
Acetaldehyde dehydrogenases are dehydrogenase enzymes which catalyze the conversion of acetaldehyde into acetyl-CoA. This can be summarized as follows:
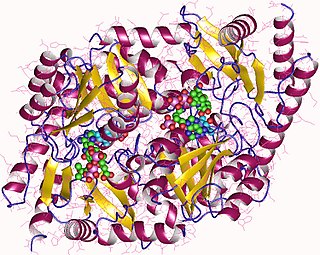
Aminolevulinic acid synthase (ALA synthase, ALAS, or delta-aminolevulinic acid synthase) is an enzyme (EC 2.3.1.37) that catalyzes the synthesis of δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) the first common precursor in the biosynthesis of all tetrapyrroles such as hemes, cobalamins and chlorophylls. The reaction is as follows:

Serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) (Vitamin B6) dependent enzyme (EC 2.1.2.1) which plays an important role in cellular one-carbon pathways by catalyzing the reversible, simultaneous conversions of L-serine to glycine and tetrahydrofolate (THF) to 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10-CH2-THF). This reaction provides the largest part of the one-carbon units available to the cell.
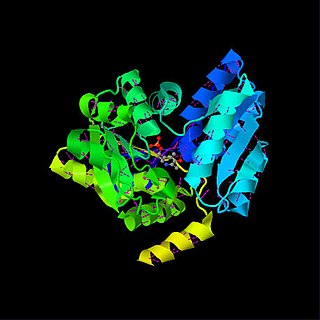
Serine dehydratase or L-serine ammonia lyase (SDH) is in the β-family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent (PLP) enzymes. SDH is found widely in nature, but its structural and properties vary among species. SDH is found in yeast, bacteria, and the cytoplasm of mammalian hepatocytes. SDH catalyzes is the deamination of L-serine to yield pyruvate, with the release of ammonia.
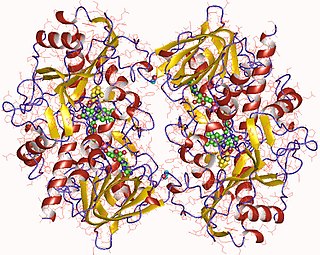
In enzymology, a choline oxidase (EC 1.1.3.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Amine oxidase (copper-containing) (AOC) (EC 1.4.3.21 and EC 1.4.3.22; formerly EC 1.4.3.6) is a family of amine oxidase enzymes which includes both primary-amine oxidase and diamine oxidase; these enzymes catalyze the oxidation of a wide range of biogenic amines including many neurotransmitters, histamine and xenobiotic amines. They act as a disulphide-linked homodimer. They catalyse the oxidation of primary amines to aldehydes, with the subsequent release of ammonia and hydrogen peroxide, which requires one copper ion per subunit and topaquinone as cofactor:

Glycine decarboxylase also known as glycine cleavage system P protein or glycine dehydrogenase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GLDC gene.
In enzymology, an amino-acid racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
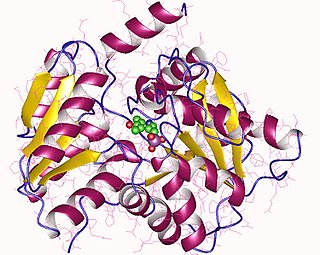
The enzyme L-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme threo-3-hydroxyaspartate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.16) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Threonine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.19, systematic name L-threonine ammonia-lyase (2-oxobutanoate-forming), also commonly referred to as threonine deaminase or threonine dehydratase, is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of L-threonine into α-ketobutyrate and ammonia:

The enzyme 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate aldolase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase catalyzes the reversible chemical reaction

The enzyme threonine aldolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycine C-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a glycine transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
L-allo-threonine aldolase is an enzyme catalyzing the conversion between L-allothreonine on one side and glycine plus acetaldehyde on another side. Artificial disabling (knockout) of this enzyme in wild bacteria has no significant effect. However such disabling suppresses the growth of mutants that already lack other enzyme, serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Hence L-allo-threonine aldolase provides the alternative pathway for cellular glycine when serine hydroxymethyltransferase is inert. E.coli L-allo-threonine aldolase is a highly termostable enzyme, this can be used for purification.
Low-specificity L-threonine aldolase is an enzyme with systematic name L-threonine/L-allo-threonine acetaldehyde-lyase (glycine-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
3-hydroxy-D-aspartate aldolase is an enzyme with systematic name 3-hydroxy-D-aspartate glyoxylate-lyase (glycine-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glycine C-acetyltransferase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GCAT gene.











