Related Research Articles

The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India. It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flood basalt that together are more than about 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) thick, cover an area of about 500,000 square kilometres (200,000 sq mi), and have a volume of about 1,000,000 cubic kilometres (200,000 cu mi). Originally, the Deccan Traps may have covered about 1,500,000 square kilometres (600,000 sq mi), with a correspondingly larger original volume. This volume overlies the Archean age Indian Shield, which is likely the lithology the province passed through during eruption. The province is commonly divided into four subprovinces: the main Deccan, the Malwa Plateau, the Mandla Lobe, and the Saurashtran Plateau.
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering 70,560,000 km2 (27,240,000 sq mi) or approx. 20% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean, or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has large marginal, or regional seas, such as the Andaman Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Laccadive Sea.

The Yellowstone Caldera, sometimes referred to as the Yellowstone Supervolcano, is a volcanic caldera and supervolcano in Yellowstone National Park in the Western United States. The caldera and most of the park are located in the northwest corner of the state of Wyoming. The caldera measures 43 by 28 miles, and postcaldera lavas spill out a significant distance beyond the caldera proper.

The Réunion hotspot is a volcanic hotspot which currently lies under the island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean. The Chagos-Laccadive Ridge and the southern part of the Mascarene Plateau are volcanic traces of the Réunion hotspot.
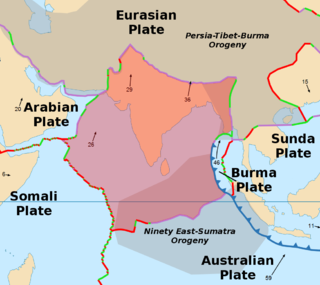
The Indian Plate is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana 100 million years ago and began moving north, carrying Insular India with it. It was once fused with the adjacent Australian Plate to form a single Indo-Australian Plate; recent studies suggest that India and Australia have been separate plates for at least 3 million years. The Indian Plate includes most of modern South Asia and a portion of the basin under the Indian Ocean, including parts of South China, western Indonesia, and extending up to but not including Ladakh, Kohistan, and Balochistan.

The Mascarene Plateau is a submarine plateau in the Indian Ocean, north and east of Madagascar. The plateau extends approximately 2,000 km (1,200 mi), from Seychelles in the north to Réunion in the south. The plateau covers an area of over 115,000 km2 (44,000 sq mi) of shallow water, with depths ranging from 8–150 m (30–490 ft), plunging to 4,000 m (13,000 ft) to the abyssal plain at its edges.
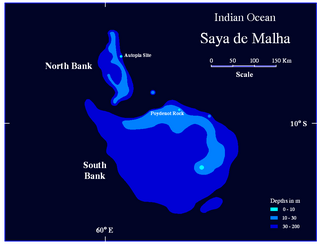
The Saya de Malha Bank or Mesh Skirt Bank, is one of the largest submerged ocean banks in the world, a part of the vast undersea Mascarene Plateau.

The Kerguelen Plateau, also known as the Kerguelen–Heard Plateau, is an oceanic plateau and large igneous province (LIP) located on the Antarctic Plate, in the southern Indian Ocean. It is about 3,000 km (1,900 mi) to the southwest of Australia and is nearly three times the size of California. The plateau extends for more than 2,200 km (1,400 mi) in a northwest–southeast direction and lies in deep water.

The geology of India is diverse. Different regions of the Indian subcontinent contain rocks belonging to different geologic periods, dating as far back as the Eoarchean Era. Some of the rocks are very deformed and altered. Other deposits include recently deposited alluvium that has yet to undergo diagenesis. Mineral deposits of great variety are found in the subcontinent in huge quantities. Even India's fossil record is impressive in which stromatolites, invertebrates, vertebrates and plant fossils are included. India's geographical land area can be classified into the Deccan Traps, Gondwana and Vindhyan.

