Cliola, Illinois | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates: 39°59′42″N91°17′38″W / 39.99500°N 91.29389°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Illinois |
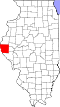
| County | Adams |
| Elevation | 718 ft (219 m) |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central (CST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| Area code | 217 |
| GNIS feature ID | 1785269 [1] |
Cliola is an unincorporated historical community in Ellington Township, Adams County, Illinois, United States. Cliola was located along a railroad line northeast of Quincy. In a September 14, 1899 article in The Quincy Whig about the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad laying a new railroad switch between Eubanks and Cliola it was mentioned that after completion Cliola would no longer exist. [2] There was previously a post office located in Cliola that was established on August 1, 1868. [3]