
The Orchidaceae are a diverse and widespread family of flowering plants, with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant, commonly known as the orchid family.

Ophrys apifera, known in Europe as the bee orchid, is a perennial herbaceous plant of the family Orchidaceae. It serves as an example of sexually deceptive pollination and floral mimicry, as well as of a highly selective and highly evolved plant–pollinator relationship.

Vanda, abbreviated in the horticultural trade as V., is a genus in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. There are about 80 species, and the genus is commonly cultivated for the marketplace. This genus and its allies are considered to be among the most specifically adapted of all orchids within the Orchidaceae. The genus is highly prized in horticulture for its showy, fragrant, long-lasting, and intensely colorful flowers. Vanda species are widespread across East Asia, Southeast Asia, and New Guinea, with a few species extending into Queensland and some of the islands of the western Pacific.

The genus Ophrys is a large group of orchids from the alliance Orchis in the subtribe Orchidinae. They are widespread across much of Europe, North Africa, Caucasus, the Canary Islands, and the Middle East as far east as Turkmenistan.

Aerangis, abbreviated as Aergs in horticultural trade, is a genus of the Orchid family (Orchidaceae). The name of this genus has been derived from the Greek words 'aer' (air) and 'angos' (urn), referring to the form of the lip. It is the type genus of the subtribe Aerangidinae, which has recently been subsumed in the subtribe Angraecinae. Approximately 50 species in this genus are known mostly from tropical Africa, but also from the Comoro Islands, Madagascar and Sri Lanka.

Mexipedium is a monotypic genus of the Orchid family Orchidaceae, subfamily Cypripedioideae, consisting of only one species, Mexipedium xerophyticum. It is also the single genus of tribe Mexipedieae and subtribe Mexipediinae.
Bee orchid is a common name for several orchids and may refer to:

The taxonomy of the Orchidaceae has evolved slowly during the last 250 years, starting with Carl Linnaeus who in 1753 recognized eight genera. De Jussieu recognized the Orchidaceae as a separate family in his Genera Plantarum in 1789. Olof Swartz recognized 25 genera in 1800. Louis Claude Richard provided us in 1817 with the descriptive terminology of the orchids.. The next step was taken in 1830-1840 by John Lindley, who recognized four subfamilies. He is generally recognized as the father of orchid taxonomy. The next important step was taken by George Bentham with a new classification, recognizing subtribes for the first time. This classification was first presented in a paper that Bentham read to the Royal Society in 1881. Then it was published in 1883 in the final volume of Genera Plantarum. The next great contributors were Pfitzer (1887), Schlechter (1926), Mansfeld (1937), Dressler and Dodson (1960), Garay, Vermeulen (1966), again Dressler (1981). and Burns-Balogh and Funk (1986). Dressler's 1993 book had considerable influence on later work.

Epidendrum, abbreviated Epi in the horticultural trade, is a large neotropical genus of the orchid family. With more than 1,500 species, some authors describe it as a mega-genus. The genus name refers to its epiphytic growth habit.

Microtis, commonly known as onion orchids or mignonette orchids is a genus of about 20 species of plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Onion orchids are terrestrial herbs with a single leaf at the base of the plant. They are similar to orchids in the genus Prasophyllum in that they have an onion-like leaf. The flowers are small but often scented and attractive to their insect pollinators. They are widespread in Asia, Australia and some Pacific islands.

Ophrys insectifera, the fly orchid, is a species of orchid and the type species of the genus Ophrys. It is remarkable as an example of sexually-deceptive pollination and floral mimicry as well as of a highly-selective and highly evolved plant-pollinator relationship.

Rhynchostylis is a genus in the orchid family (Orchidaceae), closely allied to the genus Vanda and comprising four currently accepted species native to the Indian Subcontinent, China, Indochina, Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines. The name consists of a compound of two Greek elements : rhynchos 'beak' and stylis 'column' – in reference to the very broad, fleshy column of the flower. The flowers are borne in dense racemes and are noted for their intense, spicy fragrance. Although lacking in pseudobulbs, the plants have leathery leaves that are drought-resistant. These orchids grow naturally in warm, moist, shaded tropical areas and will thrive in cultivation if given consistent warmth, uniform moisture and bright, but indirect light. Hobbyists wanting to grow them will need a warm, humid growing environment with gentle air movement. They can be grown in pots, but are better grown in baskets, owing to the extreme fleshiness of their roots. Their unusually fragrant blooms often appear in the slightly cooler winter months.

Sarcochilus, commonly known as butterfly orchids or fairy bells is a genus of about twenty species of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Most species are epiphytes but a few species only grow on rocks or in leaf litter. Orchids in this genus usually have short stems, leaves arranged in two rows and flowers arranged along unbranched flowering stems. Most species are endemic to Australia but some are found in New Guinea and New Caledonia.

Neofinetia was a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae, that is now classified as a Vanda. It contained three species and was distributed in China, Korea, and Japan.

Brachycorythis is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains approximately 40-50 species native mostly to Africa and Madagascar but also some from South and East Asia.

Diplocentrum is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It has two known species:
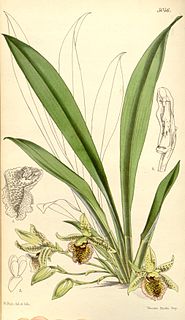
Kefersteinia is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It has about 40-50 species, widespread across much of Latin America. The genus was named for Keferstein of Kröllwitz, an orchidologist.

Sedirea is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. They are found in sub-tropical areas of China, Korea, and Japan, usually as epiphytes. The genus name is formed by spelling 'Aerides' backwards, a reference to the genus in which they were originally placed. The genus is abbreviated Sed.

Zygopetalinae is an orchid subtribe in the tribe Cymbidieae with 418 species.


















