The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments.

The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English feet, or 1,760 yards. The statute mile was standardised between the British Commonwealth and the United States by an international agreement in 1959, when it was formally redefined with respect to SI units as exactly 1,609.344 metres.
The pound or pound-mass is a unit of mass used in British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. Various definitions have been used; the most common today is the international avoirdupois pound, which is legally defined as exactly 0.45359237 kilograms, and which is divided into 16 avoirdupois ounces. The international standard symbol for the avoirdupois pound is lb; an alternative symbol is lbm, #, and ℔ or ″̶.

Troy weight is a system of units of mass that originated in 15th-century England, and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The troy weight units are the grain, the pennyweight, the troy ounce, and the troy pound. The troy grain is equal to the grain unit of the avoirdupois system, but the troy ounce is heavier than the avoirdupois ounce, and the troy pound is lighter than the avoirdupois pound. One troy ounce equals exactly 31.1034768 grams.

A grain is a unit of measurement of mass, and in the troy weight, avoirdupois, and apothecaries' systems, equal to exactly 64.79891 milligrams. It is nominally based upon the mass of a single ideal seed of a cereal. From the Bronze Age into the Renaissance, the average masses of wheat and barley grains were part of the legal definitions of units of mass. Expressions such as "thirty-two grains of wheat, taken from the middle of the ear" appear to have been ritualistic formulas, essentially the premodern equivalent of legal boilerplate. Another source states that it was defined such that 252.458 units would balance 1 cubic inch (16 cm3) of distilled water at an ambient air-water pressure and temperature of 30 inches of mercury (100 kPa) and 62 °F (17 °C) respectively. Another book states that Captain Henry Kater, of the British Standards Commission, arrived at this value experimentally.
The ounce is any of several different units of mass, weight or volume and is derived almost unchanged from the uncia, an Ancient Roman unit of measurement.
The foot (pl. feet), standard symbol: ft, is a unit of length in the British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. The prime symbol, ′, is a customarily used alternative symbol. Since the International Yard and Pound Agreement of 1959, one foot is defined as 0.3048 meters exactly. In both customary and imperial units, one foot comprises 12 inches and one yard comprises three feet.

The avoirdupois system is a measurement system of weights that uses pounds and ounces as units. It was first commonly used in the 13th century AD and was updated in 1959.
The minim is a unit of volume in both the imperial and U.S. customary systems of measurement. Specifically it is 1⁄60 of a fluid drachm or 1⁄480 of a fluid ounce.
The dram is a unit of mass in the avoirdupois system, and both a unit of mass and a unit of volume in the apothecaries' system. It was originally both a coin and a weight in ancient Greece. The unit of volume is more correctly called a fluid dram, fluid drachm, fluidram or fluidrachm.

Grivna (гривна) was a currency as well as a measure of weight used in Kievan Rus' and other East Slavic countries since the 11th century.
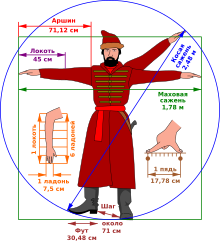
A verst is an obsolete Russian unit of length defined as 500 sazhen. This makes a verst equal to 1.0668 kilometres.

Pood is a unit of mass equal to 40 funt. Since 1899 it is set to approximately 16.38 kilograms. It was used in Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine. Pood was first mentioned in a number of 12th-century documents. Unlike funt, which came at least in the 14th century from Middle High German: phunt, Old East Slavic: пудъ pud is a much older borrowing from Late Latin "pondo", from Classical "pondus".
A system of measurement is a collection of units of measurement and rules relating them to each other. Systems of measurement have historically been important, regulated and defined for the purposes of science and commerce. Systems of measurement in use include the International System of Units or SI, the British imperial system, and the United States customary system.
A zolotnik was a small Russian unit of weight, equal to 0.1505 avoirdupois ounces, or 4.2658 grams. Used from the 10th to 20th centuries, its name is derived from the Russian word zoloto, meaning gold. As a unit, the zolotnik was the standard for silver manufacture, much as the troy ounce is currently used for gold and other precious metals.

Both the British Imperial and United States customary systems of measurement derive from earlier English systems used in the Middle Ages, that were the result of a combination of the local Anglo-Saxon units inherited from Germanic tribes and Roman units brought by William the Conqueror after the Norman Conquest of England in 1066.
A dessiatin or desyatina is an archaic, rudimentary land measurement used in tsarist Russia. A dessiatin is equal to 2,400 square sazhens and is approximately equivalent to 2.702 English acres or 10,926.512 square metres.
The international yard and pound are two units of measurement that were the subject of an agreement among representatives of six nations signed on 1 July 1959; the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. The agreement defined the yard as exactly 0.9144 meters and the (avoirdupois) pound as exactly 0.45359237 kilograms.

Sazhen-S is a Soviet laser/optical space surveillance system, used to analyse the orbital parameters of space craft. There are several installations across the former Soviet Union. One of which is based at space ground station NIP-19 near Dunaivtsi in Ukraine. It is named after the sazhen, a former Russian unit of measurement which translates as fathom and has a length of 2.1 metres (6.9 ft). A similar system is Sazhen-T.

The imperial and US customary measurement systems are both derived from an earlier English system of measurement which in turn can be traced back to Ancient Roman units of measurement, and Carolingian and Saxon units of measure.