Related Research Articles

The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments. The imperial units replaced the Winchester Standards, which were in effect from 1588 to 1825. The system came into official use across the British Empire in 1826. By the late 20th century, most nations of the former empire had officially adopted the metric system as their main system of measurement but imperial units are still used in the United Kingdom, Canada and other countries formerly part of the British Empire. The imperial system developed from what were first known as English units, as did the related system of United States customary units.

The metre or meter is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). The SI unit symbol is m. The metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in a vacuum in 1/299 792 458 of a second. The metre was originally defined in 1793 as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's circumference is approximately 40000 km. In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar. In 1960, the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and slightly modified for the sake of precision in 2019.

Metrication or metrification is the act or process of converting the system of measurement traditionally used in a country to the metric system. All over the world, nations have transitioned from their local and traditional units of measurement to the metric system. This process first began in France during the 1790s and continues more than two centuries later, and the metric system has not been fully adopted in all countries and sectors.

The tonne is a metric unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is commonly referred to as a metric ton in the United States. It is equivalent to approximately 2,204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons (US) or approximately 0.984 long tons (UK). The official SI unit is the megagram, a less common way to express the same mass.

A metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the International System of Units (SI), under the oversight of an international standards body.

Chinese units of measurement, known in Chinese as the shìzhì, are the traditional units of measurement of the Han Chinese. Although Chinese numerals have been decimal (base-10) since the Shang, several Chinese measures use hexadecimal (base-16). Local applications have varied, but the Chinese dynasties usually proclaimed standard measurements and recorded their predecessor's systems in their histories.
The foot (pl. feet), abbreviation and IEEE standard symbol: ft, is a unit of length in the imperial and US customary systems of measurement. The prime symbol, ′, is a customarily used alternative symbol. Since the International Yard and Pound Agreement of 1959, one foot is defined as 0.3048 meters exactly. In customary and imperial units, one foot comprises 12 inches and one yard comprises three feet.
Mesures usuelles were a French system of measurement introduced by Napoleon I in 1812 to act as compromise between the metric system and traditional measurements. The system was restricted to use in the retail industry and continued in use until 1840, when the laws of measurement from the 1795 and 1799 were reinstituted.
A system of measurement is a collection of units of measurement and rules relating them to each other. Systems of measurement have historically been important, regulated and defined for the purposes of science and commerce. Systems of measurement in use include the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system, the imperial system, and United States customary units.

France has a unique history of units of measurement due to the radical decision to invent and adopt the metric system after the French Revolution.
Traditional Japanese units of measurement or the shakkanhō is the traditional system of measurement used by the people of the Japanese archipelago. It is largely based on the Chinese system, which spread to Japan and the rest of the Sinosphere in antiquity. It has remained mostly unaltered since the adoption of the measures of the Tang Dynasty in 701. Following the 1868 Meiji Restoration, Imperial Japan adopted the metric system and defined the traditional units in metric terms on the basis of a prototype metre and kilogram. The present values of most Korean and Taiwanese units of measurement derive from these values as well, owing to their occupations by the Japanese.
A toise is a unit of measure for length, area and volume originating in pre-revolutionary France. In North America, it was used in colonial French establishments in early New France, French Louisiana (Louisiane), Acadia (Acadie) and Quebec. The related toesa was used in Portugal, Brazil and other parts of the Portuguese Empire until the adoption of the Metric system.

The hectare is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about 0.405 hectare and one hectare contains about 2.47 acres.
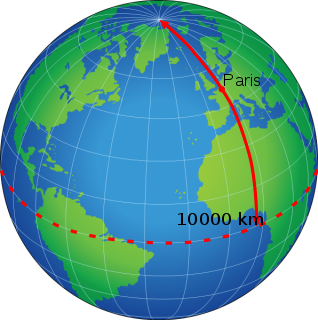
The history of the metre starts with the scientific revolution that began with Nicolaus Copernicus's work in 1543. Increasingly accurate measurements were required, and scientists looked for measures that were universal and could be based on natural phenomena rather than royal decree or physical prototypes. Rather than the various complex systems of subdivision in use, they also preferred a decimal system to ease their calculations.
A number of units of measurement were used in Indonesia to measure length, mass, capacity, etc. Metric system adopted in 1923 and has been compulsory in Indonesia since 1938.
A number of units of measurement were used in Mexico to measure length, mass, area, capacity, etc. The Metric system was optional from 1857, and has been compulsory since 1896.
A number of units of measurement were used in Paraguay to measure quantities including length, mass, area, capacity, etc. Metric system had been optional since 1890, and adopted since 1899 in Paraguay.
A number of units of measurement were used in Switzerland to measure length, mass, etc. Metric system was optional in 1868, and has been compulsory since 1877.
A number of different units of measurement were used in Libya to measure length, mass, area, etc. Metric system adopted in Libya in 1927.

The klafter is an historical unit of length, volume and area that was used in Central Europe.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Washburn, E.W. (1926). International Critical Tables of Numerical Data, Physics, Chemistry and Technology. New York: McGraw-Hil Book Company, Inc. p. 8.
- 1 2 Cardarelli, F. (2003). Encyclopaedia of Scientific Units, Weights and Measures. Their SI Equivalences and Origins . London: Springer. pp. 156. ISBN 978-1-4471-1122-1.