Crotonic acid Last updated August 14, 2025 Crotonic acid Names Preferred IUPAC name Other names (E )-But-2-enoic acidE )-2-Butenoic acidtrans -2-Butenoic acid
Identifiers ChEBI ChEMBL ChemSpider DrugBank ECHA InfoCard 100.003.213 UNII InChI=1S/C4H6O2/c1-2-3-4(5)6/h2-3H,1H3,(H,5,6)/b3-2+
Y Key:
LDHQCZJRKDOVOX-NSCUHMNNSA-N
Y InChI=1/C4H6O2/c1-2-3-4(5)6/h2-3H,1H3,(H,5,6)/b3-2+
Key: LDHQCZJRKDOVOX-NSCUHMNNBH
Properties C 4 H 6 O 2 Molar mass g·mol−1 Density 1.02 g/cm3 Melting point 70 to 73 °C (158 to 163 °F; 343 to 346 K) Boiling point 185 to 189 °C (365 to 372 °F; 458 to 462 K) Acidity (pK a ) 4.69 [ 1] Hazards Safety data sheet (SDS) SIRI.org Related compounds crotonate propionic acid acrylic acid butyric acid succinic acid malic acid tartaric acid fumaric acid pentanoic acid tetrolic acid Related compounds
butanol butyraldehyde crotonaldehyde 2-butanone Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25
°C [77
°F], 100
kPa).
Chemical compound
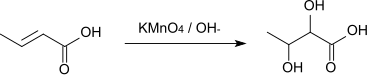
Crotonic acid ((2E )-but-2-enoic acid ) is a short-chain unsaturated carboxylic acid described by the formula CH3 CH=CHCO2 H. The name crotonic acid was given because it was erroneously thought to be a saponification product of croton oil . [ 2] It crystallizes as colorless needles from hot water. With a cis -alkeneIsocrotonic acid is an isomer of crotonic acid. Crotonic acid is soluble in water and many organic solvents. Its odor is similar to that of butyric acid .
Use Crotonic acid is mainly used as a comonomer with vinyl acetate. [ 14] The resulting copolymers are used in paints and adhesives . [ 4]
Crotonyl chloride reacts with N -ethyl-2-methylaniline (N -ethyl-o -toluidine) to provide crotamiton , which is used as an agent against scabies . [ 15]
Crotamiton synthesis Safety Its LD50 is 1 g/kg (oral, rats). [ 4] It irritates eyes, skin, and respiratory system. [ 14]
References ↑ Dawson, R. M. C.; et al. (1959). Data for Biochemical Research . Oxford: Clarendon Press. ↑ Chisholm, Hugh , ed. (1911). "Crotonic Acid" . Encyclopædia Britannica . Vol. 7 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 511. 1 2 Beyer, Hans; Walter, Wolfgang (1984). Organische Chemie (in German). Stuttgart: S. Hirzel Verlag. ISBN 3-7776-0406-2 1 2 3 Schulz, R. P.; Blumenstein, J.; Kohlpaintner, C. (2005). "Crotonaldehyde and Crotonic Acid". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi :10.1002/14356007.a08_083 . ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2 ↑ Rinne, A.; Tollens, B. (1871). "Ueber das Allylcyanür oder Crotonitril" [ On allyl cyanide or crotononitrile] . Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie . 159 (1): 105– 109. doi :10.1002/jlac.18711590110 . ↑ Pomeranz, C. (1906). "Ueber Allylcyanid und Allylsenföl" [ On allyl cyanide and allylic mustard oil] . Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie . 351 (1– 3): 354– 362. doi :10.1002/jlac.19073510127 . ↑ Beilstein, F. (1893). Handbuch der organischen Chemie 1 (3rd ed.). Verlag Leopold Voss. p. 506. ↑ Shimizu, S.; Kekka, S.; Kashino, S.; Haisa, M. (1974). "Topochemical Studies. III. The Crystal and Molecular Structures of Crotonic Acid, CH3 CH=CHCO2 H, and Crotonamide, CH3 CH=CHCONH2 " . Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan . 47 (7): 1627– 1631. doi : 10.1246/bcsj.47.1627 . 1 2 3 4 Heilbron (1953). "Crotonic acid" . Dictionary of Organic Compounds . 1 : 615. ↑ Lovén, J. M.; Johansson, H. (1915). "Einige schwefelhaltige β-Substitutionsderivate der Buttersäure" [ Some sulfur-containing β-substitution derivatives of butyric acid] . Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft . 48 (2): 1254– 1262. doi :10.1002/cber.19150480205 . ↑ Clover, A. M.; Richmond, G. F. (1903). "The Hydrolysis of Organic Peroxides and Peracids" . American Chemical Journal . 29 (3): 179– 203. ↑ Beilstein, F. (1893). Handbuch der organischen Chemie 1 (3rd ed.). Verlag Leopold Voss. p. 562. ↑ Carter, H. E.; West, H. D. (1955). "dl -Threonine" . Organic Syntheses ; Collected Volumes , vol. 3, p. 813. 1 2 Entry on Butensäuren . at: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved January 7, 2020. ↑ Kleemann, A.; Engel, J. Pharmazeutische Wirkstoffe: Synthesen, Patente, Anwendungen . Vol. 5 (2nd rev. and updated ed.). Stuttgart & New York: Georg Thieme Verlag. p. 251. ISBN 3-13-558402-X This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.