
Glareolidae is a family of birds in the wader suborder Charadrii. It contains two distinct groups, the pratincoles and the coursers. The atypical Egyptian plover, traditionally placed in this family, is now known to be only distantly related.

Pterocarya, often called wingnuts in English, are trees in the walnut family Juglandaceae. They are native to Asia. The botanic name is from Ancient Greek πτερον (pteron) "wing" + κάρυον (karyon) "nut".

Pseudolarix is a genus of coniferous trees in the pine family Pinaceae containing three species, the extant Pseudolarix amabilis and the extinct species Pseudolarix japonica and Pseudolarix wehrii. Pseudolarix species are commonly known as golden larch, but are not true larches (Larix) being more closely related to Keteleeria, Abies and Cedrus. P. amabilis is native to eastern China, occurring in small areas in the mountains of southern Anhui, Zhejiang, Fujian, Jiangxi, Hunan, Hubei and eastern Sichuan, at altitudes of 100–1,500 m (328–4,921 ft). P. wehrii is described from fossils dating to the Early Eocene (Ypresian), of Western North America where it is found in the Eocene Okanagan Highlands Allenby and Klondike Mountain Formations. The youngest known occurrence is of mummified fossils found in the Late Eocene Buchanan Lake Formation on Axel Heiberg Island. P. japonica is known from Middle Miocene to Pliocene sediments in Japan and Miocene deposits of Korea. Fossils assigned to Pseudolarix as a genus date possibly as old as the Early Cretaceous Hauterivian stage in Mongolia.

Ocotea is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Lauraceae. Many are evergreen trees with lauroid leaves.
Annamocarya is a genus of flowering plants in the family Juglandaceae, containing only one species, Annamocarya sinensis, native to southwestern China and northern Vietnam. It is related to the hickories, and was formerly included in the same genus Carya, as Carya sinensis, but also shares a number of characteristics with the walnuts in the genus Juglans. It is grouped with Carya in the subtribe Caryinae. It is sometimes called Chinese hickory or beaked hickory.

Phoebe is a genus of evergreen trees and shrubs belonging to the Laurel family, Lauraceae. There are 75 accepted species in the genus, distributed in tropical and subtropical Asia and New Guinea. 35 species occur in China, of which 27 are endemic. The first description of the genus was of the type species P. lanceolata made in 1836 by Christian Gottfried Daniel Nees von Esenbeck in Systema Laurinarum, p. 98.

Viscum is a genus of about 70–100 species of mistletoes, native to temperate and tropical regions of Europe, Africa, Asia and Australasia. Traditionally, the genus has been placed in its own family Viscaceae, but recent genetic research by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group shows this family to be correctly placed within a larger circumscription of the sandalwood family, Santalaceae. Its name is the origin of the English word viscous, after the Latin viscum, a sticky bird lime made from the plants' berries.
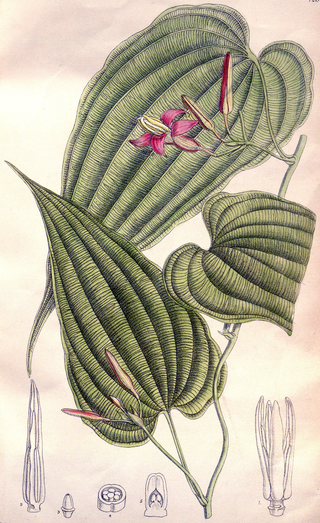
Stemona is a genus of vines and subshrubs in the family Stemonaceae, described as a genus in 1790.

Pterocarya fraxinifolia is a species of tree in the Juglandaceae family. It is commonly known as the Caucasian wingnut or Caucasian walnut. It is native to the Caucasian region Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Iran, Russia, Ukraine and Turkey. It was introduced to France in 1784, and to Great Britain after 1800.

Rehderodendron is a genus of five species of flowering plants in the family Styracaceae, native to southeastern Asia, from southwestern China south to Myanmar and Vietnam.

Platycarya is a genus of flowering plants in the family Juglandaceae native to eastern Asia in China, Korea, and Japan.

Hrádek nad Nisou is a town in Liberec District in the Liberec Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 7,700 inhabitants. The town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument zone.

Pterocarya stenoptera, the Chinese wingnut, is a small-winged wingnut tree of the Juglandaceae family. It is originally from Southeast China.

Eucommia is a genus of small trees now native to China, with a fossil record that shows a much wider distribution. The single living species, Eucommia ulmoides, is near threatened in the wild, but is widely cultivated in China for its bark, and is highly valued in herbology such as traditional Chinese medicine.

Bombus trophonius is an extinct species of bumble bee known from a Miocene fossil found in Europe. It belongs to the Bombus subgenus Cullumanobombus and is considered most similar to the living species Bombus rufocinctus of North America.

Proserpinaca, commonly called mermaidweed, is a genus of flowering plants in the watermilfoil family (Haloragaceae). It is a small genus, comprising only two to three extant species, all of which are native to eastern North America and the West Indies. All species in this genus are found in aquatic or terrestrial wetland habitats.

Taxodium dubium is an extinct species of cypress in the genus Taxodium in the family Cupressaceae which lived from the Late Paleocene to the Pliocene in North America and Europe. The species was first described in 1823 by Kaspar Maria von Sternberg.

Pseudolarix wehrii is an extinct species of golden larch in the pine family (Pinaceae). The species is known from early Eocene fossils of northern Washington state, United States, and southern British Columbia, Canada, along with late Eocene mummified fossils found in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada.

Dipteronia brownii is an extinct species in the soapberry family (Sapindaceae) described in 2001. Fossils of D. brownii are known from stratigraphic formations in North America and Asia ranging in age between Paleocene to Early Oligocene.

Pteroceltis is a genus of small trees in the family Cannabaceae and containing the living species Pteroceltis tatarinowii. The genus is now restricted to an endemic range in China and Mongolia. The genus has a fossil record which includes species described from Korea, Japan, Germany, and the United States.





















