Related Research Articles

Aryabhata or Aryabhata I was the first of the major mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. His works include the Āryabhaṭīya and the Arya-siddhanta.
Keļallur Nilakantha Somayaji, also referred to as Keļallur Comatiri, was a major mathematician and astronomer of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. One of his most influential works was the comprehensive astronomical treatise Tantrasamgraha completed in 1501. He had also composed an elaborate commentary on Aryabhatiya called the Aryabhatiya Bhasya. In this Bhasya, Nilakantha had discussed infinite series expansions of trigonometric functions and problems of algebra and spherical geometry. Grahapariksakrama is a manual on making observations in astronomy based on instruments of the time. Known popularly as Kelallur Chomaathiri, he is considered an equal to Vatasseri Parameshwaran Nambudiri.
Vatasseri Parameshvara Nambudiri was a major Indian mathematician and astronomer of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics founded by Madhava of Sangamagrama. He was also an astrologer. Parameshvara was a proponent of observational astronomy in medieval India and he himself had made a series of eclipse observations to verify the accuracy of the computational methods then in use. Based on his eclipse observations, Parameshvara proposed several corrections to the astronomical parameters which had been in use since the times of Aryabhata. The computational scheme based on the revised set of parameters has come to be known as the Drgganita or Drig system. Parameshvara was also a prolific writer on matters relating to astronomy. At least 25 manuscripts have been identified as being authored by Parameshvara.
Lalla was an Indian mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer who belonged to a family of astronomers. Lalla was the son of Trivikrama Bhatta and the grandson of Śâmba. He lived in central India, possibly in the Lāṭa region in modern south Gujarat. Lalla was known as being one of the leading Indian astronomers of the eighth century. Only two of his works are currently thought to be extant.

Indian astronomy refers to astronomy practiced in Indian subcontinent. It has a long history stretching from pre-historic to modern times. Some of the earliest roots of Indian astronomy can be dated to the period of Indus Valley civilisation or earlier. Astronomy later developed as a discipline of Vedanga, or one of the "auxiliary disciplines" associated with the study of the Vedas dating 1500 BCE or older. The oldest known text is the Vedanga Jyotisha, dated to 1400–1200 BCE.
Jyeṣṭhadeva was an astronomer-mathematician of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics founded by Madhava of Sangamagrama. He is best known as the author of Yuktibhāṣā, a commentary in Malayalam of Tantrasamgraha by Nilakantha Somayaji (1444–1544). In Yuktibhāṣā, Jyeṣṭhadeva had given complete proofs and rationale of the statements in Tantrasamgraha. This was unusual for traditional Indian mathematicians of the time. The Yuktibhāṣā is now believed to contain the essential elements of calculus like Taylor and infinity series. Jyeṣṭhadeva also authored Drk-karana, a treatise on astronomical observations.

Aryabhatiya or Aryabhatiyam, a Sanskrit astronomical treatise, is the magnum opus and only known surviving work of the 5th century Indian mathematician Aryabhata. Philosopher of astronomy Roger Billard estimates that the book was composed around 510 CE based on historical references it mentions.

Tantrasamgraha, or Tantrasangraha, is an important astronomical treatise written by Nilakantha Somayaji, an astronomer/mathematician belonging to the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. The treatise was completed in 1501 CE. It consists of 432 verses in Sanskrit divided into eight chapters. Tantrasamgraha had spawned a few commentaries: Tantrasamgraha-vyakhya of anonymous authorship and Yuktibhāṣā authored by Jyeshtadeva in about 1550 CE. Tantrasangraha, together with its commentaries, bring forth the depths of the mathematical accomplishments the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics, in particular the achievements of the remarkable mathematician of the school Sangamagrama Madhava. In his Tantrasangraha, Nilakantha revised Aryabhata's model for the planets Mercury and Venus. According to George G Joseph his equation of the centre for these planets remained the most accurate until the time of Johannes Kepler in the 17th century.

Krishna Venkateswara Sarma (1919–2005) was an Indian historian of science, particularly the astronomy and mathematics of the Kerala school. He was responsible for bringing to light several of the achievements of the Kerala school. He was editor of the Vishveshvaranand Indological Research Series, and published the critical edition of several source works in Sanskrit, including the Aryabhatiya of Aryabhata. He was recognised as "the greatest authority on Kerala's astronomical tradition".

Sadratnamala is an astronomical-mathematical treatise in Sanskrit written by Sankara Varman, an astronomer-mathematician of the Kerala school of mathematics, in 1819. Even though the book has been written at a time when western mathematics and astronomy had been introduced in India, it is composed purely in the traditional style followed by the mathematicians of the Kerala school. Sankara Varman has also written a detailed commentary on the book in Malayalam.

