
Papilio helenus, the red Helen, is a large swallowtail butterfly found in forests of southern India and parts of southeast Asia.

Junonia lemonias, the lemon pansy, is a common nymphalid butterfly found in Cambodia and South Asia. It is found in gardens, fallow land, and open wooded areas.

Spialia galba, the Indian grizzled skipper, is a hesperiid butterfly which is found in South Asia and parts of Southeast Asia.

Charaxes bernardus, the tawny rajah, is a butterfly that belongs to the rajahs and nawabs group, that is, the Charaxinae group of the brush-footed butterflies family. This species can be found in India, China, Indomalaya, and onwards to Indonesia.

Polyura delphis, the jewelled nawab, is a butterfly found in India and Southeast Asia that belongs to the rajahs and nawabs group, that is, the Charaxinae subfamily of the brush-footed butterflies family. The front wings have a concave outer edge and hind wings bear two tails.The upperside is white, largely marked with brown at the apex of the forewings. The reverse is metallic white decorated with yellow chevron lines and red marks. The wingspan is about 2.75 inches (70 mm).

Poritia hewitsoni, the common gem, is a small butterfly found in India, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia and Vietnam that belongs to the lycaenids or blues family.

Taraka hamada, the forest Pierrot, is a small species of butterfly found in Asia, that belongs to the lycaenids family.

Megisba malaya, the Malayan, is a small species of butterfly found in South Asia and Southeast Asia. It belongs to the family of gossamer-winged butterflies (Lycaenidae). The species was first described by Thomas Horsfield in 1928.

Chilades parrhasius, the small Cupid, is a small butterfly that belongs to the lycaenids or blues family. It is found in Nepal, southern Turan, southern Ghissar, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, United Arab Emirates, Oman and southern, central and north-west India.

Hypolycaena erylus, the common tit, is a small but striking butterfly found in India and South-East Asia that belongs to the lycaenids or blues family. The species was first described by Jean-Baptiste Godart in 1823.

Chliaria othona, the orchid tit, is a species of lycaenid or blue butterfly found in Asia.

Faunis canens, the common faun, is a butterfly from South and South East Asia that belongs to the Morphinae, a subfamily of the brush-footed butterflies. This species may include the Indian faun, Faunis arcesilaus.

Enispe intermedia is a butterfly found in South Asia that belongs to the Morphinae subfamily of the brush-footed butterflies family.

Prosotas lutea or Brown Lineblue is a species of blue (Lycaenidae) butterfly found in Asia.

Dacalana cotys, the white-banded royal is a species of blue butterfly (Lycaenidae) found in South East Asia.

Pratapa icetoides, the blue royal, is a species of blue butterfly (Lycaenidae) found in the Indomalayan realm.

The blue tit is a species of lycaenid or blue butterfly found in parts of South Asia and Southeast Asia. It was traditionally called Chliaria kina but the genus Chliaria is merged into Hypolycaena by many recent authors.

Rathinda is a butterfly genus in the family Lycaenidae. It consists of a single species, Rathinda amor, the monkey puzzle, found in Sri Lanka and India.
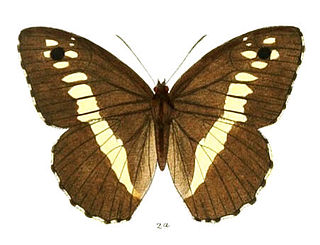
Aulocera swaha, the common satyr, is a brown (Satyrinae) butterfly that is found in the Himalayas.




























