| Dot-underwing | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Male | |
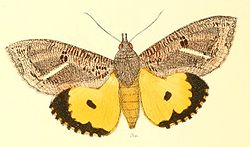 | |
| Female | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Lepidoptera |
| Superfamily: | Noctuoidea |
| Family: | Erebidae |
| Genus: | Eudocima |
| Species: | E. materna |
| Binomial name | |
| Eudocima materna | |
| Synonyms | |
| |

Eudocima materna, the dot-underwing moth, [1] [2] is a moth of the family Erebidae found in widespread parts of the world, mainly in tropical Asia extending to New Guinea and Australia [3] as well as in Africa. Reports from the United States, Canada and the French Antilles are now considered to be Eudocima apta . The species can be differentiated from other Eudocima moths by the presence of small central black dot in each hindwing. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1767 12th edition of Systema Naturae.






