
Cymbopogon, also known as lemongrass, barbed wire grass, silky heads, oily heads, Cochin grass, Malabar grass, citronella grass or fever grass, is a genus of Asian, African, Australian, and tropical island plants in the grass family. Some species are commonly cultivated as culinary and medicinal herbs because of their scent, resembling that of lemons . The name Cymbopogon derives from the Greek words kymbe and pogon "which mean [that] in most species, the hairy spikelets project from boat-shaped spathes." Lemongrass and its oil are believed to possess therapeutic properties.
Xanthorrhoea is a genus of about 30 species of succulent flowering plants in the family Asphodelaceae. They are endemic to Australia. Common names for the plants include grasstree, grass gum-tree, kangaroo tail, balga, yakka, yamina (Tasmania), and black boy. The most common species is Xanthorrhoea australis, and some of these names are applied specifically to this species.

Chromolaena odorata is a tropical and subtropical species of flowering shrub in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the Americas, from Florida and Texas in the United States south through Mexico and the Caribbean to South America. It has been introduced to tropical Asia, West Africa, and parts of Australia.

Lagurus is a genus of Old World plants in the grass family, native to the Mediterranean Basin and nearby regions, from Madeira and the Canary Islands to Crimea and Saudi Arabia. It is also naturalized in Australia, New Zealand, the Azores, Ireland and Great Britain, and scattered locations in the Americas. The only known species is Lagurus ovatus, commonly called hare's-tail, hare's-tail grass or bunnytail. It is also grown as an ornamental plant for its attractive flower panicles.

Cymbopogon nardus, common name citronella grass, is a species of perennial aromatic plant from the family Poaceae, originating in tropical Asia. C. nardus cannot be eaten because of its unpalatable nature and is an invasive species that renders pastureland useless, since cattle will starve even in its abundance.

Cymbopogon citratus, commonly known as West Indian lemon grass or simply lemon grass, is a tropical plant native to South Asia and Maritime Southeast Asia and introduced to many tropical regions.

Tussock grasses or bunch grasses are a group of grass species in the family Poaceae. They usually grow as singular plants in clumps, tufts, hummocks, or bunches, rather than forming a sod or lawn, in meadows, grasslands, and prairies. As perennial plants, most species live more than one season. Tussock grasses are often found as forage in pastures and ornamental grasses in gardens.

Cymbopogon schoenanthus, the camel grass, camel's hay, straw of Mecca,fever grass, geranium grass, or West Indian lemon grass, is a herbal plant of Southern Asia and Northern Africa, with fragrant foliage.

The flora of Australia comprises a vast assemblage of plant species estimated to over 21,000 vascular and 14,000 non-vascular plants, 250,000 species of fungi and over 3,000 lichens. The flora has strong affinities with the flora of Gondwana, and below the family level has a highly endemic angiosperm flora whose diversity was shaped by the effects of continental drift and climate change since the Cretaceous. Prominent features of the Australian flora are adaptations to aridity and fire which include scleromorphy and serotiny. These adaptations are common in species from the large and well-known families Proteaceae (Banksia), Myrtaceae, and Fabaceae.
Exotheca is a monotypic genus of African and Southeast Asian plants in the grass family.

Trachypogon is a small genus of African and Latin American plants in the grass family. Crinkleawn grass is a common name for plants in this genus.

Ottochloa is a genus of African, Asian, and Australian plants in the grass family.

Monachather, common name mulga oats, is a genus of Australian plants in the grass family.

Gahnia grandis is a tussock-forming perennial plant found in southeastern mainland Australia and Tasmania.

Hakea pulvinifera, also known as Lake Keepit Hakea, is a small, prickly shrub in the family Proteaceae, found only on one rocky hillside at Lake Keepit near Gunnedah in New South Wales, Australia. The species was first described in 1962, believed extinct in 1971 and rediscovered in 1988. The entire species may be of only one genetically unique individual. It is one of only two Hakea species that reproduce solely through basal shoots or 'suckering', reducing genetic variation.
Cymbopogon commutatus is a perennial grass species, commonly known as incense grass, aromatic rush, camel's hay, or lemon grass. Its range extends from South Asia to parts of Africa and Arabia. Foliage has a sweet lemony odor when mashed. It appeared on a 4 riyal Qatari stamp. It is used for medicinal purposes in northeastern Arabia.

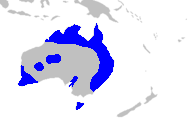
Cymbopogon bombycinus, or citronella grass is a species of perennial grass in the family Poaceae that is native to Australia.

Cymbopogon refractus, commonly known as barbed wire grass, is a species of perennial grass in the genus Cymbopogon of the family Poaceae. It is native to Australia.

Cymbopogon winterianus, common name Java citronella, is a perennial aromatic plant from the family Poaceae, originating in western Malesia. Used in perfumery products and cosmetics, a source of Citronella oil.

Styphelia obtecta is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a shrub that typically grows to a height of 1–2 ft (0.30–0.61 m) or more. Its leaves are rigid, broadly heart-shaped to round, and 8.5–12.5 mm (0.33–0.49 in) long and overlap each other with a small point on the tip. The flowers are arranged singly or in pairs in leaf axils and are shorter than the leaves. There are small bracts and broad bracteoles less than half as long as the sepals. The sepals are about 4 mm (0.16 in) long, the petals joined at the base to form a tube about as long as the sepals with lobes shorter than the petal tube.

