The Kerguelen hotspot is a volcanic hotspot at the Kerguelen Plateau in the Southern Indian Ocean. The Kerguelen hotspot has produced basaltic lava for about 130 million years and has also produced the Kerguelen Islands, Naturaliste Plateau, Heard Island, the McDonald Islands, the Comei large igneous province in south Tibet, and the Rajmahal Traps. One of the associated features, the Ninety East Ridge, is distinguished by its over 5,000 km (3,100 mi) length, being the longest linear tectonic feature on Earth. The total volume of magma erupted in 130 million years with associated features has been estimated to be about 25,000,000 km3 (6,000,000 cu mi). However, as well as large igneous provinces and seamounts the hotspot has interacted with other seafloor spreading features, so this volume figure has some uncertainty.

Cylindraspis is a genus of recently extinct giant tortoises. All of its species lived in the Mascarene Islands in the Indian Ocean and all are now extinct due to hunting and introduction of non-native predators.

The Central Indian Ridge (CIR) is a north–south-trending mid-ocean ridge in the western Indian Ocean.

The Southeast Indian Ridge (SEIR) is a mid-ocean ridge in the southern Indian Ocean. A divergent tectonic plate boundary stretching almost 6,000 km (3,700 mi) between the Rodrigues Triple Junction in the Indian Ocean and the Macquarie Triple Junction in the Pacific Ocean, the SEIR forms the plate boundary between the Australian and Antarctic plates since the Oligocene (anomaly 13).
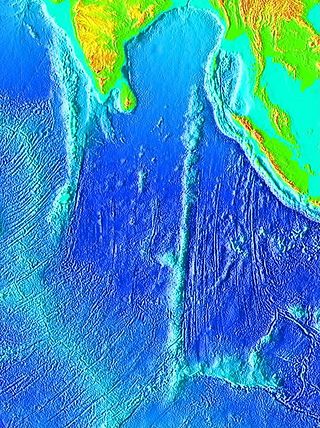
The Ninety East Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge on the Indian Ocean floor named for its near-parallel strike along the 90th meridian at the center of the Eastern Hemisphere. It is approximately 5,000 kilometres (3,100 mi) in length and can be traced topographically from the Bay of Bengal southward towards the Southeast Indian Ridge (SEIR), though the feature continues to the north where it is hidden beneath the sediments of the Bengal Fan. The ridge extends between latitudes 31°S and 9°N and has an average width of 200 km (120 mi).

The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia, mostly situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it spans major landmasses from the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Although the terms "Indian subcontinent" and "South Asia" are often used interchangeably to denote the region, the geopolitical term of South Asia frequently includes Afghanistan, which is not considered part of the subcontinent.

The Seychelles Microcontinent is a microcontinent underlying Seychelles in the western Indian Ocean made of Late Precambrian rock.

Mauritia was a Precambrian microcontinent that was situated between India and Madagascar until their separation about 70 million years ago. Being initially attached to the Indian continent, Mauritia separated from it about 60 million years ago and further fragmented into a ribbon-like structure as the mid-ocean ridge jumped several times. The jumps of the mid-ocean ridge are thought to have been caused of its interaction with the Réunion hotspot as it passed under the West margin of the Indian continent and then under Mauritia. As of today, the fragments of Mauritia include the Laccadives–Maldives–Chagos Ridge, Nazareth Bank, the Saya de Malha Bank, and Hawkins Bank, as well as the islands of Réunion and Mauritius, where the continual crust is buried under basaltic lavas of the Réunion hotspot.
Réunion is a mafic island formed as a result of the Réunion hotspot in the Indian Ocean, the same hotspot that produced the massive basalt flows of the Deccan Traps, when it was beneath India more than 66 million years ago.
The geology of Seychelles is an example of a felsic granite microcontinent that broke off from the supercontinent Gondwana within the past 145 million years and become isolated in the Indian Ocean. The islands are primarily granite rock, with some sequences of sedimentary rocks formed during rift basin periods or times when the islands were submerged in shallow water.
The geology of Mauritius and Rodrigues is comparatively recent. The oldest rocks on Mauritius are only 10 million years old and 1.54 million years old on Rodrigues Island. The mafic basalts of the two islands formed in relation to the hotspot that generated the Deccan Traps and coral reefs built on the volcanoes forming non-volcanic sediments.
References
- ↑ Moores, E.M.; Fairbridge, Rhodes W. (1997). Encyclopedia of European & Asian Regional Geology. Springer. p. 534.