Methionine is an essential amino acid in humans.

Homocystinuria or HCU is an inherited disorder of the metabolism of the amino acid methionine due to a deficiency of cystathionine beta synthase or methionine synthase. It is an inherited autosomal recessive trait, which means a child needs to inherit a copy of the defective gene from both parents to be affected. Symptoms of homocystinuria can also be caused by a deficiency of vitamins B6, B12, or folate.

Homoserine (also called isothreonine) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH2CH2OH. L-Homoserine is not one of the common amino acids encoded by DNA. It differs from the proteinogenic amino acid serine by insertion of an additional -CH2- unit into the backbone. Homoserine, or its lactone form, is the product of a cyanogen bromide cleavage of a peptide by degradation of methionine.

Succinyl coenzyme A synthetase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible reaction of succinyl-CoA to succinate. The enzyme facilitates the coupling of this reaction to the formation of a nucleoside triphosphate molecule from an inorganic phosphate molecule and a nucleoside diphosphate molecule. It plays a key role as one of the catalysts involved in the citric acid cycle, a central pathway in cellular metabolism, and it is located within the mitochondrial matrix of a cell.
Cysteine metabolism refers to the biological pathways that consume or create cysteine. The pathways of different amino acids and other metabolites interweave and overlap to creating complex systems.

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).

Cystathionine-β-synthase, also known as CBS, is an enzyme (EC 4.2.1.22) that in humans is encoded by the CBS gene. It catalyzes the first step of the transsulfuration pathway, from homocysteine to cystathionine:
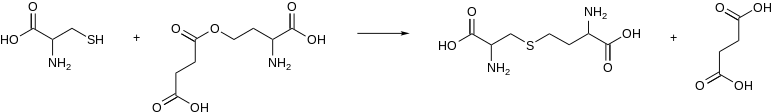
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate (α-ketobutyrate), and ammonia:

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.
In enzymology, a 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltriglutamate—homocysteine S-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cystathionine beta-lyase, also commonly referred to as CBL or β-cystathionase, is an enzyme that primarily catalyzes the following α,β-elimination reaction

In enzymology, a 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions of 3-mercaptopyruvate. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically the sulfurtransferases. This enzyme participates in cysteine metabolism. It is encoded by the MPST gene.

In enzymology, a dihydrofolate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a methionine—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tetrahydrofolate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a homoserine O-succinyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an O-acetylhomoserine aminocarboxypropyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology and molecular biology, a holo-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase (CDS) is the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol from cytidine triphosphate and phosphatidate.
In molecular biology, the Cys/Met metabolism PLP-dependent enzyme family is a family of proteins including enzymes involved in cysteine and methionine metabolism which use PLP (pyridoxal-5'-phosphate) as a cofactor.