In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP+ or NAD+ as cofactors. Transmembrane oxidoreductases create electron transport chains in bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria, including respiratory complexes I, II and III. Some others can associate with biological membranes as peripheral membrane proteins or be anchored to the membranes through a single transmembrane helix.

Dicarbonyl/L-xylulose reductase, also known as carbonyl reductase II, is an enzyme that in human is encoded by the DCXR gene located on chromosome 17.
In enzymology, a carbonyl reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.184) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dihydrokaempferol 4-reductase (EC 1.1.1.219) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.34) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a methylglyoxal reductase (NADPH-dependent) (EC 1.1.1.283) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a salutaridine reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.248) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tropinone reductase I (EC 1.1.1.206) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 2-alkenal reductase (EC 1.3.1.74) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a precorrin-6A reductase (EC 1.3.1.54) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
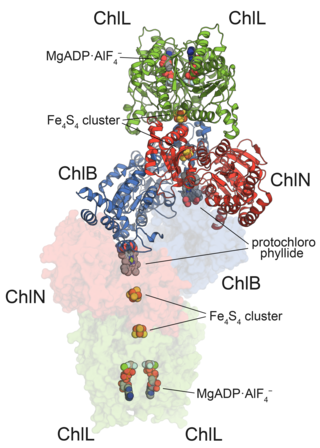
In enzymology, protochlorophyllide reductases (POR) are enzymes that catalyze the conversion from protochlorophyllide to chlorophyllide a. They are oxidoreductases participating in the biosynthetic pathway to chlorophylls.
In enzymology, a cob(II)alamin reductase (EC 1.16.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.2) abbreviated FNR, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

[Methionine synthase] reductase, or Methionine synthase reductase, encoded by the gene MTRR, is an enzyme that is responsible for the reduction of methionine synthase inside human body. This enzyme is crucial for maintaining the one carbon metabolism, specifically the folate cycle. The enzyme employs one coenzyme, flavoprotein.
In enzymology, a rubredoxin—NAD(P)+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, 6,7-dihydropteridine reductase (EC 1.5.1.34, also Dihydrobiopterin reductase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CoA-glutathione reductase (EC 1.8.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Flavin reductase a class of enzymes. There are a variety of flavin reductases, which bind free flavins and through hydrogen bonding, catalyze the reduction of these molecules to a reduced flavin. Riboflavin, or vitamin B, and flavin mononucleotide are two of the most well known flavins in the body and are used in a variety of processes which include metabolism of fat and ketones and the reduction of methemoglobin in erythrocytes. Flavin reductases are similar and often confused for ferric reductases because of their similar catalytic mechanism and structures.

Methionine synthase reductase, also known as MSR, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTRR gene.
Adrenodoxin-NADP+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.6, adrenodoxin reductase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-adrenodoxin reductase, ADR, NADPH:adrenal ferredoxin oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name adrendoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction








