
Glenelg (or Glenelg Intrigue) is a location on Mars near the Mars Science Laboratory ( Curiosity rover ) landing site (Bradbury Landing) in Gale Crater marked by a natural intersection of three kinds of terrain. [1] [2]

Glenelg (or Glenelg Intrigue) is a location on Mars near the Mars Science Laboratory ( Curiosity rover ) landing site (Bradbury Landing) in Gale Crater marked by a natural intersection of three kinds of terrain. [1] [2]
The location was named Glenelg by NASA scientists for two reasons: all features in the immediate vicinity were given names associated with Yellowknife in northern Canada, and Glenelg is the name of a geological feature there. Furthermore, the name is a palindrome, and as the Curiosity rover is planned to visit the location twice (once coming, and once going) this was an appealing feature for the name. [3] The original Glenelg is a village in Scotland which on 20 October 2012 had a ceremony, including a live link to NASA, to celebrate their "twinning" with Glenelg on Mars. [4]
The trek to Glenelg will send the rover 400 m (1,300 ft) east-southeast of its landing site. One of the three types of terrain intersecting at Glenelg is layered bedrock, which is attractive as the first drilling target.[ citation needed ]

Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a robotic space probe mission to Mars launched by NASA on November 26, 2011, which successfully landed Curiosity, a Mars rover, in Gale Crater on August 6, 2012. The overall objectives include investigating Mars' habitability, studying its climate and geology, and collecting data for a human mission to Mars. The rover carries a variety of scientific instruments designed by an international team.

A Mars landing is a landing of a spacecraft on the surface of Mars. Of multiple attempted Mars landings by robotic, uncrewed spacecraft, ten have had successful soft landings. There have also been studies for a possible human mission to Mars including a landing, but none have been attempted.

Gale is a crater, and probable dry lake, at 5.4°S 137.8°E in the northwestern part of the Aeolis quadrangle on Mars. It is 154 km (96 mi) in diameter and estimated to be about 3.5–3.8 billion years old. The crater was named after Walter Frederick Gale, an amateur astronomer from Sydney, Australia, who observed Mars in the late 19th century. Mount Sharp is a mountain in the center of Gale and rises 5.5 km (18,000 ft) high. Aeolis Palus is the plain between the northern wall of Gale and the northern foothills of Aeolis Mons. Peace Vallis, a nearby outflow channel, 'flows' down from the hills to the Aeolis Palus below and seems to have been carved by flowing water. Several lines of evidence suggest that a lake existed inside Gale shortly after the formation of the crater.
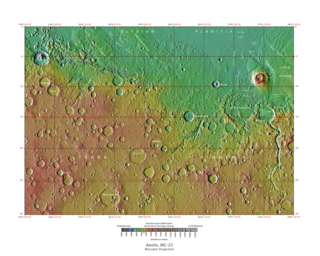
The Aeolis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Aeolis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-23 . The Aeolis quadrangle covers 180° to 225° W and 0° to 30° south on Mars, and contains parts of the regions Elysium Planitia and Terra Cimmeria. A small part of the Medusae Fossae Formation lies in this quadrangle.

The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.

Mount Sharp, officially Aeolis Mons, is a mountain on Mars. It forms the central peak within Gale crater and is located around 5.08°S 137.85°E, rising 5.5 km (18,000 ft) high from the valley floor. Its ID in the United States Geological Survey's Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature is 15000.
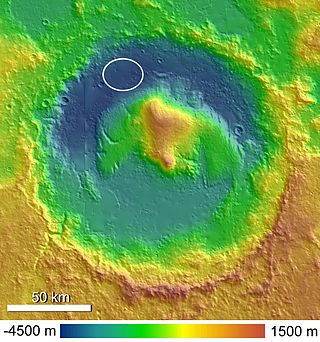
Aeolis Palus is a plain between the northern wall of Gale crater and the northern foothills of Aeolis Mons on Mars. It is located at 4.47°S 137.42°E.

Curiosity is a car-sized Mars rover exploring Gale crater and Mount Sharp on Mars as part of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. Curiosity was launched from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS) on November 26, 2011, at 15:02:00 UTC and landed on Aeolis Palus inside Gale crater on Mars on August 6, 2012, 05:17:57 UTC. The Bradbury Landing site was less than 2.4 km (1.5 mi) from the center of the rover's touchdown target after a 560 million km (350 million mi) journey.

The Mars Science Laboratory and its rover, Curiosity, were launched from Earth on 26 November 2011. As of December 13, 2024, Curiosity has been on the planet Mars for 4392 sols since landing on 6 August 2012. (See Current status.)

Bradbury Landing is the August 6, 2012, landing site within Gale crater on planet Mars of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) Curiosity rover. On August 22, 2012, on what would have been his 92nd birthday, NASA named the site for author Ray Bradbury, who had died on June 5, 2012. The coordinates of the landing site on Mars are: 4.5895°S 137.4417°E.

Jake Matijevic is a pyramidal rock on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars. The approximate site coordinates are: 4.59°S 137.44°E.

Peace Vallis is an ancient stream valley on the northern rim of Gale Crater on the planet Mars. It is notable for its associated alluvial fan which lies near the Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity landing site. The valley and alluvial fan provide evidence for geologically recent (Amazonian-aged) fluvial activity and sustained water flow on Mars. Recent high-resolution orbital images of Peace Vallis and its watershed also suggest that at least one glacial episode affected Gale crater. All of this evidence has implications for the history of water on Mars and the planet's long-term habitability. Understanding Peace Vallis and its fan also provides geologic context for the rocks observed on the ground by the Curiosity rover.

Bathurst Inlet is a rock on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars. The rock was encountered by the Curiosity rover on the way from Bradbury Landing to Glenelg Intrigue on September 30, 2012 and was named after Bathurst Inlet, a deep inlet located along the northern coast of the Canadian mainland. The "approximate" site coordinates are: 4.59°S 137.44°E.

Hottah is a rock outcrop on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars.

Rocknest is a sand patch on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars. The patch was encountered by the Curiosity rover on the way from Bradbury Landing to Glenelg Intrigue on September 28, 2012. The approximate site coordinates are: 4.59°S 137.44°E.

Link is a rock outcrop on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars. The outcrop was encountered by the Curiosity rover on the way from Bradbury Landing to Glenelg Intrigue on September 2, 2012, and was named after a significant rock formation in the Northwest Territories of Canada. The "approximate" site coordinates are: 4.59°S 137.44°E.

Goulburn, also known as Goulburn Scour, is a rock outcrop on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars. The outcrop was encountered by the Curiosity rover on landing at the Bradbury Landing on August 6, 2012 and is named after a two-billion year-old sequence of rocks in Northern Canada. The "approximate" site coordinates are: 4.59°S 137.44°E.

Rocknest 3 is a rock on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars. The approximate site coordinates are: 4.59°S 137.44°E.

Tintina is a rock on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars. The approximate site coordinates are: 4.59°S 137.44°E.

Yellowknife Bay is a geologic formation in Gale Crater on the planet Mars. NASA's Mars Science Laboratory rover, named Curiosity, arrived at the low lying depression on December 17, 2012, 125 sols, or Martian days, into its 668-sol planned mission on the planet. Primary mission goals of the Mars Science Laboratory were to assess the potential habitability of the planet and whether or not the Martian environment is, or has ever been, capable of supporting life.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)