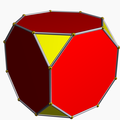
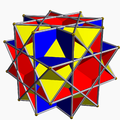
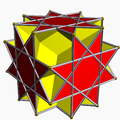
| Great cubicuboctahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Uniform star polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 20, E = 48 V = 24 (χ = −4) |
| Faces by sides | 8{3}+6{4}+6{8/3} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Wythoff symbol | 3 4 | 4/3 4 3/2 | 4 |
| Symmetry group | Oh, [4,3], *432 |
| Index references | U 14, C 50, W 77 |
| Dual polyhedron | Great hexacronic icositetrahedron |
| Vertex figure |  3.8/3.4.8/3 |
| Bowers acronym | Gocco |

In geometry, the great cubicuboctahedron is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U14. It has 20 faces (8 triangles, 6 squares and 6 octagrams), 48 edges, and 24 vertices. [1] Its square faces and its octagrammic faces are parallel to those of a cube, while its triangular faces are parallel to those of an octahedron: hence the name cubicuboctahedron. The prefix great serves to distinguish it from the small cubicuboctahedron, which also has faces in the aforementioned directions. [2]