Kaṭapayādi system of numerical notation is an ancient Indian alphasyllabic numeral system to depict letters to numerals for easy remembrance of numbers as words or verses. Assigning more than one letter to one numeral and nullifying certain other letters as valueless, this system provides the flexibility in forming meaningful words out of numbers which can be easily remembered.
In astronomy, Jyotirmimamsa is a treatise on the methodology of astronomical studies authored by Nilakantha Somayaji (1444–1544) in around 1504 CE. Nilakantha somayaji was an important astronomer-mathematician of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics and was the author of the much celebrated astronomical work titled Tantrasamgraha. This book stresses the necessity and importance of astronomical observations to obtain correct parameters for computations and to develop more and more accurate theories. It even discounts the role of revealed wisdom and divine intuitions in studying astronomical phenomena. Jyotirmimamsa is sometimes cited as proof to establish that modern methodologies of scientific investigations were known to ancient and medieval Indians. Neelkantha Somayaji insisted that computational results should tally with that of observations and astronomical parameters and constants should be revised periodically. To come to more precise conclusions, Neelkantha Somayaji have discussions with the astronomer and mathematicians of other schools.
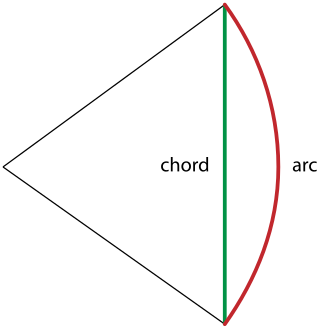
Āryabhata's sine table is a set of twenty-four numbers given in the astronomical treatise Āryabhatiya composed by the fifth century Indian mathematician and astronomer Āryabhata, for the computation of the half-chords of a certain set of arcs of a circle. The set of numbers appears in verse 12 in Chapter 1 Dasagitika of Aryabhatiya. It is not a table in the modern sense of a mathematical table; that is, it is not a set of numbers arranged into rows and columns. Āryabhaṭa's table is also not a set of values of the trigonometric sine function in a conventional sense; it is a table of the first differences of the values of trigonometric sines expressed in arcminutes, and because of this the table is also referred to as Āryabhaṭa's table of sine-differences.
Veṇvāroha is a work in Sanskrit composed by Mādhava of Sangamagrāma, the founder of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. It is a work in 74 verses describing methods for the computation of the true positions of the Moon at intervals of about half an hour for various days in an anomalistic cycle. This work is an elaboration of an earlier and shorter work of Mādhava himself titled Sphutacandrāpti. Veṇvāroha is the most popular astronomical work of Mādhava.
Chandravākyas are a collection of numbers, arranged in the form of a list, related to the motion of the Moon in its orbit around the Earth. These numbers are couched in the katapayadi system of representation of numbers and so apparently appear like a list of words, or phrases or short sentences written in Sanskrit and hence the terminology Chandravākyas. In Sanskrit, Chandra is the Moon and vākya means a sentence. The term Chandravākyas could thus be translated as Moon-sentences.
Parahita is a system of astronomy prevalent in Kerala and Tamil Nadu, India. It was introduced by the Kerala astronomer Haridatta,. Nilakantha Somayaji (1444–1544), in his Dr̥kkaraṇa, relates how Parahita was created based on the combined observations of a group of scholars who had gathered for a festival at Tirunāvāy on the banks of the Bhāratappuzha River. The Sanskrit etymology literally means "for the benefit of the common man", and the intention was to simplify astronomical computations so that everyone could do it.
A History of the Kerala School of Hindu Astronomy (in perspective) is the first definitive book giving a comprehensive description of the contribution of Kerala to astronomy and mathematics. The book was authored by K. V. Sarma who was a Reader in Sanskrit at Vishveshvaranand Institute of Sanskrit and Indological Studies, Panjab University, Hoshiarpur, at the time of publication of the book (1972). The book, among other things, contains details of the lives and works of about 80 astronomers and mathematicians belonging to the Kerala School. It has also identified 752 works belonging to the Kerala school.
Drigganita, also called the Drik system, is a system of astronomical computations followed by several traditional astronomers, astrologers and almanac makers in India. In this system the computations are performed using certain basic constants derived from observations of astronomical phenomena. The almanacs computed using the methods of Drigganita are referred to as Drigganita Panchngas. In Tamil speaking world, they are also known as Thiru-ganita Panchangas.
Kali ahargaṇa is an integer associated with a civil day. The integer represents the number of civil days in a collection of consecutive days beginning with a special day called the kali epoch and ending with a specified day. Kali ahargaṇa is one of the basic parameters of Indian astronomy and it is extensively in all sorts of astronomical computations.
References
- 1 2 K. V. Sarma (1997), "Haridatta", Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures, edited by Helaine Selin, Springer, ISBN 978-1-4020-4559-2.
- ↑ K. Chandra Hari (2002). "Date of Haridatta, promulgator of the Parahita system of astronomy in Kerala". Indian Journal of History of Science. 37 (3): 223–236.
- ↑ K.V. Sarma (1972). "Parahita system of astronomy". A History of the Kerala School of Hindu Astronomy . Hoshiarpur: Vishveshwaranand Institute. pp. 7–9.
- ↑ K.V. Sarma (1954). Grahacaranibandhana: A Parahita manual by Haridatta. Madras: Kuppuswamy Research Foundation.