Related Research Articles

A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group, which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster, which is part of the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex. The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the Hubble expansion. The number of superclusters in the observable universe is estimated to be 10 million.

The Virgo Supercluster or the Local Supercluster was a formerly defined supercluster containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least 100 galaxy groups and clusters are located within its diameter of 33 megaparsecs. The Virgo SC is one of about 10 million superclusters in the observable universe and is in the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex, a galaxy filament.

Coma Berenices is an ancient asterism in the northern sky, which has been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is in the direction of the fourth galactic quadrant, between Leo and Boötes, and it is visible in both hemispheres. Its name means "Berenice's Hair" in Latin and refers to Queen Berenice II of Egypt, who sacrificed her long hair as a votive offering. It was introduced to Western astronomy during the third century BC by Conon of Samos and was further corroborated as a constellation by Gerardus Mercator and Tycho Brahe. It is the only modern constellation named for a historic person.
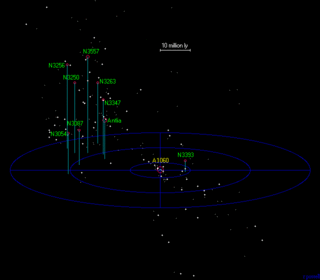
The Hydra–Centaurus Supercluster, or the Hydra and Centaurus Superclusters, was a previously defined supercluster in two parts, which prior to the identification of Laniakea Supercluster in 2014 is the closest neighbour of the former Virgo Supercluster. Its center is located about 39 Mpc (127 Mly) away, with it extending to a maximum distance of around 69 Mpc (225 Mly).

The Antlia Cluster is a cluster of galaxies located in the Hydra–Centaurus Supercluster. The Antlia Cluster is the third-nearest to the Local Group after the Virgo Cluster and Fornax Cluster. Antlia's distance from Earth is 40.5 megaparsecs to 40.9 Mpc (133.4 Mly) and can be viewed from Earth in the constellation Antlia. The Antlia Cluster should not be confused with the Antlia Dwarf galaxy.

In cosmology, galaxy filaments are the largest known structures in the universe, consisting of walls of galactic superclusters. These massive, thread-like formations can commonly reach 50/h to 80/h Megaparsecs —with the largest found to date being the Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall at around 3 gigaparsecs (9.8 Gly) in length—and form the boundaries between voids. Due to the accelerating expansion of the universe, the individual clusters of gravitationally bound galaxies that make up galaxy filaments are moving away from each other at an accelerated rate; in the far future they will dissolve.

Zeta Mensae, Latinized from ζ Mensae, is a solitary, white-hued star in the southern constellation of Mensa. It is faintly visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of +5.64. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 8.2879 mas as seen from GAIA, it is located around 394 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction factor of 0.088 due to interstellar dust. Eggen (1995) listed it as a proper motion candidate for membership in the IC 2391 supercluster.
Abell 223 is a galaxy cluster. It is located at a distance of 2.4 billion light-years from Earth. The cluster is connected to nearby cluster Abell 222 by a filament of matter. Research has shown that only 20% of that matter is normal. The rest is thought to be dark matter. This means that this would form the Abell 222/ Abell 223 Supercluster as we understand them.

NGC 7090 is a spiral galaxy in the southern constellation of Indus located about 31 million light-years away. English astronomer John Herschel first observed this galaxy on 4 October 1834.

The Coma I Group is a group of galaxies located about 14.5 Mpc (47.3 Mly) away in the constellation Coma Berenices. The brightest member of the group is NGC 4725. The Coma I Group is rich in spiral galaxies while containing few elliptical and lenticular galaxies. Coma I lies in the foreground of the more distant Coma and Leo clusters and is located within the Virgo Supercluster.

NGC 4061 is an elliptical galaxy located 310 light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 27, 1785. It was rediscovered by John Herschel on April 29, 1832. It is listed both as NGC 4061 and NGC 4055. NGC 4061 is a member of the NGC 4065 Group and forms an interacting pair with its companion, NGC 4065 as evidenced by distortions in their optical isophotes.

NGC 4076 is a spiral galaxy located 290 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 27, 1785 and is a member of the NGC 4065 Group.

NGC 4093 is an elliptical galaxy located 340 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on May 4, 1864. NGC 4093 is a member of the NGC 4065 Group and is a radio galaxy with a two sided jet.

The NGC 4065 Group is a group of galaxies located about 330 Mly (100 Mpc) in the constellation Coma Berenices. The group's brightest member is NGC 4065 and located in the Coma Supercluster.

NGC 4298 is a flocculent spiral galaxy located about 53 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 8, 1784 and is a member of the Virgo Cluster.

NGC 4302 is an edge-on spiral galaxy located about 55 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 8, 1784 and is a member of the Virgo Cluster.

NGC 4324 is a lenticular galaxy located about 85 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on March 4, 1862. NGC 4324 has a stellar mass of 5.62 × 1010M☉, and a baryonic mass of 5.88 × 1010M☉. The galaxy's total mass is around 5.25 × 1011M☉. NGC 4324 is notable for having a ring of star formation surrounding its nucleus. It was considered a member of the Virgo II Groups until 1999, when its distance was recalculated and it was placed in the Virgo W Group.

NGC 3599 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Leo. It was discovered by William Herschel on March 14, 1784. The galaxy is located at a distance of 67 million light-years (20.4 Mpc) from the Sun. NGC 3599 is a member of the Leo II group of galaxies in the Virgocentric flow.

NGC 4325 is an elliptical galaxy located about 330 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on April 15, 1865, who described it as "vF, vS, iR, nf of 2". Despite being listed in the Virgo Cluster catalog as VCC 616, it is not a member of the Virgo Cluster but instead a background galaxy.
References
- ↑ Finoguenov, A.; Briel, U. G.; Henry, J. P. (2013). "XMM-Newton Discovery of an X-Ray Filament in Coma". Astrophysics and Space Science Library. 309 (3). Springer Science & Business Media: 45. arXiv: astro-ph/0309019 . doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20031319. ISBN 978-1-4020-2564-8. S2CID 14876413 . Retrieved 30 May 2017.
- ↑ Fontanelli, P. (September 1984). "The Coma/A 1367 filament of galaxies". Astronomy and Astrophysics . 138 (1): 85–92. Bibcode:1984A&A...138...85F. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ↑ THE ASTRONOMICAL JOURNAL, 115:1745-1777, 1998 May; THE STAR FORMATION PROPERTIES OF DISK GALAXIES: Hα IMAGING OF GALAXIES IN THE COMA SUPERCLUSTER
- ↑ Fuller, C.; Davies, J. I.; Smith, M. W. L. (9 March 2016). "H-ATLAS: The Far-Infrared properties of galaxies in and around the Coma Cluster". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society . 458 (1): 582–602. arXiv: 1603.02970 . Bibcode:2016MNRAS.458..582F. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stw305 .