
Euroscepticism means criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies and seek reform, to those who oppose EU membership outright and see the EU as unreformable. The opposite of Euroscepticism is known as pro-Europeanism.

The Treaty of Nice was signed by European leaders on 26 February 2001 and came into force on 1 February 2003.

The krona is the currency of Iceland. Iceland is the second smallest country, after the Seychelles, to have its own currency and monetary policy.

The eurozone, officially called the euro area, is a monetary union of 19 of the 28 European Union (EU) member states which have adopted the euro (€) as their common currency and sole legal tender. The monetary authority of the eurozone is the Eurosystem. The other nine members of the European Union continue to use their own national currencies, although most of them are obliged to adopt the euro in the future.

The krone is the official currency of Denmark, Greenland, and the Faroe Islands, introduced on 1 January 1875. Both the ISO code "DKK" and currency sign "kr." are in common use; the former precedes the value, the latter in some contexts follows it. The currency is sometimes referred to as the Danish crown in English, since krone literally means crown. Historically, krone coins have been minted in Denmark since the 17th century.

Referendums in the United Kingdom are occasionally held at a national, regional or local level. National referendums can be permitted by an Act of Parliament and regulated through the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000, but they are by tradition extremely rare due to the principle of parliamentary sovereignty meaning that they cannot be constitutionally binding on either the Government or Parliament, although they usually have a persuasive political effect.

This is a list of referendums related to the European Union, or referendums related to the European Communities, which were predecessors of the European Union. Since 1972, a total of 48 referendums have been held by EU member states, candidate states, and their territories, with several additional referendums held in countries outside of the EU. The referendums have been held most commonly on the subject of whether to become a member of European Union as part of the accession process, although the EU does not require any candidate country to hold a referendum to approve membership or as part of treaty ratification. Other EU-related referendums have been held on the adoption of the euro and on participation in other EU-related policies.

A consultative referendum on the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was held in the Netherlands on 1 June 2005 to decide whether the government should ratify the proposed Constitution of the European Union. The result was a "No"-vote.
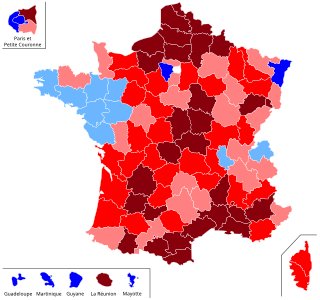
The French referendum on the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was held on 29 May 2005 to decide whether France should ratify the proposed Constitution of the European Union. The result was a victory for the "No" campaign, with 55% of voters rejecting the treaty on a turnout of 69%.
The Danish referendum on the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was a planned referendum to be held on 27 September 2005, that would have put the proposed Constitution to the voters of Denmark for ratification. However, after voters voted down the Constitution in both the French and Dutch referendums before the Danish vote could take place, Danish prime minister Anders Fogh Rasmussen indicated that the referendum would be cancelled. On April 24, 2008 the Danish parliament ratified the Treaty's successor, the Treaty of Lisbon without a referendum.
Sweden does not currently use the euro as its currency and has no plans to replace the krona in the near future. Sweden's Treaty of Accession of 1994 made it subject to the Treaty of Maastricht, which obliges states to join the eurozone once they meet the necessary conditions. Sweden maintains that joining the ERM II is voluntary, and has chosen to remain outside pending public approval by a referendum, thereby intentionally avoiding the fulfilment of the adoption requirements.

The euro came into existence on 1 January 1999, although it had been a goal of the European Union (EU) and its predecessors since the 1960s. After tough negotiations, particularly due to opposition from the United Kingdom, the Maastricht Treaty entered into force in 1993 with the goal of creating an economic and monetary union by 1999 for all EU states except the UK and Denmark.

Denmark uses the krone as its currency and does not use the euro, having negotiated the right to opt-out from participation under the Maastricht Treaty of 1992. In 2000, the government held a referendum on introducing the euro, which was defeated with 46.8% voting yes and 53.2% voting no. The Danish krone is part of the ERM II mechanism, so its exchange rate is tied to within 2.25% of the euro.
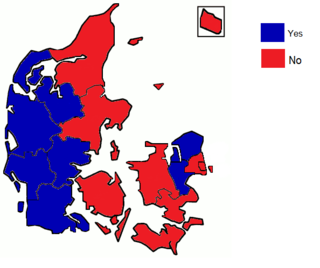
A referendum on the Maastricht Treaty was held in Denmark on 2 June 1992. It was rejected by 50.7% of voters with a turnout of 83.1%. The rejection was considered somewhat of a blow to the process of European integration, although the process continued. The result of the referendum, along with the "petit oui" in the French Maastricht referendum are considered to be signals of the end of the "permissive consensus" on European integration which had existed in most of continental Europe until then. This was expressed by Pascal Lamy, chef de cabinet for Jacques Delors, the president of the European Commission, who remarked that, “Europe was built in a St. Simonian [i.e., technocratic] way from the beginning, this was Monnet’s approach: The people weren’t ready to agree to integration, so you had to get on without telling them too much about what was happening. Now St. Simonianism is finished. It can’t work when you have to face democratic opinion.” From this point forward issues relating to European integration were subject to much greater scrutiny across much of Europe, and overt euroscepticism gained prominence. Only France, Denmark and Ireland held referendums on Maastricht ratification.

The enlargement of the eurozone is an ongoing process within the European Union (EU). All member states of the European Union, except Denmark and the United Kingdom which negotiated opt-outs from the provisions, are obliged to adopt the euro as their sole currency once they meet the criteria, which include: complying with the debt and deficit criteria outlined by the Stability and Growth Pact, keeping inflation and long-term governmental interest rates below certain reference values, stabilising their currency's exchange rate versus the euro by participating in the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, and ensuring that their national laws comply with the ECB statute, ESCB statute and articles 130+131 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union. The obligation for EU member states to adopt the euro was first outlined by article 109.1j of the Maastricht Treaty of 1992, which became binding on all new member states by the terms of their treaties of accession.
Denmark holds opt-outs from European Union policies in relation to security and defence, citizenship, police and justice, and the adoption of the euro. They were secured under the Edinburgh Agreement in 1992 after a referendum for the ratification of the Maastricht Treaty was rejected by Danish voters, as a package of measure to assuage concerns raised during that referendum.
The 2003 Estonian European Union membership referendum took place on 14 September 2003 to decide whether Estonia should join the European Union (EU). Just over two-thirds of voters voted Yes and Estonia joined the EU on 1 May 2004.
The Thirtieth Amendment of the Constitution Act 2012 amended the Constitution of Ireland to permit Ireland to ratify the 2012 European Fiscal Compact and to preclude measures taken under the Compact from being held to be inconsistent with the Irish constitution. It was approved by referendum on 31 May 2012, by 60.3% to 39.7%, on a turnout of 50% and was signed into law by President Michael D. Higgins on 27 June 2012.
Denmark in the European Union refers to the historical and current issues of Denmark's membership in the European Union. Denmark has a permanent representation to the European Union led by ambassador Jeppe Tranholm-Mikkelsen, in Brussels. The current Foreign Minister and Minister for European Affairs is Anders Samuelsen.

Since the foundation of the European Communities, the United Kingdom has been an important neighbour and is currently a major member, until its withdrawal.


















