
A world's fair or world fair is a large international exhibition designed to showcase achievements of nations. These exhibitions vary in character and are held in different parts of the world at a specific site for a period of time, ranging usually from three to six months.

Hanoi is the capital of Vietnam. It covers an area of 3,328.9 square kilometres (1,285 sq mi). With an estimated population of 8.1 million as of 2019, it is the second largest city in Vietnam. The metropolitan area, encompassing nine additional neighbouring provinces, has an estimated population of 16 million. Located in the central area of the Red River Delta, Hanoi is the commercial, cultural, and educational centre of Northern Vietnam. Having an estimated nominal GDP of US$32.8 billion, it is the second most productive economic centre of Vietnam, following Ho Chi Minh City.

Joseph Athanase Doumer, commonly known as Paul Doumer, was the President of France from 13 June 1931 until his assassination on 7 May 1932.

The Exposition Universelle of 1900, better known in English as the 1900 Paris Exposition, was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 14 April to 12 November 1900, to celebrate the achievements of the past century and to accelerate development into the next. The fair, visited by nearly 50 million, displayed many technological innovations, including the Grande Roue de Paris Ferris wheel, the moving sidewalk, diesel engines, talking films, escalators, and the telegraphone. It also brought international attention to the Art Nouveau style. Additionally, it showcased France as a major colonial power through numerous pavilions built on the hill of the Trocadero Palace. Major structures remaining from the Exposition include the Grand Palais, the Petit Palais, the Pont Alexandre III, the Gare d'Orsay railroad station (now the Musée d'Orsay and two of original entrances of Paris Métro stations by Hector Guimard.

The Trocadéro, site of the Palais de Chaillot, is an area of Paris, France, in the 16th arrondissement, across the Seine from the Eiffel Tower. It is also the name of the 1878 palace which was demolished in 1937 to make way for the Palais de Chaillot. The hill of the Trocadéro is the hill of Chaillot, a former village.

The Exposition Internationale des Arts et Techniques dans la Vie Moderne was held from 25 May to 25 November 1937 in Paris, France. Both the Palais de Chaillot, housing the Musée de l'Homme, and the Palais de Tokyo, which houses the Musée d'Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris, were created for this exhibition that was officially sanctioned by the Bureau International des Expositions.

The Exposition Universelle of 1889 was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 6 May to 31 October 1889. It was the fourth of eight expositions held in the city between 1855 and 1937. It attracted more than thirty-two million visitors. The most famous structure created for the Exposition, and still remaining, is the Eiffel Tower.

Bắc Kạn is the capital of Bắc Kạn Province, Vietnam. The province's only city, it is bordered by Bạch Thông District to the north, north-east and west and Chợ Mới District to the south-east and south-west.

The Petit Palais is an art museum in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France.

The Exposition universelle, internationale et coloniale was a world's fair including a colonial exhibition in the French City of Lyon in 1894. The site was the parc de la Tête d'or in the north of the city. The exposition drew unwanted attention with the assassination of French President Sadi Carnot during his visit on 24 July 1894; he died the day after.

French Colonial describes several styles of architecture used by the French during colonization. Many former French colonies, especially those in Southeast Asia, have previously been reluctant to promote their colonial architecture as an asset for tourism; however, in recent times, the new generation of local authorities has somewhat "embraced" the architecture and advertise it. French Colonial architecture has a long history, beginning in North America in 1604 and being most active in the Western Hemisphere until the 19th century, when the French turned their attention more to Africa, Asia, and the Pacific.

The Hanoi Opera House, or the Grand Opera House is an opera house in central Hanoi, Vietnam. It was erected by the French colonial administration between 1901 and 1911.

Hoàn Kiếm is an urban district (quận) of Hanoi, the capital city of Vietnam, named after the scenic Hoàn Kiếm Lake. The lake is in the heart of the district and serves as the focal point of the city's public life. The majority of tourist attractions in Hanoi are also located in the district.
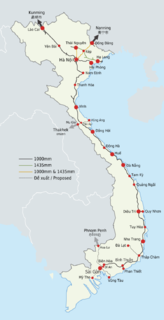
The railway system in Vietnam is owned and operated by the state-owned Vietnam Railways. The principal route, the single track North-South Railway running between Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, accounts for 1,726 kilometres (1,072 mi) of the network's total length of 2,600 kilometres (1,600 mi). The national railway network uses mainly metre gauge, although there are several standard gauge and mixed gauge lines in the north of the country.

The Faux Namti Bridge, also known as Wujiazhai Railway Bridge (五家寨铁路桥), or as the Inverted V Bridge, is a single-span railway bridge located in Wantang Township (湾塘乡) of Pingbian County, in the Nanxi River valley region in the Chinese province of Yunnan. The bridge spans a gorge 102 m (335 ft) above the Sicha River, a tributary of the Nanxi. It is located at kilometer 111 of the Kunming–Hekou Railway, the Chinese portion of part of the Kunming–Haiphong railway. Construction of the bridge was carried out by the French Batignolles Construction Company, beginning in March 1907 and ending in December 1908.
Alix Angèle Marguerite Aymé was a female French painter who lived in China and Vietnam.
The following is a timeline of the history of Hanoi, the capital city of Vietnam:

Tonkin, or Bắc Kỳ (北圻), was a French protectorate encompassing modern Northern Vietnam.

The Grand Palais or Grand Palais de l'Exposition was an exhibition and trade fair complex in Hanoi, Vietnam. It was built for the 1902 Hanoi Exhibition world trade fair, as the city became the capital of French Indochina. It was completely destroyed by airstrikes at the end of World War II.



















