
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐CH2‐COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to the "flexibility" caused by such a small R group. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a Clostridium tetani infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction.
Cudmore is a national park in Central West Queensland, Australia, 844 km northwest of Brisbane. The terrain of the park has an elevation of 398 meters.

Lathraea (toothwort) is a small genus of five to seven species of flowering plants, native to temperate Europe and Asia. They are parasitic plants on the roots of other plants, and are completely lacking chlorophyll. They are classified in the family Orobanchaceae.

Glycine is a genus in the bean family Fabaceae. The best known species is the cultivated soybean. While the majority of the species are found only in Australia, the soybean's native range is in East Asia. A few species extend from Australia to East Asia . Glycine species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species: the engrailed, nutmeg and turnip moths have all been recorded on soybean.
Mary Douglas Tindale was an Australia Australian botanist. She was an Australian botanist specialising in pteridology (ferns) and the genera Acacia and Glycine. She devoted her life to the study of ferns, and her name is widely associated with the group of flowerless plants.
Rostkovia is a genus of plant in family Juncaceae described as a genus in 1809.
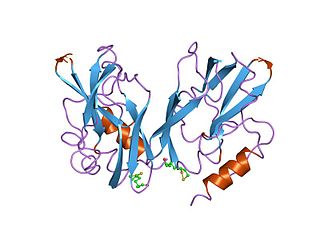
The glycine cleavage system (GCS) is also known as the glycine decarboxylase complex or GDC. The system is a series of enzymes that are triggered in response to high concentrations of the amino acid glycine. The same set of enzymes is sometimes referred to as glycine synthase when it runs in the reverse direction to form glycine. The glycine cleavage system is composed of four proteins: the T-protein, P-protein, L-protein, and H-protein. They do not form a stable complex, so it is more appropriate to call it a "system" instead of a "complex". The H-protein is responsible for interacting with the three other proteins and acts as a shuttle for some of the intermediate products in glycine decarboxylation. In both animals and plants, the glycine cleavage system is loosely attached to the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Mutations in this enzymatic system are linked with glycine encephalopathy.

Glycine tabacina, commonly known as variable glycine, is a scrambling plant in the bean family found in Australia. It grows in areas of high rainfall, ranging to semi-arid areas. The leaves are in threes, 7 cm long by 2 cm wide. Bluish to purple flowers form on racemes in the warmer months. The bean pod is up to 3 cm long. The habitat is among grasses, often in open country.
Lyndley Alan Craven was a botanist who became the Principal Research Scientist of the Australian National Herbarium.
The Burrinjuck Nature Reserve is a protected nature reserve on the south west slopes of New South Wales, Australia. The 5,250-hectare (13,000-acre) reserve is located adjacent to the Burrinjuck Dam, with 5,118 hectares of the reserve located on the northern side of the reservoir, and the remaining 89 hectares located on the southern side of the reservoir to the northeast of Black Andrew Nature Reserve. It includes land formerly managed as the Burrinjuck State Forest and Burrinjuck State Recreation Area.

Glycine latrobeana, the clover glycine or Australian anchor plant, is a species of perennial herb endemic to south-eastern Australia. Its leaves are similar in appearance to the common pasture clover. It is native to Tasmania, Victoria, New South Wales and South Australia.
Dr Sze Peng Flett is a Principal Scientist and the interim Director for the Horticulture Centre of Excellence in the Victoria Department of Environment and Primary Industries.
Oxychloe is a genus of plants in family Juncaceae described as a genus in 1860.
Corymbia clandestina, commonly known as Drummond Range bloodwood, is a species of small tree that is endemic to Queensland. It has rough, tessellated bark on the trunk and branches, lance-shaped adult leaves, flower buds in groups of seven, white flowers and urn-shaped to barrel-shaped fruit.

Lathraea clandestina, the purple toothwort also known as clandestine in France, is a parasitic plant species in the flowering plant family Orobanchaceae. It is native to western Europe.
Cyathochaeta clandestina is a sedge of the family Cyperaceae that is native to Australia.

Glycine canescens, common name Silky Glycine, is trailing or twining herb. It is a species of soybean native to Australia. A perennial living across the Outback in extremely hot and dry conditions, it is being studied for its potential to improve the cultivated soybean . Grows in sandy or stony soils in a variety of habitats.

Glycine tomentella, called the woolly glycine or rusty glycine, is a species of soybean found in Australia, New Guinea, New Caledonia, the Philippines, Taiwan and southeast coastal China. In Australia, it is found in New South Wales, Queensland, the Northern Territory and Western Australia. Glycine tomentella is a complex of polyploid forms, with 2n=38, 2n=40, 2n=78 and 2n=80 chromosome counts detected in different populations. All four forms are found in Australia, the 40‑chromosome and 78‑chromosome forms are also found in New Guinea, and the 80‑chromosome form is found across the entire range.

The Lowland Grassy Woodland, or the Illawarra and South Coast Lowland Grassy Woodland is a grassland-savannah community mostly found in the South Coast region of New South Wales, Australia. Stretching from the southern parts of the Illawarra in the north to the South East Corner in the south, it is an endangered ecological community that lies in a rain shadow area.

Glycine cyrtoloba is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to Queensland and New South Wales in Australia. It is a crop wild relative of soybean, and shows high resistance to salinity.











