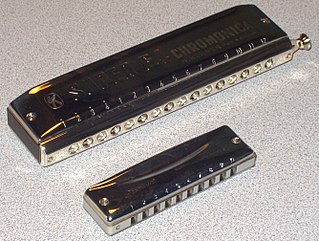
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica include diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, orchestral, and bass versions. A harmonica is played by using the mouth to direct air into or out of one holes along a mouthpiece. Behind each hole is a chamber containing at least one reed. The most common is the diatonic Richter-tuned with ten air passages and twenty reeds, often called the blues harp. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring typically made of brass, stainless steel, or bronze, which is secured at one end over a slot that serves as an airway. When the free end is made to vibrate by the player's air, it alternately blocks and unblocks the airway to produce sound.

Renaissance music is traditionally understood to cover European music of the 15th and 16th centuries, later than the Renaissance era as it is understood in other disciplines. Rather than starting from the early 14th-century ars nova, the Trecento music was treated by musicology as a coda to Medieval music and the new era dated from the rise of triadic harmony and the spread of the contenance angloise style from Britain to the Burgundian School. A convenient watershed for its end is the adoption of basso continuo at the beginning of the Baroque period.

The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B♭ or C trumpet.

String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner.

In organology, the study of musical instruments, many methods of classifying instruments exist. Most methods are specific to a particular cultural group and were developed to serve that culture's musical needs. Culture-based classification methods sometimes break down when applied outside that culture. For example, a classification based on instrument use may fail when applied to another culture that uses the same instrument differently.
Hornbostel–Sachs or Sachs–Hornbostel is a system of musical instrument classification devised by Erich Moritz von Hornbostel and Curt Sachs, and first published in the Zeitschrift für Ethnologie in 1914. An English translation was published in the Galpin Society Journal in 1961. It is the most widely used system for classifying musical instruments by ethnomusicologists and organologists. The system was updated in 2011 as part of the work of the Musical Instrument Museums Online (MIMO) Project.

An idiophone is any musical instrument that creates sound primarily by the vibration of the instrument itself, without the use of air flow, strings (chordophones), membranes (membranophones) or electricity (electrophones). It is the first of the four main divisions in the original Hornbostel–Sachs system of musical instrument classification. The early classification of Victor-Charles Mahillon called this group of instruments autophones. The most common are struck idiophones, or concussion idiophones, which are made to vibrate by being struck, either directly with a stick or hand or indirectly, with scraping or shaking motions. Various types of bells fall into both categories. A common plucked idiophone is the Jew's harp.

The Jew's harp, also known as jaw harp, juice harp, or mouth harp, is a lamellophone instrument, consisting of a flexible metal or bamboo tongue or reed attached to a frame. Contrary to the colloquial name, the Jew's harp most likely originated in Siberia, specifically in or around the Altai Mountains and has no relation to the Jewish people.

A lamellophone is a member of the family of musical instruments that makes its sound by a thin vibrating plate called a lamella or tongue, which is fixed at one end and has the other end free. When the musician depresses the free end of a plate with a finger or fingernail, and then allows the finger to slip off, the released plate vibrates. An instrument may have a single tongue or a series of multiple tongues.

The morsing is an instrument similar to the Jew's harp, mainly used in Rajasthan, in the Carnatic music of South India, and in Sindh, Pakistan. It can be categorized under lamellophones, which is a sub-category of plucked idiophones. The instrument consists of a metal ring in the shape of a horseshoe with two parallel forks which form the frame, and a metal tongue in the middle, between the forks, fixed to the ring at one end and free to vibrate at the other. The metal tongue, also called the trigger, is bent at the free end in a plane perpendicular to the circular ring so that it can be struck and made to vibrate.

A slit drum or slit gong is a hollow percussion instrument. In spite of the name, it is not a true drum but an idiophone, usually carved or constructed from bamboo or wood into a box with one or more slits in the top. Most slit drums have one slit, though two and three slits occur. If the resultant tongues are different width or thicknesses, the drum will produce two different pitches. It is used throughout Africa, Southeast Asia, and Oceania. In Africa such drums, strategically situated for optimal acoustic transmission, have been used for long-distance communication.
There are numerous techniques available for playing the harmonica, including bending, overbending, and tongue blocking.
Articulation is a musical parameter that determines how a single note or other discrete event is sounded. Articulations primarily structure an event's start and end, determining the length of its sound and the shape of its attack and decay. They can also modify an event's timbre, dynamics, and pitch. Musical articulation is analogous to the articulation of speech, and during the Baroque and Classical periods it was taught by comparison to oratory.

Derived from the mouth harp of the Hmong people, Đàn môi is the Vietnamese name of a traditional musical instrument widely used in minority ethnic groups in Vietnam. An inward orientated idioglot, mouth harp somewhat similar to the metal heteroglot/compound jaw harp, the dan moi, rather than being held against the teeth while being played, like a jaw harp, is held against the lips while being played.
The lamella is...cut into the material,...such as...the brass dan moi from the Hmong people in northern Vietnam and Cambodia. ...To play...the instrument is held against the lips to connect it to the sound-box and the action of the lamella is triggered...by plucking.

A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who plays a musical instrument is known as an instrumentalist. The history of musical instruments dates to the beginnings of human culture. Early musical instruments may have been used for rituals, such as a horn to signal success on the hunt, or a drum in a religious ceremony. Cultures eventually developed composition and performance of melodies for entertainment. Musical instruments evolved in step with changing applications and technologies.

The Karinding is Sundanese traditional musical instrument from West Java, Indonesia. It is similar to the Jew's harp and are usually made from bamboo and midribs of palm trees. Karindings made of palm tree midribs are traditionally used by male players, and bamboo instruments are used by female players.

Music technology is the study or the use of any device, mechanism, machine or tool by a musician or composer to make or perform music; to compose, notate, playback or record songs or pieces; or to analyze or edit music.

Mechanical music technology is the use of any device, mechanism, machine or tool by a musician or composer to make or perform music; to compose, notate, play back or record songs or pieces; or to analyze or edit music. The earliest known applications of technology to music was prehistoric peoples' use of a tool to hand-drill holes in bones to make simple flutes. Ancient Egyptians developed stringed instruments, such as harps, lyres and lutes, which required making thin strings and some type of peg system for adjusting the pitch of the strings. Ancient Egyptians also used wind instruments such as double clarinets and percussion instruments such as cymbals. In Ancient Greece, instruments included the double-reed aulos and the lyre. Numerous instruments are referred to in the Bible, including the horn, pipe, lyre, harp, and bagpipe. During Biblical times, the cornet, flute, horn, organ, pipe, and trumpet were also used. During the Middle Ages, hand-written music notation was developed to write down the notes of religious Plainchant melodies; this notation enabled the Catholic church to disseminate the same chant melodies across its entire empire.

The angkouch is a Cambodian jaw harp. It is a folk instrument made of bamboo and carved into a long, flat shape with a hole in the center and a tongue of bamboo across the hole. The bamboo is not removable, which makes the instrument an idioglot.

Sundanese Music is an umbrella term that encompasses diverse musical traditions of the West Java and Banten in western part of Java, Indonesia. The term of "West Java" is preferred by scholars in this field. The word "Sundanese" originally referred to western part of Java Island and has a strong association with the highly centralized Sunda Kingdom based on Java Island and its high culture practiced by the nobleman class in its capital Parahyangan. By contrast, scholars who cover a much broader region lay emphasis on folk culture.

















