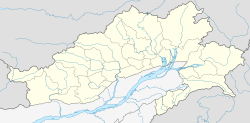
Arunachal Pradesh is a state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and largest town. It borders the Indian states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region in the north at the McMahon Line. Arunachal Pradesh is claimed by China as South Tibet as part of the Tibet Autonomous Region; China occupied some regions of Arunachal Pradesh in 1962 but later withdrew its forces.

Dibang Valley (Pron:/dɪˈbæŋ/) is a district of Arunachal Pradesh named after the Dibang River or the Talon as the Mishmis call it. It is the least populated district in India and has an area of 9,129 square kilometres (3,525 sq mi).
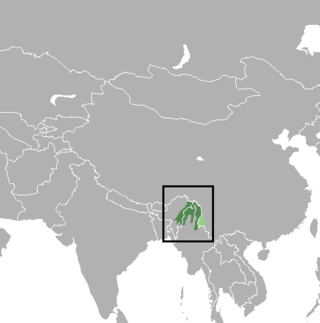
The leaf muntjac, leaf deer or Putao muntjac is a small species of muntjac. It was documented in 1997 by biologist Alan Rabinowitz during his field study in the isolated Nogmung Township in Myanmar. Rabinowitz discovered the species by examining the small carcass of a deer that he initially believed was the juvenile of another species; however, it proved to be the carcass of an adult female. He managed to obtain specimens, from which DNA analysis revealed a new cervid species. Local hunters knew of the species and called it the leaf deer because its body could be completely wrapped by a single large leaf. It is found in Myanmar and India.

Lohit is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India. The district headquarters is located at Tezu. As of 2011 it is the third most populous district of Arunachal Pradesh, after Papum Pare and Changlang.

West Siang district is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India.

Anini is the headquarters of the Dibang Valley district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in Northeast India. Anini was also the district headquarters of the undivided Dibang Valley district. Most of this location's population consists of the Idu Mishmi tribal people. Due to its remote location, Anini remains a small and underdeveloped town. However, it still has basic road and air links to the rest of India. The town is fully dependent on the nearest major settlement, Roing, which is in the Lower Dibang Valley District, for most commercial needs.

Walong is an administrative town and the headquarters of eponymous circle in the Anjaw district in eastern-most part of Arunachal Pradesh state in India. It also has a small cantonment of the Indian Army. Walong is on banks of Lohit River, which enters India 35 km north of Walong at India-China LAC at Kaho pass.
Mouling National Park is a national park located in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh, spread primarily over the Upper Siang district and parts of the West Siang and East Siang district. It was the second national park to be created in the state, after Namdapha National Park in 1972. The Mouling National Park and the Dibang Wildlife Sanctuary are located fully or partly within Dihang-Dibang Biosphere Reserve.

Anjaw District (Pron:/ˈændʒɔ:/) is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in north-east India. It was created district in 2004, by splitting off from the Lohit district under the Arunachal Pradesh Re-organization of Districts Amendment Act. The district borders China on the north. Hawai, at an altitude of 1296 m above sea level, is the district headquarters, located on the banks of the Lohit River, a tributary of the Brahmaputra River. It is the easternmost district in India. The furthest villages towards the border with China are Dong, Walong, Kibithu and Kaho.

The Lower Dibang Valley district (Pron:/dɪˈbæŋ/) is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in northeastern India. It is the tenth least populous district in the country.

Petaurista is a genus of rodent in the family Sciuridae. They are large to very large flying squirrels found in forests and other wooded habitats in southern and eastern Asia.

Anwaruddin Choudhury is an Indian naturalist, noted for his expertise on the fauna of North-East India.

The Dibang Wildlife Sanctuary is one of the eight wildlife sanctuaries of Arunachal Pradesh, India.

Upper Siang is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India. It is the fourth least populous district in the country.

The Mishmi Hills are located at the northeastern tip of India, in northeastern Arunachal Pradesh. On the Chinese side, they form the southern parts of Nyingchi Prefecture in the Tibet Autonomous Region.

Arunachal Pradesh is primarily a hilly tract nestled in the foothills of the Himalayas in northeast India. It is spread over an area of 83,743 km2 (32,333 sq mi). 98% of the geographical area is land out of which 80% is forest cover; 2% is water. River systems in the region, including those from the higher Himalayas and Patkoi and Arakan Ranges, eventually drain into the Brahmaputra River.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Arunachal Pradesh:
The Mishmi giant flying squirrel is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae. First described in 2009 from East Himalayan forests at altitudes of 600–1,600 m (2,000–5,200 ft) in the Mishmi Hills of northeastern Arunachal Pradesh in India, the taxonomic status and position of this giant flying squirrel is not fully resolved.
The Mebo giant flying squirrel is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae. It was first described in 2013 from the East Himalayan forests of Upper Siang District, Arunachal Pradesh in India.