Fundamental analysis, in accounting and finance, is the analysis of a business's financial statements ; health; and competitors and markets. It also considers the overall state of the economy and factors including interest rates, production, earnings, employment, GDP, housing, manufacturing and management. There are two basic approaches that can be used: bottom up analysis and top down analysis. These terms are used to distinguish such analysis from other types of investment analysis, such as quantitative and technical.

A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument, but its legal definition varies by jurisdiction. In some countries and languages people commonly use the term "security" to refer to any form of financial instrument, even though the underlying legal and regulatory regime may not have such a broad definition. In some jurisdictions the term specifically excludes financial instruments other than equities and fixed income instruments. In some jurisdictions it includes some instruments that are close to equities and fixed income, e.g., equity warrants.

In finance, equity is an ownership interest in property that may be offset by debts or other liabilities. Equity is measured for accounting purposes by subtracting liabilities from the value of the assets owned. For example, if someone owns a car worth $24,000 and owes $10,000 on the loan used to buy the car, the difference of $14,000 is equity. Equity can apply to a single asset, such as a car or house, or to an entire business. A business that needs to start up or expand its operations can sell its equity in order to raise cash that does not have to be repaid on a set schedule.
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets. The WACC is commonly referred to as the firm's cost of capital. Importantly, it is dictated by the external market and not by management. The WACC represents the minimum return that a company must earn on an existing asset base to satisfy its creditors, owners, and other providers of capital, or they will invest elsewhere.
In finance, a convertible bond, convertible note, or convertible debt is a type of bond that the holder can convert into a specified number of shares of common stock in the issuing company or cash of equal value. It is a hybrid security with debt- and equity-like features. It originated in the mid-19th century, and was used by early speculators such as Jacob Little and Daniel Drew to counter market cornering.

In finance, valuation is the process of determining the value of a (potential) investment, asset, or security. Generally, there are three approaches taken, namely discounted cashflow valuation, relative valuation, and contingent claim valuation.
Stock valuation is the method of calculating theoretical values of companies and their stocks. The main use of these methods is to predict future market prices, or more generally, potential market prices, and thus to profit from price movement – stocks that are judged undervalued are bought, while stocks that are judged overvalued are sold, in the expectation that undervalued stocks will overall rise in value, while overvalued stocks will generally decrease in value. A target price is a price at which an analyst believes a stock to be fairly valued relative to its projected and historical earnings.
In economics and accounting, the cost of capital is the cost of a company's funds, or from an investor's point of view is "the required rate of return on a portfolio company's existing securities". It is used to evaluate new projects of a company. It is the minimum return that investors expect for providing capital to the company, thus setting a benchmark that a new project has to meet.
In financial accounting, free cash flow (FCF) or free cash flow to firm (FCFF) is the amount by which a business's operating cash flow exceeds its working capital needs and expenditures on fixed assets. It is that portion of cash flow that can be extracted from a company and distributed to creditors and securities holders without causing issues in its operations. As such, it is an indicator of a company's financial flexibility and is of interest to holders of the company's equity, debt, preferred stock and convertible securities, as well as potential lenders and investors.
Enterprise value (EV), total enterprise value (TEV), or firm value (FV) is an economic measure reflecting the market value of a business. It is a sum of claims by all claimants: creditors and shareholders. Enterprise value is one of the fundamental metrics used in business valuation, financial analysis, accounting, portfolio analysis, and risk analysis.
Shareholder value is a business term, sometimes phrased as shareholder value maximization. It became prominent during the 1980s and 1990s along with the management principle value-based management or "managing for value".
Post-money valuation is a way of expressing the value of a company after an investment has been made. This value is equal to the sum of the pre-money valuation and the amount of new equity.
Business valuation is a process and a set of procedures used to estimate the economic value of an owner's interest in a business. Here various valuation techniques are used by financial market participants to determine the price they are willing to pay or receive to effect a sale of the business. In addition to estimating the selling price of a business, the same valuation tools are often used by business appraisers to resolve disputes related to estate and gift taxation, divorce litigation, allocate business purchase price among business assets, establish a formula for estimating the value of partners' ownership interest for buy-sell agreements, and many other business and legal purposes such as in shareholders deadlock, divorce litigation and estate contest.
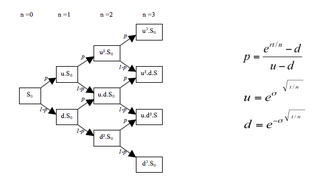
In finance, a lattice model is a technique applied to the valuation of derivatives, where a discrete time model is required. For equity options, a typical example would be pricing an American option, where a decision as to option exercise is required at "all" times before and including maturity. A continuous model, on the other hand, such as Black–Scholes, would only allow for the valuation of European options, where exercise is on the option's maturity date. For interest rate derivatives lattices are additionally useful in that they address many of the issues encountered with continuous models, such as pull to par. The method is also used for valuing certain exotic options, where because of path dependence in the payoff, Monte Carlo methods for option pricing fail to account for optimal decisions to terminate the derivative by early exercise, though methods now exist for solving this problem.

Financial statement analysis is the process of reviewing and analyzing a company's financial statements to make better economic decisions to earn income in future. These statements include the income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, notes to accounts and a statement of changes in equity. Financial statement analysis is a method or process involving specific techniques for evaluating risks, performance, valuation, financial health, and future prospects of an organization.
Stock option expensing is a method of accounting for the value of share options, distributed as incentives to employees within the profit and loss reporting of a listed business. On the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement the loss from the exercise is accounted for by noting the difference between the market price of the shares and the cash received, the exercise price, for issuing those shares through the option.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:

Stocks consist of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided. A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporation in proportion to the total number of shares. This typically entitles the shareholder (stockholder) to that fraction of the company's earnings, proceeds from liquidation of assets, or voting power, often dividing these up in proportion to the amount of money each stockholder has invested. Not all stock is necessarily equal, as certain classes of stock may be issued, for example, without voting rights, with enhanced voting rights, or with a certain priority to receive profits or liquidation proceeds before or after other classes of shareholders.

A financial ratio or accounting ratio states the relative magnitude of two selected numerical values taken from an enterprise's financial statements. Often used in accounting, there are many standard ratios used to try to evaluate the overall financial condition of a corporation or other organization. Financial ratios may be used by managers within a firm, by current and potential shareholders (owners) of a firm, and by a firm's creditors. Financial analysts use financial ratios to compare the strengths and weaknesses in various companies. If shares in a company are traded in a financial market, the market price of the shares is used in certain financial ratios.

Corporate finance is the area of finance that deals with the sources of funding, and the capital structure of corporations, the actions that managers take to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders, and the tools and analysis used to allocate financial resources. The primary goal of corporate finance is to maximize or increase shareholder value.



