
Paradetis is a monotypic moth genus in the family Geometridae. Its only species, Paradetis porphyrias, also known as the orange and purple fern looper, is endemic to New Zealand. The genus and species were first described by Edward Meyrick, the genus in 1885 and the species in 1883.

Batrachedra agaura is a species of moth in the family Batrachedridae. It is endemic to New Zealand. This species is distributed throughout the country. The species inhabits native forest especially beech and kanuka forest or manuka scrubland. The larvae of this species is associated with sooty mold and with sooty beech scale. It has been hypothesised that the larvae feed on sooty beech scale. However they may also feed on the sooty mold itself. The adult female is lighter in appearance than the male and the species shows considerable variation in patterns on forewing. Adults are on the wing from October to February. They are nocturnal and occasionally attracted to light.

Batrachedra tristicta is a species of moth in the family Batrachedridae. It is endemic to New Zealand and has been found in both the North and South Islands. The larvae feel on the flowers and seed heads of rushes in the genus Juncus. The adults of this species are on the wing in March.
Heterocrossa epomiana is a species moth in the family Carposinidae. It is endemic to New Zealand.

Heterocrossa exochana is a species of moth in the family Carposinidae. It is endemic to New Zealand.

Heterocrossa iophaea is a species of moth in the family Carposinidae. It is endemic to New Zealand.
Dryadaula are a genus of moths belonging to the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1893, and it belongs to the subfamily or family Dryadaulidae, according to most recent taxonomies.

Gadira petraula is a species of moth in the family Crambidae. This species is endemic to New Zealand and is only found in mid Canterbury. G. petraula inhabits coastal, montane and low alpine rock sites. The larvae live in rock crevices in a silk shelter from which they emerge to feed. Their host plants are moss or lichens. The adult female is flightless and the male is on the wing in March. This species is classified as "At Risk, Naturally Uncommon" by the Department of Conservation. The 2010 and 2011 Christchurch earthquakes destroyed much of this species preferred habitat. Rock climbers cleaning rocks of the larval host plants are also a threat to the survival of this species.

Pyrgotis pyramidias is a species of moth in the family Tortricidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. It is classified as "At Risk, Naturally Uncommon" by the Department of Conservation. This species is regarded as having two 'forms' although doubt has been expressed whether these are the same species.

Eudonia chalara is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1901. It is endemic to New Zealand.

Elachista melanura is a species of moth in the family Elachistidae. This species is endemic to New Zealand. It is classified as "Data Deficient" by the Department of Conservation.

Crypsitricha roseata is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1913. This species is endemic to New Zealand. The type locality of this species is the suburb of Wadestown, in Wellington.

Crypsitricha roseata is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1914. This species is endemic to New Zealand.
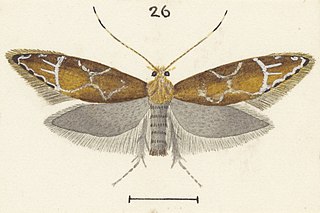
Dryadaula castanea is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was described by Alfred Philpott in 1915. This species is endemic to New Zealand.

Dryadaula myrrhina is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1905. This species is endemic to New Zealand.

Erechthias exospila is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1901 using a specimen he collected in Whangārei in December. This species is endemic to New Zealand.

Erechthias hemiclistra is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1911. This species is endemic to New Zealand. Entomologist George Hudson reared this moth from caterpillars and cocoons in the flower stems of Chionochloa conspicua at Makara. The adults emerged in November and February. The food of the larvae of this species is apparently dead woody fibre.

Eschatotypa halosparta, also known as the salt and pepper fungus moth, is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1919 from a specimen collected by George Vernon Hudson at Wainuiomata in December. This species is endemic to New Zealand. This species has also been collected near the Tui Mine in Te Aroha.

Lysiphragma epixyla is a species of moth in the family Tineidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1888 using specimens collected from Wellington, Lake Wakatipu and Invercargill in December and January. Meyrick notes that this moth can usually be found at rest on tree trunks. This species is endemic to New Zealand.

Dasyuris enysii is a species of moth in the family Geometridae. It is endemic to New Zealand. This moth is classified as "At Risk, Naturally Uncommon" by the Department of Conservation.



















