
Bivalvia, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. The class includes the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. Shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances.

Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.

The Turonian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, the second age in the Late Cretaceous Epoch, or a stage in the Upper Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 93.9 ± 0.8 Ma and 89.8 ± 1 Ma. The Turonian is preceded by the Cenomanian Stage and underlies the Coniacian Stage.
The Coniacian is an age or stage in the geologic timescale. It is a subdivision of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series and spans the time between 89.8 ± 1 Ma and 86.3 ± 0.7 Ma. The Coniacian is preceded by the Turonian and followed by the Santonian.

Trigoniidae is a taxonomic family of saltwater clams, marine bivalve mollusks in the superfamily Trigonioidea. There is only one living genus, Neotrigonia, but in the geological past this family was well represented, widespread and common. The shells of species in this family are morphologically unusual, with very elaborate hinge teeth, and the exterior of the shell is highly ornamented.

Inoceramus is an extinct genus of fossil marine pteriomorphian bivalves that superficially resembled the related winged pearly oysters of the extant genus Pteria. They lived from the Early Jurassic to latest Cretaceous.

Platyceramus was a genus of Cretaceous bivalve molluscs belonging to the extinct inoceramid lineage. It is sometimes classified as a subgenus of Inoceramus.

A calcite sea is a sea in which low-magnesium calcite is the primary inorganic marine calcium carbonate precipitate. An aragonite sea is the alternate seawater chemistry in which aragonite and high-magnesium calcite are the primary inorganic carbonate precipitates. The Early Paleozoic and the Middle to Late Mesozoic oceans were predominantly calcite seas, whereas the Middle Paleozoic through the Early Mesozoic and the Cenozoic are characterized by aragonite seas.

Carbonate hardgrounds are surfaces of synsedimentarily cemented carbonate layers that have been exposed on the seafloor. A hardground is essentially, then, a lithified seafloor. Ancient hardgrounds are found in limestone sequences and distinguished from later-lithified sediments by evidence of exposure to normal marine waters. This evidence can consist of encrusting marine organisms, borings of organisms produced through bioerosion, early marine calcite cements, or extensive surfaces mineralized by iron oxides or calcium phosphates. Modern hardgrounds are usually detected by sounding in shallow water or through remote sensing techniques like side-scan sonar.

Ptychodus is a genus of extinct large durophagous (shell-crushing) sharks from the Cretaceous period, spanning from the Albian to the Campanian. Fossils of Ptychodus teeth are found in many Late Cretaceous marine sediments worldwide. At least 16 species are considered valid, with the largest members of the genus suggested to have grown up to 10 meters long. The youngest remains date to around 85 million years ago. A large number of remains have been found in the former Western Interior Seaway.

Pycnodonte is a genus of extinct oysters, fossil marine bivalve mollusks in the family Gryphaeidae, the foam oysters or honeycomb oysters. Shells of species in this genus are found around the world in fossil shell beds from the Valanginian to the Early Pleistocene. They are a commonly found fossil in Cretaceous shellbeds of the Navesink Formation in New Jersey.

The Straight Cliffs Formation is a stratigraphic unit in the Kaiparowits Plateau of south central Utah. It is Late Cretaceous in age and contains fluvial, paralic, and marginal marine (shoreline) siliciclastic strata. It is well exposed around the margin of the Kaiparowits Plateau in the Grand Staircase – Escalante National Monument in south central Utah. The formation is named after the Straight Cliffs, a long band of cliffs creating the topographic feature Fiftymile Mountain.

The Inoceramidae are an extinct family of bivalves ("clams") in the Class Mollusca. Fossils of inoceramids are found in marine sediments of Permian to latest Cretaceous in age. Inoceramids tended to live in upper bathyal and neritic environments. Many species of inoceramid are found all over the world, demonstrating the wide distribution of their preferred ecosystems, and possibly long-lived planktotrophic larvae. Despite their wide distribution, the pace of evolution of inoceramids was great, with species ranges commonly averaging 0.2-0.5 Ma.
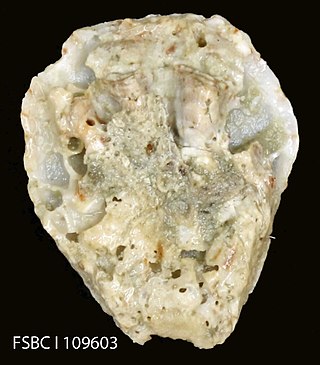
Ostrea equestris, commonly known as the crested oyster or horse oyster, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Ostreidae. It can be found along the Atlantic coast of North and South America, ranging from Virginia to Patagonia.

Actinoceramus is an extinct genus of fossil saltwater clams, marine pteriomorphian bivalve molluscs. These bivalves were facultatively mobile infaunal suspension feeders.

The Greenhorn Limestone or Greenhorn Formation is a geologic formation in the Great Plains Region of the United States, dating to the Cenomanian and Turonian ages of the Late Cretaceous period. The formation gives its name to the Greenhorn cycle of the Western Interior Seaway.

Inoceramus cuvieri is an extinct species of the extinct genus Inoceramus of Bivalve mollusks that serves as an index fossil of chalky rocks of Turonian age of the Cretaceous Period in Europe and North America.

Goulmimichthys is an extinct genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Pachyrhizodontidae. The genus, first described by Cavin in 1995, is known from various Turonian age formations. The type species G. arambourgi from the Akrabou Formation in the El Rachidia Province of Morocco, and other fossils described are G. gasparini of the La Frontera Formation, Colombia, and G. roberti from the Agua Nueva Formation of Mexico.
Cladoceramus is an extinct genus of fossil marine pteriomorphian bivalves that superficially resembled the related winged pearly oysters of the extant genus Pteria. They lived in the Santonian stage of the Late Cretaceous.
Liostrea is a genus of extinct oysters, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Gryphaeidae.






















