography and Computed Tomography Angiography. Although ultrasound does not traditionally exhibit the high resolution of MRI or CT, high-frequency ultrasound (HFU) achieves relatively high resolution by sacrificing some penetration depth. HFU typically uses waves between 20 and 100 MHz and achieves resolution of 16-80μm at depths of 3-12mm. Although HFU has exhibited adequate resolution to monitor things like tumor growth in the skin layers, on its own it lacks the depth and contrast necessary for imaging blood vessels. Acoustic angiography overcomes the weaknesses of HFU by combining contrast-enhanced ultrasound with the use of a dual-element ultrasound transducer to achieve high resolution visualization of blood vessels at relatively deep penetration levels.
References
- ↑ Rouvillois C, Tricoire J, Mariel L, Portier F (November 1973). "[Thermography using contact plates in the diagnosis of breast cancers]". Chirurgie; Mémoires de l'Académie de Chirurgie (in French). 99 (11): 866–72. PMID 4792563.
- ↑ Tricoire J (1975). "[Study of breast cancer by means of liquid crystals thermography]". Journal de Gynécologie, Obstétrique et Biologie de la Reproduction (in French). 4 SUPPL 2: 123–30. PMID 1194631.
- ↑ Dodd, Gerald D. (June 1977). "Present status of thermography, ultrasound and mammography in breast cancer detection". Cancer. 39 (6 Suppl): 2796–805. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197706)39:6<2796::AID-CNCR2820390667>3.0.CO;2-0 . PMID 872067.
- ↑ Montruccoli GC, Montruccoli Salmi D, Casali F (January–March 2004). "A new type of breast contact thermography plate: a preliminary and qualitative investigation of its potentiality on phantoms". Physica Medica. 20 (1): 27–31.
- 1 2 3 Longatto Filho A, Costa SM, Milanezi F, et al. (November 2007). "Immunohistochemical expression of VEGF-A and its ligands in non-neoplastic lesions of the breast sampling-assisted by dynamic angiothermography". Oncology Reports. 18 (5): 1201–6. doi: 10.3892/or.18.5.1201 . PMID 17914573.
- ↑ Isard HJ, Becker W, Shilo R, Ostrum BJ (August 1972). "Breast thermography after four years and 10000 studies". The American Journal of Roentgenology, Radium Therapy, and Nuclear Medicine. 115 (4): 811–21. doi: 10.2214/ajr.115.4.811 . PMID 5054275.
- ↑ Kennedy DA, Lee T, Seely D (March 2009). "A comparative review of thermography as a breast cancer screening technique". Integrative Cancer Therapies. 8 (1): 9–16. doi: 10.1177/1534735408326171 . PMID 19223370.
- ↑ Berrington de González A, Reeves G (September 2005). "Mammographic screening before age 50 years in the UK: comparison of the radiation risks with the mortality benefits". British Journal of Cancer. 93 (5): 590–6. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602683. PMC 2361593 . PMID 16136033.
- ↑ Boone JM, Kwan AL, Yang K, Burkett GW, Lindfors KK, Nelson TR (April 2006). "Computed tomography for imaging the breast". Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia. 11 (2): 103–11. doi:10.1007/s10911-006-9017-1. PMID 17053979. S2CID 25758608.
- ↑ Naccarato AG, Viacava P, Bocci G, et al. (December 2003). "Definition of the microvascular pattern of the normal human adult mammary gland". Journal of Anatomy. 203 (6): 599–603. doi:10.1046/j.1469-7580.2003.00244.x. PMC 1571199 . PMID 14686695.
- ↑ Choi BB, Kim SH, Park CS, Cha ES, Lee AW (February 2011). "Radiologic findings of lobular carcinoma in situ: mammography and ultrasonography". Journal of Clinical Ultrasound. 39 (2): 59–63. doi:10.1002/jcu.20772. PMID 21213330. S2CID 22540643.