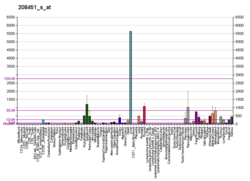
| C4A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | C4A , C4, C4A2, C4A3, C4A4, C4A6, C4AD, C4S, CO4, CPAMD2, RG, complement component 4A (Rodgers blood group), complement C4A (Rodgers blood group) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 120810; MGI: 88228; HomoloGene: 36030; GeneCards: C4A; OMA:C4A - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Complement C4-A is a kind of the Complement component 4 protein that in humans is encoded by the C4A gene. [5]