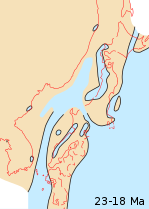
- Japanese archipelago, Sea of Japan and surrounding part of continental East Asia in Early Miocene (23–18 Ma)
- Japanese archipelago, Sea of Japan and surrounding part of continental East Asia in Middle Pliocene to Late Pliocene (3.5-2 Ma)
- Japanese archipelago at the Last Glacial Maximum about 20,000 years ago, thin black line indicates present-day shorelinesVegetated landUnvegetated landOcean

The islands of Japan are primarily the result of several large ocean movements occurring over hundreds of millions of years from the mid-Silurian to the Pleistocene, as a result of the subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate beneath the continental Eurasian plate to the south, and subduction of the Pacific Plate under the North American Plate to the north.
Contents
- Geological history
- Orogeny phase
- Island arc phase
- Current state
- Research
- Geological hazards
- See also
- References
- Further reading
- External links
Japan was originally attached to the eastern coast of the Eurasian continent. The subducting Philippine and Pacific plates descended beneath the Asian plate into the eastward flow of the asthenosphere. [1] This change in pressure from the asthenosphere pushing back on the subjected plates pulled Japan eastward off of Asia in the process of back-arc extension. This opened up the Sea of Japan around 15 million years ago. [2] The Strait of Tartary and the Korea Strait opened much later.
Japan is situated in a volcanic zone on the Pacific Ring of Fire. Frequent low intensity earth tremors and occasional volcanic activity are felt throughout the islands. Destructive earthquakes, often resulting in tsunamis, occur several times per century. The most recent major quakes include the 2024 Noto earthquake, the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, the 2004 Chūetsu earthquake, and the Great Hanshin earthquake of 1995.