
Pyrotechnics is the science and craft of creating such things as fireworks, safety matches, oxygen candles, explosive bolts and other fasteners, parts of automotive airbags, as well as gas-pressure blasting in mining, quarrying, and demolition. This trade relies upon self-contained and self-sustained exothermic chemical reactions to make heat, light, gas, smoke and/or sound. The name comes from the Greek words pyr ("fire") and tekhnikos.

Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it can move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from current electricity, where an electric charge flows through an electrical conductor.

The flash point of a material is the "lowest liquid temperature at which, under certain standardized conditions, a liquid gives off vapours in a quantity such as to be capable of forming an ignitable vapour/air mixture".
Coal dust is a fine-powdered form of coal which is created by the crushing, grinding, or pulverization of coal rock. Because of the brittle nature of coal, coal dust can be created by mining, transporting, or mechanically handling it.
A flashover is the near-simultaneous ignition of most of the directly exposed combustible material in an enclosed area. When certain organic materials are heated, they undergo thermal decomposition and release flammable gases. Flashover occurs when the majority of the exposed surfaces in a space are heated to their autoignition temperature and emit flammable gases. Flashover normally occurs at 500 °C (932 °F) or 590 °C (1,100 °F) for ordinary combustibles and an incident heat flux at floor level of 20 kilowatts per square metre (2.5 hp/sq ft).
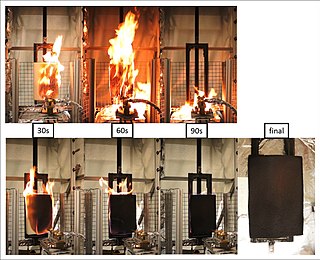
Flame retardants are a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an ignition source and prevent or slow the further development of flames by a variety of different physical and chemical mechanisms. They may be added as a copolymer during the polymerisation process, or later added to the polymer at a moulding or extrusion process or applied as a topical finish. Mineral flame retardants are typically additive, while organohalogen and organophosphorus compounds can be either reactive or additive.

Firefighting is a profession aimed at controlling and extinguishing fire. A person who engages in firefighting is known as a firefighter or fireman. Firefighters typically undergo a high degree of technical training. This involves structural firefighting and wildland firefighting. Specialized training includes aircraft firefighting, shipboard firefighting, aerial firefighting, maritime firefighting, and proximity firefighting.

Fire safety is the set of practices intended to reduce destruction caused by fire. Fire safety measures include those that are intended to prevent the ignition of an uncontrolled fire and those that are used to limit the spread and impact of a fire.

In electrical and safety engineering, hazardous locations are places where fire or explosion hazards may exist. Sources of such hazards include gases, vapors, dust, fibers, and flyings, which are combustible or flammable. Electrical equipment installed in such locations can provide an ignition source, due to electrical arcing, or high temperatures. Standards and regulations exist to identify such locations, classify the hazards, and design equipment for safe use in such locations.

A fire retardant is a substance that is used to slow down or stop the spread of fire or reduce its intensity. This is commonly accomplished by chemical reactions that reduce the flammability of fuels or delay their combustion. Fire retardants may also cool the fuel through physical action or endothermic chemical reactions. Fire retardants are available as powder, to be mixed with water, as fire-fighting foams and fire-retardant gels. Fire retardants are also available as coatings or sprays to be applied to an object.
Mixtures of dispersed combustible materials and oxygen in the air will burn only if the fuel concentration lies within well-defined lower and upper bounds determined experimentally, referred to as flammability limits or explosive limits. Combustion can range in violence from deflagration through detonation.
Active fire protection (AFP) is an integral part of fire protection. AFP is characterized by items and/or systems, which require a certain amount of motion and response in order to work, contrary to passive fire protection.
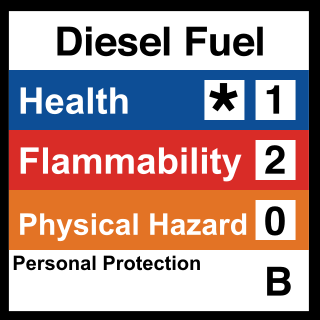
The Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS) is a proprietary numerical hazard rating that incorporates the use of labels with color bars developed by the American Coatings Association as a compliance aid for the OSHA Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard. The name and abbreviation is a trademark of the American Coatings Association.

Fire-retardant fabrics are textiles that are more resistant to fire than others through chemical treatment of flame-retardant or manufactured fireproof fibers.

Potassium nitrate is an oxidizer so storing it near fire hazards or reducing agents should be avoided to minimise risk in case of a fire.

A combustible material is a material that can burn in air under certain conditions. A material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable material catches fire immediately on exposure to flame.

A dust explosion is the rapid combustion of fine particles suspended in the air within an enclosed location. Dust explosions can occur where any dispersed powdered combustible material is present in high-enough concentrations in the atmosphere or other oxidizing gaseous medium, such as pure oxygen. In cases when fuel plays the role of a combustible material, the explosion is known as a fuel-air explosion.

Hydrogen safety covers the safe production, handling and use of hydrogen, particularly hydrogen gas fuel and liquid hydrogen. Hydrogen possesses the NFPA 704's highest rating of four on the flammability scale because it is flammable when mixed even in small amounts with ordinary air. Ignition can occur at a volumetric ratio of hydrogen to air as low as 4% due to the oxygen in the air and the simplicity and chemical properties of the reaction. However, hydrogen has no rating for innate hazard for reactivity or toxicity. The storage and use of hydrogen poses unique challenges due to its ease of leaking as a gaseous fuel, low-energy ignition, wide range of combustible fuel-air mixtures, buoyancy, and its ability to embrittle metals that must be accounted for to ensure safe operation.

In fire classes, a Class B fire is a fire in flammable liquids or flammable gases, petroleum greases, tars, oils, oil-based paints, solvents, lacquers, or alcohols. For example, propane, natural gas, gasoline and kerosene fires are types of Class B fires. The use of lighter fluid on a charcoal grill, for example, creates a Class B fire. Some plastics are also Class B fire materials.
In fire and explosion prevention engineering, inerting refers to the introduction of an inert (non-combustible) gas into a closed system to make a flammable atmosphere oxygen deficient and non-ignitable.














