
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other vertebrates. Human malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria.

A protease is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in many biological functions, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism, and cell signaling.

Artemether is a medication used for the treatment of malaria. The injectable form is specifically used for severe malaria rather than quinine. In adults, it may not be as effective as artesunate. It is given by injection in a muscle. It is also available by mouth in combination with lumefantrine, known as artemether/lumefantrine.
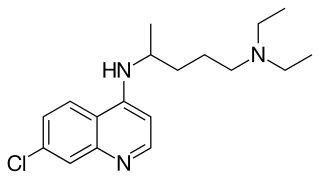
Chloroquine is a medication primarily used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to its effects. Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication. Chloroquine is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus. While it has not been formally studied in pregnancy, it appears safe. It was studied to treat COVID-19 early in the pandemic, but these studies were largely halted in the summer of 2020, and is not recommended for this purpose. It is taken by mouth.

Proguanil, also known as chlorguanide and chloroguanide, is a medication used to treat and prevent malaria. It is often used together with chloroquine or atovaquone. When used with chloroquine the combination will treat mild chloroquine resistant malaria. It is taken by mouth.

FOXP3, also known as scurfin, is a protein involved in immune system responses. A member of the FOX protein family, FOXP3 appears to function as a master regulator of the regulatory pathway in the development and function of regulatory T cells. Regulatory T cells generally turn the immune response down. In cancer, an excess of regulatory T cell activity can prevent the immune system from destroying cancer cells. In autoimmune disease, a deficiency of regulatory T cell activity can allow other autoimmune cells to attack the body's own tissues.

Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and porphyria cutanea tarda. It is taken by mouth, often in the form of hydroxychloroquine sulfate.

N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) is an amide derivative of the monosaccharide glucose. It is a secondary amide between glucosamine and acetic acid. It is significant in several biological systems.

Platelet factor 4 (PF4) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family that is also known as chemokine ligand 4 (CXCL4). This chemokine is released from alpha-granules of activated platelets during platelet aggregation, and promotes blood coagulation by moderating the effects of heparin-like molecules. Due to these roles, it is predicted to play a role in wound repair and inflammation. It is usually found in a complex with proteoglycan.

Interleukin 17 family is a family of pro-inflammatory cystine knot cytokines. They are produced by a group of T helper cell known as T helper 17 cell in response to their stimulation with IL-23. Originally, Th17 was identified in 1993 by Rouvier et al. who isolated IL17A transcript from a rodent T-cell hybridoma. The protein encoded by IL17A is a founding member of IL-17 family. IL17A protein exhibits a high homology with a viral IL-17-like protein encoded in the genome of T-lymphotropic rhadinovirus Herpesvirus saimiri. In rodents, IL-17A is often referred to as CTLA8.
The non-mevalonate pathway—also appearing as the mevalonate-independent pathway and the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate/1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (MEP/DOXP) pathway—is an alternative metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of the isoprenoid precursors isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP). The currently preferred name for this pathway is the MEP pathway, since MEP is the first committed metabolite on the route to IPP.
T helper 17 cells (Th17) are a subset of pro-inflammatory T helper cells defined by their production of interleukin 17 (IL-17). They are related to T regulatory cells and the signals that cause Th17s to differentiate actually inhibit Treg differentiation. However, Th17s are developmentally distinct from Th1 and Th2 lineages. Th17 cells play an important role in maintaining mucosal barriers and contributing to pathogen clearance at mucosal surfaces; such protective and non-pathogenic Th17 cells have been termed as Treg17 cells.
Protein kinase C theta (PKC-θ) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCQ gene. PKC-θ, a member of serine/threonine kinases, is mainly expressed in hematopoietic cells with high levels in platelets and T lymphocytes, where plays a role in signal transduction. Different subpopulations of T cells vary in their requirements of PKC-θ, therefore PKC-θ is considered as a potential target for inhibitors in the context of immunotherapy.
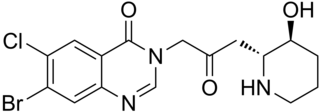
Halofuginone, sold under the brand name Halocur, is a coccidiostat used in veterinary medicine. It is a synthetic halogenated derivative of febrifugine, a natural quinazolinone alkaloid which can be found in the Chinese herb Dichroa febrifuga. Collgard Biopharmaceuticals is developing halofuginone for the treatment of scleroderma and it has received orphan drug designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
PfATP6, also known as PfSERCA or PfATPase6, is a calcium ATPase gene encoded by the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. The protein is thought to be a P-type ATPase involved in calcium ion transport.
Project 523 is a code name for a 1967 secret military project of the People's Republic of China to find antimalarial medications. Named after the date the project launched, 23 May, it addressed malaria, an important threat in the Vietnam War. At the behest of Ho Chi Minh, Prime Minister of North Vietnam, Zhou Enlai, the Premier of the People's Republic of China, convinced Mao Zedong, Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party, to start the mass project "to keep [the] allies' troops combat-ready", as the meeting minutes put it. More than 500 Chinese scientists were recruited. The project was divided into three streams. The one for investigating traditional Chinese medicine discovered and led to the development of a class of new antimalarial drugs called artemisinins. Launched during and lasting throughout the Cultural Revolution, Project 523 was officially terminated in 1981.
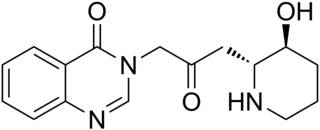
Febrifugine is a quinazolinone alkaloid first isolated from the Chinese herb Dichroa febrifuga, but also found in the garden plant Hydrangea. Laboratory synthesis of febrifugine determined that the originally reported stereochemistry was incorrect.
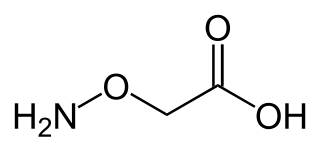
Aminooxyacetic acid, often abbreviated AOA or AOAA, is a compound that inhibits 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase (GABA-T) activity in vitro and in vivo, leading to less gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) being broken down. Subsequently, the level of GABA is increased in tissues. At concentrations high enough to fully inhibit 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase activity, aminooxyacetic acid is indicated as a useful tool to study regional GABA turnover in rats.

Tabernaemontanine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Tabernaemontana divaricata.
David A. Fidock, is the CS Hamish Young Professor of Microbiology and Immunology and Professor of Medical Sciences at Columbia University Irving Medical Center in Manhattan.
















