Related Research Articles

Greenwashing, also called green sheen, is a form of advertising or marketing spin that deceptively uses green PR and green marketing to persuade the public that an organization's products, goals, or policies are environmentally friendly. Companies that intentionally adopt greenwashing communication strategies often do so to distance themselves from their environmental lapses or those of their suppliers.

Environment friendly processes, or environmental-friendly processes, are sustainability and marketing terms referring to goods and services, laws, guidelines and policies that claim reduced, minimal, or no harm upon ecosystems or the environment.

The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) is a non-profit organisation which aims to set standards for sustainable fishing. Fisheries that wish to demonstrate they are well-managed and sustainable compared to the MSC's standards are assessed by a team of Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs).
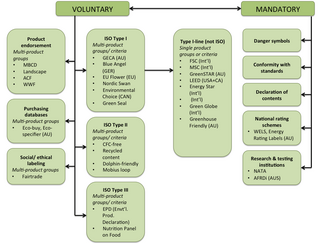
Ecolabels and Green Stickers are labeling systems for food and consumer products. The use of ecolabels is voluntary, whereas green stickers are mandated by law; for example, in North America major appliances and automobiles use Energy Star. They are a form of sustainability measurement directed at consumers, intended to make it easy to take environmental concerns into account when shopping. Some labels quantify pollution or energy consumption by way of index scores or units of measurement, while others assert compliance with a set of practices or minimum requirements for sustainability or reduction of harm to the environment. Many ecolabels are focused on minimising the negative ecological impacts of primary production or resource extraction in a given sector or commodity through a set of good practices that are captured in a sustainability standard. Through a verification process, usually referred to as "certification", a farm, forest, fishery, or mine can show that it complies with a standard and earn the right to sell its products as certified through the supply chain, often resulting in a consumer-facing ecolabel.

The Blue Angel is an environmental label in Germany that has been awarded to particularly environmentally friendly products and services since 1978. The owner of the label is the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety.

Tissue paper or simply tissue is a lightweight paper or light crêpe paper. Tissue can be made from recycled paper pulp on a paper machine.

The Environmental Choice Program is an ecolabelling scheme that was established by Environment Canada in 1988 with over 300 categories of products to help consumers identify services/products which are less harmful to the environment.

The Eugene Green Energy Standard was an international standard to which national or international green electricity labelling schemes could be accredited to confirm that they provide genuine environmental benefits. It was designed to encourage the generation and use of additional renewable energy sources for electricity generation, although the limited use of additional natural gas-fired cogeneration plant was also supported. Initially funded in part through the EU's clean-e programme, but also including some participants from outside Europe, the Eugene standard was formally discontinued after February 2009.
Sustainable seafood is seafood that is caught or farmed in ways that consider the long-term vitality of harvested species and the well-being of the oceans, as well as the livelihoods of fisheries-dependent communities. It was first promoted through the sustainable seafood movement which began in the 1990s. This operation highlights overfishing and environmentally destructive fishing methods. Through a number of initiatives, the movement has increased awareness and raised concerns over the way our seafood is obtained.

The Nordic Ecolabel or Nordic swan is the official sustainability ecolabel for products from the Nordic countries. It was introduced by the Nordic Council of Ministers in 1989. The logo is based on the logo of the Nordic Council adopted in 1984 which symbolises trust, integrity and freedom. The Nordic Swan covers 67 different product groups, from hand soap to furniture to hotels.

Green Seal is a non-profit environmental standard development and certification organization. Its flagship program is the certification of products and services. Certification is based on Green Seal standards, which contain performance, health, and sustainability criteria.
An eco hotel, or a green hotel, is an environmentally sustainable hotel or accommodation that has made important environmental improvements to its structure in order to minimize its impact on the natural environment. The basic definition of an eco-friendly hotel is an environmentally responsible lodging that follows the practices of green living. These hotels have to be certified green by an independent third-party or by the state they are located in. Traditionally, these hotels were mostly presented as ecolodges because of their location, often in jungles, and their design inspired by the use of traditional building methods applied by skilled local craftsmen in areas, such as Costa Rica and Indonesia.

Environmental Choice New Zealand (ECNZ) is the official ecolabel of New Zealand. The label is owned and endorsed by the Ministry for the Environment of the New Zealand Government. The Environmental Choice programme, which started in 1992, is administered by the New Zealand Ecolabelling Trust on behalf of, but independently from, the Ministry for the Environment. The trust and the programme are part of the Global Ecolabelling Network.

Friend of the Sea is a project of the World Sustainability Organization for the certification and promotion of seafood from sustainable fisheries and sustainable aquaculture. It is the only certification scheme which, with the same logo, certifies both wild and farmed seafood.
The Green Council (GC) is a non-profit, non-partisan environmental association of Hong Kong formed by a group of individuals from different sectors of industry and academics who share a vision to turn Hong Kong into a green city for the betterment of the future.

EKOenergy is a globally active nonprofit ecolabel for renewable energy. It is owned by the Finnish Association for Nature Conservation and managed in cooperation with other environmental NGOs.

100Green, operating as Green Energy (UK) Ltd, is a British independent-energy company based in Ware, Hertfordshire. It was established in 2001 by CEO Douglas Stewart. The company provides Ofgem-certified renewable electricity and green gas to domestic and business customers throughout Great Britain. It is currently the only energy supplier in the UK to offer 100% green gas.
Sustainable products are products either sustainably sourced, manufactured or processed and provide environmental, social, and economic benefits while protecting public health and the environment throughout their whole life cycle, from the extraction of raw materials to the final disposal.
Environmental certification is a form of environmental regulation and development where a company can voluntarily choose to comply with predefined processes or objectives set forth by the certification service. Most certification services have a logo which can be applied to products certified under their standards. This is seen as a form of corporate social responsibility allowing companies to address their obligation to minimise the harmful impacts to the environment by voluntarily following a set of externally set and measured objectives.

EU Ecolabel or EU Flower is a voluntary ecolabel scheme established in 1992 by the European Union.
References
- 1 2 Global Ecolabelling Network Archived 2011-06-16 at the Wayback Machine , retrieved at 15 December 2020.
- 1 2 "SEC gets elected to Global Ecolabelling Network's board of directors". Eco-Business. 2015-10-29. Archived from the original on 2021-10-08. Retrieved 2021-10-08.
- ↑ Global Ecolabelling Network 2020, Past World Ecolabel Day Celebrations Archived 2020-12-03 at the Wayback Machine , retrieved at 15 December 2020.
- ↑ Global Ecolabelling Network 2020, Full Members List Archived 2020-11-30 at the Wayback Machine , retrieved at 15 December 2020.
