Related Research Articles
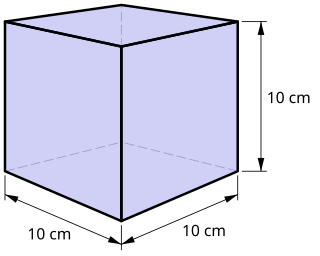
The litre or liter is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3). A cubic decimetre occupies a volume of 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre.

A bushel is an imperial and US customary unit of volume based upon an earlier measure of dry capacity. The old bushel is equal to 2 kennings (obsolete), 4 pecks, or 8 dry gallons, and was used mostly for agricultural products, such as wheat. In modern usage, the volume is nominal, with bushels denoting a mass defined differently for each commodity.
A league is a unit of length. It was common in Europe and Latin America, but is no longer an official unit in any nation. Derived from an ancient Celtic unit and adopted by the Romans as the leuga, the league became a common unit of measurement throughout western Europe. It was intended to represent, roughly, the distance a person could walk in an hour. Since the Middle Ages, many values have been specified in several countries.
There are a number of Spanish units of measurement of length or area that are virtually obsolete due to metrication. They include the vara, the cordel, the league and the labour. The units of area used to express the area of land are still encountered in some transactions in land today.
A number of different units of measurement were used in Argentina as its national system was derived from Spanish Castillian. The metric system was legally optional since 1863 and has been compulsory since 1887.
A number of different units of measurement were used in Bolivia to measure, for example, mass. Older system was basically derived from Spain. In Bolivia, International Metric system was legally optional since 1871, and International Metric system has been compulsory since 1893 even though, even in 1890s also, metric system was recognised at the custom-houses and other units which were of Spanish origin was also used.
A number of different units of measurement were used in Brazil to measure quantities including length, area, volume, and mass as those units were derived from Portugal and had significant local variances.
A number of different units of measurement were used in Chile to measure quantities like length, mass, area, capacity, etc. From 1848, the metric system has been compulsory in Chile.
A variety of units of measurement were used in Colombia to measure quantities like length, mass and area. In Colombia, International Metric System has adopted since 1853, and has been compulsory since 1854.
A number of units of measurement were used in Costa Rica to measure measurements in length, mass, area, capacity, etc. In Costa Rica, metric system has been adopted since 1910, and has been compulsory since 1912, by a joint convention among Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and Salvador.
A number of units of measurement were used in Honduras for length, mass, volume etc. In Honduras, the metric system was adopted in 1910, and has been compulsory since 1912, under a joint convention between Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and El Salvador.
A number of units of measurement were used in Nicaragua to measure measurements in mass, area, volume, etc. In Nicaragua, the metric system was adopted in 1910, and has been compulsory since 1912, by a joint convention between Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and El Salvador.
A number of units of measurement were used in Indonesia to measure length, mass, capacity, etc. Metric system adopted in 1923 and has been compulsory in Indonesia since 1938.
A number of units of measurement were used in Mexico to measure length, mass, area, capacity, etc. The Metric system was optional from 1857, and has been compulsory since 1896.
A number of units of measurement were used in Morocco to measure length, mass, capacity, etc. Metric system has been compulsory in Morocco since 1923.
A number of units of measurement were used in Paraguay to measure quantities including length, mass, area, capacity, etc. Metric system had been optional since 1890, and adopted since 1899 in Paraguay.
A number of units of measurement were used in Peru to measure length, mass, area, etc. The Metric system adopted in 1862 and has been compulsory since 1869 in Peru.
A number of different units of measurement were used in Libya to measure length, mass, area, etc. Metric system adopted in Libya in 1927.
A number of units of measurement were used in Venezuela to measure quantities like length, mass, etc. Metric system was optional in Venezuela since 1857, and has been compulsory since 1914.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Washburn, E.W. (1926). International Critical Tables of Numerical Data, Physics, Chemistry and Technology. New York: McGraw-Hil Book Company, Inc. pp. 5.
international critical tables 1926.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Clark, W.J. (1898), Commercial Cuba, New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons, p. 246
- 1 2 3 Cardarelli, F. (2003). Encyclopaedia of Scientific Units, Weights and Measures. Their SI Equivalences and Origins. London: Springer. p. 180. ISBN 978-1-4471-1122-1.