
Perforin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRF1 gene and the Prf1 gene in mice.

Complement component 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C5 gene.

Mannan-binding lectin serine protease 1 also known as mannose-associated serine protease 1 (MASP-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MASP1 gene.

Mannan-binding lectin serine protease 2 also known as mannose-binding protein-associated serine protease 2 (MASP-2) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MASP2 gene.

Complement receptor type 2 (CR2), also known as complement C3d receptor, Epstein-Barr virus receptor, and CD21, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR2 gene.

CD155, also known as the poliovirus receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PVR gene. It is a transmembrane protein that is involved in forming junctions between neighboring cells. It is also the molecule that poliovirus uses to enter cells. The gene is specific to the primates.

Chemokine ligand 8 (CCL8), also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 2 (MCP2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCL8 gene.
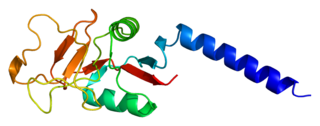
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL), also called mannan-binding lectin or mannan-binding protein (MBP), is a lectin that is instrumental in innate immunity as an opsonin and via the lectin pathway.

Factor H (FH) is a member of the regulators of complement activation family and is a complement control protein. It is a large, soluble glycoprotein that circulates in human plasma. Its principal function is to regulate the alternative pathway of the complement system, ensuring that the complement system is directed towards pathogens or other dangerous material and does not damage host tissue. Factor H regulates complement activation on self cells and surfaces by possessing both cofactor activity for the Factor I mediated C3b cleavage, and decay accelerating activity against the alternative pathway C3-convertase, C3bBb. Factor H exerts its protective action on self cells and self surfaces but not on the surfaces of bacteria or viruses. There are however, important exceptions, such as for example the bacterial pathogen, Neisseria meningitidis. This human pathogen has evolved mechanisms to recruit human FH and down-regulate the alternative pathway. Binding of FH permits the bacteria to proliferate in the bloodstream and cause disease.
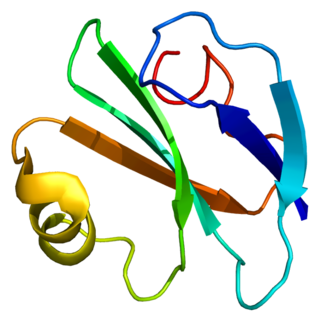
CD59 glycoprotein, also known as MAC-inhibitory protein (MAC-IP), membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis (MIRL), or protectin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD59 gene. It is an LU domain and belongs to the LY6/uPAR/alpha-neurotoxin protein family.

Integrin, alpha E (ITGAE) also known as CD103 is an integrin protein that in human is encoded by the ITGAE gene. CD103 binds integrin beta 7 to form the complete heterodimeric integrin molecule αEβ7, which has no distinct name. The αEβ7 complex is often referred to as "CD103" though this strictly refers only to the αE chain. Note that the β7 subunit can bind with other integrin α chains, such as α4 (CD49d).

Chemokine receptor 6 also known as CCR6 is a CC chemokine receptor protein which in humans is encoded by the CCR6 gene. CCR6 has also recently been designated CD196. The gene is located on the long arm of Chromosome 6 (6q27) on the Watson (plus) strand. It is 139,737 bases long and encodes a protein of 374 amino acids.

Ficolin-2, which was initially identified as L-ficolin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FCN2 gene.

Ficolin-1, and also commonly termed M-ficolin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FCN1 gene.

Carboxypeptidase N catalytic chain is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CPN1 gene.

Regulatory factor X-associated protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFXAP gene.

Complement factor H-related protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFHR5 gene.

Glutathione peroxidase 6 (GPx-6) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GPX6 gene.

Interferon kappa, also known as IFN-kappa, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNK gene.

Autophagy related 9B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATG9B gene.






















