
The Cupedidae are a small family of beetles, notable for the square pattern of "windows" on their elytra, which give the family their common name of reticulated beetles.

Bittacidae is a family of scorpionflies commonly called hangingflies or hanging scorpionflies.

Anaxyelidae is a family of incense cedar wood wasps in the order Hymenoptera. It contains only one living genus, Syntexis, which has only a single species, native to Western North America. Fossils of the family extend back to the Middle Jurassic, belonging to over a dozen extinct genera, with a particularly high diversity during the Early Cretaceous. Syntexis lay eggs in the sapwood of conifers, preferring recently burnt wood.

Pelecinidae is a family of parasitic wasps in the superfamily Proctotrupoidea. It contains only one living genus, Pelecinus, with three species known from the Americas. The earliest fossil species are known from the Jurassic, and the group was highly diverse during the Cretaceous. Members of Pelecinus are parasitic on larval beetles, flies, green lacewings, and sawflies.

Nemestrinidae, or tangle-veined flies is a family of flies in the superfamily Nemestrinoidea, closely related to Acroceridae. The family is small but distributed worldwide, with about 300 species in 34 genera. Larvae are endoparasitoids of either grasshoppers (Trichopsideinae) or scarab beetles (Hirmoneurinae). Some are considered important in the control of grasshopper populations. Adults are often observed on flowers.
Eolepidopterigoidea is an extinct superfamily of moths, containing the single family Eolepidopterigidae, although the genus Undopterix is sometimes placed in a separate family Undopterigidae. The type-genus of the family is Eolepidopterix.
Brochocoleus is an extinct genus of beetles in the family Ommatidae, known from the Early Jurassic to the Early Late Cretaceous. 9 species are currently recognised, with many species being reassigned to other genera by Kirejtshuk's major systematic revision in 2020.

Cionocoleus is an extinct genus of beetles in the family Ommatidae.

Mesoraphidiidae is an extinct family of snakeflies in the suborder Raphidiomorpha. The family lived from the Late Jurassic through the Late Cretaceous and is known from twenty-five genera. Mesoraphidiids have been found as both compression fossils and as inclusions in amber. The family was first proposed in 1925 by the Russian paleoentomologist Andrey Vasilyevich Martynov based on Upper Jurassic fossils recovered in Kazakhstan. The family was expanded in 2002 by the synonymizing of several other proposed snakefly families. The family was divided into three subfamilies and one tribe in a 2011 paper, further clarifying the relationships of the included genera.

Artematopodidae is a family of soft-bodied plant beetles in the superfamily Elateroidea. They are mostly found in understory forest foliage. The life history of the group is obscure, larvae of the genera Eurypogon and Macropogon likely feed on moss, while the larvae of Artematopus have been fed insect remains. The oldest fossils of the family date to the Middle Jurassic.

Heloridae is a family of wasps in the order Hymenoptera known primarily from fossils, and only one extant genus, Helorus, with 12 species found worldwide. Members of Helorus are parasitic on green lacewings.

Aneuretopsychidae is an extinct family of scorpionflies known from the Mesozoic. Fossils are known from the Jurassic (Callovian-Oxfordian) to the early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian). It is part of Mesopsychoidea, a group of scorpionflies with siphonate proboscis. They are suggested to have been nectarivores, feeding off the liquid pollination drops of and acting as pollinators for now extinct insect pollinated gymnosperms such as Bennettitales.

Mesopsychidae is an extinct family of scorpionflies known from the Late Permian to Mid Cretaceous. It is part of Mesopsychoidea, a group of scorpionflies with siphonate proboscis. They are suggested to have been nectarivores, feeding off the liquid pollination drops and acting as pollinators for now extinct insect pollinated gymnosperms such as Bennettitales.
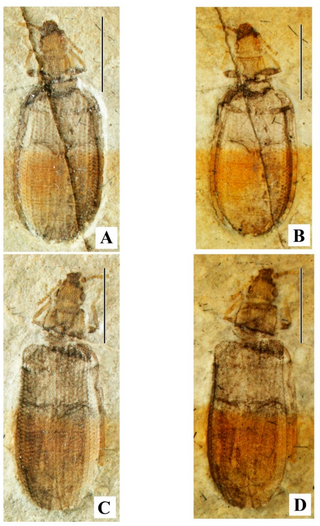
Monticupes is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. The genus is characterised by "moderately oval body, subtriangular or long (subparallelsided) head with large eyes and well raised temples, pronotum carinate and with subexplanate sides, veins well expressed with fused A1 and Cu at apex and their common vein ending on Sc, explanate elytral sides moderately wide and with diffuse small microtubercles, and abdominal ventrites co-planar (abutting)."

Procercopidae is an extinct family of froghoppers. They are known from the Early Jurassic to early Late Cretaceous of Eurasia. They are one of two main families of Mesozoic froghoppers alongside Sinoalidae. Procercopidae are considered to be the ancestral group from which modern froghoppers are derived.

Archisargidae is an extinct family of brachyceran flies known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. It is part of the extinct superfamily Archisargoidea. Most members of the family are known from the Callovian-Oxfordian Daohugou biota of Inner Mongolia, China, and the equivalently aged Karabastau Formation of Kazakhstan. The family has been found to be paraphyletic with respect to Eremochaetidae in a cladistic analysis.
Praeaulacidae is an extinct family of Mesozoic parasitic wasps in the suborder Evanioidea. It among the earliest known families of the group and is characterised by more complete wing venation in comparison to other members of the suborder. It has been found that Othniodellithidae is nested within Praeaulacidae via cladistic analysis.
Mesochrysopidae is an extinct family of lacewings known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. They are considered to be closely related to green lacewings of the family Chrysopidae. The family are also alternatively considered a paraphyletic grade leading up to crown Chrysopidae.

Susumanioidea is an extinct superfamily of Phasmatodea, known from the Middle Jurassic to Eocene. They lie outside the modern crown group of Phasmatodea. Members of the group typically possess large, fully developed wings.

Orthophlebiidae is an extinct family of scorpionflies known from the Triassic to Cretaceous, belonging to the superfamily Panorpoidea. The family is poorly defined and is probably paraphyletic, representing many primitive members of Panorpoidea with most species only known from isolated wings, and has such been considered a wastebasket taxon.















